Types of Non-Issuer Transactions
Non-issuer transactions refer to the buying and selling of securities between investors without the involvement of the issuer. These transactions can take various forms, depending on the nature of the securities and the parties involved. Here are some common types of non-issuer transactions:
1. Secondary Market Transactions
In a secondary market transaction, investors buy and sell securities that have already been issued and are trading on a secondary market, such as a stock exchange. This type of non-issuer transaction allows investors to trade securities among themselves, providing liquidity to the market.
2. Private Placements
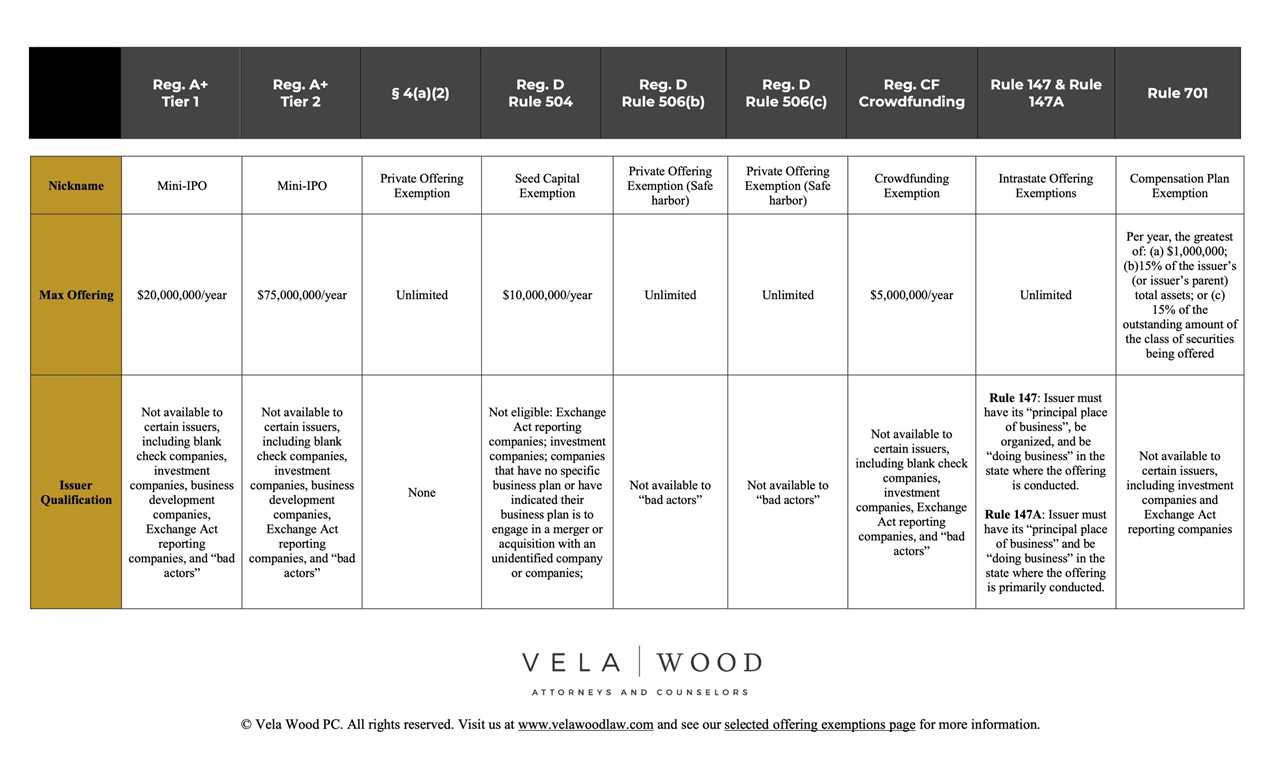
Private placements involve the sale of securities directly to a limited number of investors, usually institutional investors or high-net-worth individuals. Unlike public offerings, private placements are not registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and are subject to certain exemptions. This type of non-issuer transaction allows companies to raise capital without the extensive regulatory requirements of a public offering.
Note: Private placements are subject to securities laws and regulations in the jurisdiction where they are offered.
3. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Transactions
OTC transactions involve the buying and selling of securities directly between parties, without the involvement of an organized exchange. These transactions are typically conducted through a dealer network or electronic trading platforms. OTC markets provide a venue for trading securities that may not meet the listing requirements of traditional exchanges.
4. Intermediated Transactions
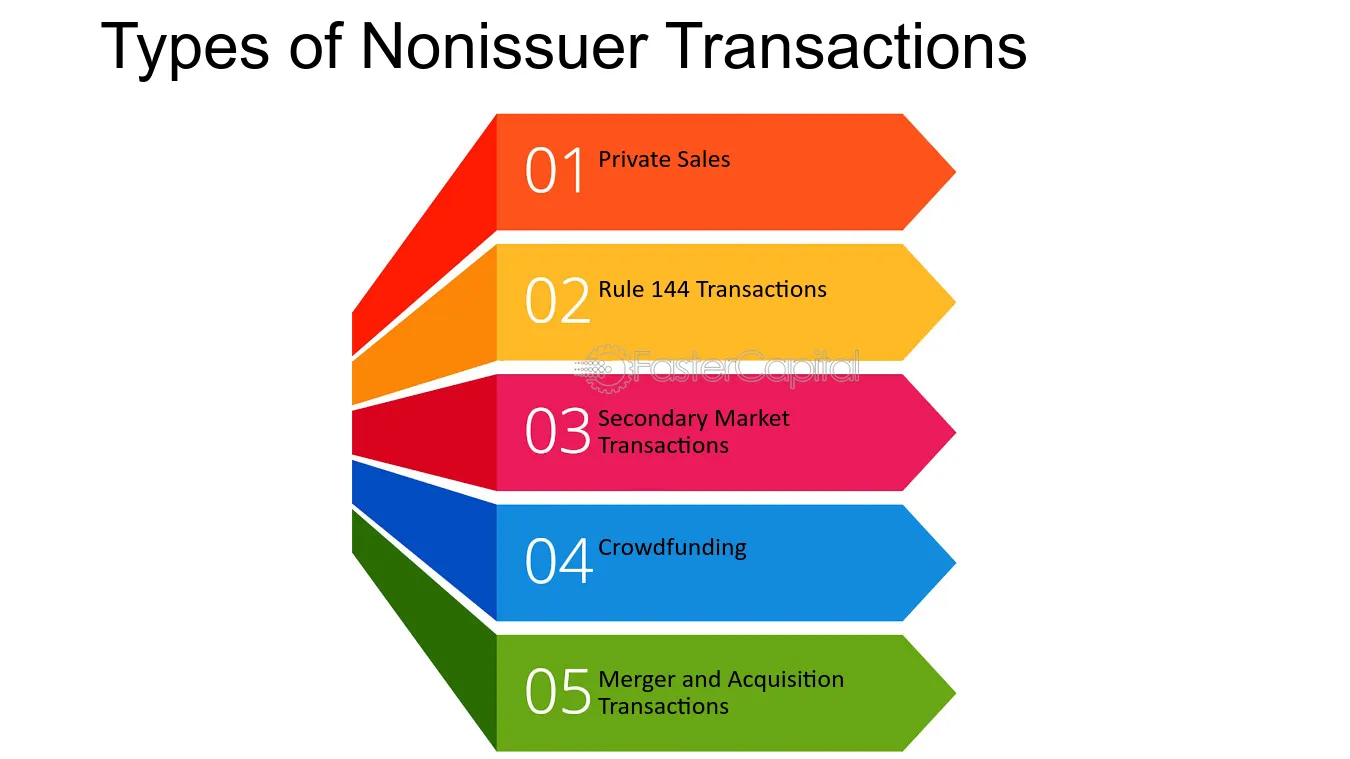
Intermediated transactions involve the use of intermediaries, such as brokers or financial institutions, to facilitate the buying and selling of securities. These intermediaries act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, providing services such as order execution, clearing, and settlement. This type of non-issuer transaction allows investors to access the securities markets and execute trades efficiently.
Benefits of Non-Issuer Transactions
Non-issuer transactions offer several benefits to investors and market participants. These transactions provide opportunities for diversification, liquidity, and flexibility in the investment process.
Diversification
Liquidity

Non-issuer transactions often provide greater liquidity compared to traditional investments. This means that investors can buy or sell their positions more easily and quickly. Liquidity is important as it allows investors to enter or exit positions without significant price impact, ensuring that they can manage their investments efficiently.
Flexibility
Non-issuer transactions offer investors greater flexibility in terms of investment strategies and risk management. Investors can choose from a variety of transaction types, such as over-the-counter trades, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and derivatives. This flexibility allows investors to tailor their investment approach to their specific goals and risk tolerance.
Furthermore, non-issuer transactions can be used for hedging purposes. Investors can use derivatives, such as options or futures, to protect their portfolios against adverse market movements. This hedging capability helps to mitigate risk and preserve capital in volatile market conditions.
| Benefits of Non-Issuer Transactions |
|---|
| Diversification |
| Liquidity |
| Flexibility |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
