Payout Ratio Explained: How to Use and Calculate

The payout ratio is a financial ratio that measures the proportion of earnings that a company distributes to its shareholders in the form of dividends. It is an important metric for investors as it provides insights into a company’s dividend policy and its ability to generate consistent returns.
The payout ratio is expressed as a percentage and is calculated by dividing the dividends paid by the company by its net income. The formula for calculating the payout ratio is as follows:
Payout Ratio = Dividends / Net Income
A high payout ratio indicates that a company is distributing a large portion of its earnings as dividends, which may be favorable for income-seeking investors. However, a very high payout ratio can also indicate that a company is not reinvesting enough in its business for future growth.
On the other hand, a low payout ratio suggests that a company is retaining a larger portion of its earnings for reinvestment or other purposes. This may be seen as a positive sign for growth-oriented investors, as it indicates that the company has more funds available for expansion or research and development.
Calculating the Payout Ratio
To calculate the payout ratio, you need to know the dividends paid by the company and its net income. Dividends paid can usually be found in the company’s financial statements or dividend history. Net income can be obtained from the company’s income statement.
Once you have the dividends and net income, simply divide the dividends by the net income and multiply by 100 to get the payout ratio as a percentage.
For example, if a company has paid $10,000 in dividends and has a net income of $50,000, the payout ratio would be:
Payout Ratio = ($10,000 / $50,000) * 100 = 20%
This means that the company is distributing 20% of its earnings as dividends.
The payout ratio is a financial ratio that measures the proportion of earnings distributed to shareholders in the form of dividends. It is an important metric for investors to assess the sustainability of a company’s dividend payments.
Calculating the payout ratio involves dividing the dividends paid by the net income of the company. The result is expressed as a percentage, indicating the portion of earnings that is being distributed to shareholders.
A high payout ratio may indicate that a company is returning a significant portion of its earnings to shareholders, which can be attractive to income-focused investors. However, it could also suggest that the company is not reinvesting enough in its business for future growth.
On the other hand, a low payout ratio may indicate that a company is retaining a larger portion of its earnings for reinvestment, which can be positive for long-term growth prospects. However, it may disappoint income-focused investors who rely on dividends for income.
Investors should also be aware that a company’s dividend policy can change over time. A company may increase or decrease its dividend payments based on various factors such as changes in earnings, cash flow, or strategic priorities.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| – Indicates the proportion of earnings distributed to shareholders | – Does not consider other uses of earnings such as reinvestment |
| – Can be attractive to income-focused investors | – Dividend policy can change over time |
| – Provides insights into a company’s dividend sustainability | – Should be analyzed in conjunction with other financial ratios and factors |
| – Helps evaluate a company’s dividend policy |
Calculating the Payout Ratio
The payout ratio is a financial ratio that measures the proportion of earnings paid out to shareholders in the form of dividends. It is an important metric for investors to assess the sustainability of dividend payments and the overall financial health of a company.
To calculate the payout ratio, you need two key pieces of information: the dividends paid and the net income of the company. The formula for calculating the payout ratio is:
Payout Ratio = Dividends Paid / Net Income
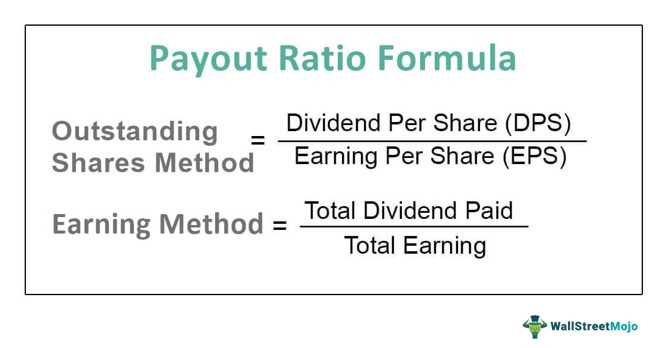
Let’s break down the components of the formula:
- Dividends Paid: This refers to the total amount of dividends distributed to shareholders during a specific period, such as a year.
Once you have the dividends paid and net income figures, you can divide the dividends paid by the net income to get the payout ratio. The result is usually expressed as a percentage.
For example, if a company has paid $1,000,000 in dividends and has a net income of $2,000,000, the payout ratio would be:
Payout Ratio = $1,000,000 / $2,000,000 = 0.5 or 50%
This means that the company is paying out 50% of its earnings as dividends to shareholders.
| Advantages of the Payout Ratio | Disadvantages of the Payout Ratio |
|---|---|
|
|

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
