What is Neoclassical Economics?
Neoclassical economics is a school of thought that emerged in the late 19th century as a response to classical economics. It is based on the principles of rational behavior, individual choice, and the efficient allocation of resources.
Neoclassical economists believe that individuals are rational actors who make decisions based on their own self-interest. They argue that individuals have preferences and make choices to maximize their utility, or satisfaction, given their limited resources.
One of the key concepts in neoclassical economics is the law of supply and demand. According to this law, the price of a good or service is determined by the interaction of its supply and demand. Neoclassical economists believe that markets are efficient and will naturally find an equilibrium where supply equals demand.
Another important concept in neoclassical economics is the idea of marginal analysis. Neoclassical economists argue that individuals make decisions at the margin, weighing the costs and benefits of each additional unit of a good or service. This concept is used to explain various economic phenomena, such as consumer behavior, production decisions, and the pricing of goods and services.
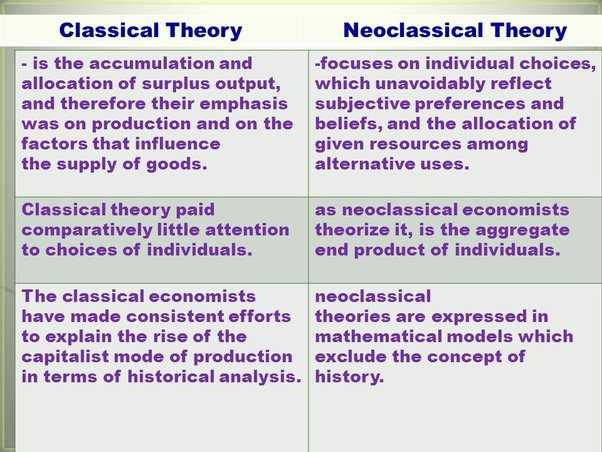
Neoclassical economics is a school of economic thought that emerged in the late 19th century and is still widely influential today. It is based on the principles of classical economics, but incorporates new ideas and concepts to better understand the workings of the economy.
At its core, neoclassical economics assumes that individuals are rational actors who make decisions based on their own self-interest. It emphasizes the importance of supply and demand in determining prices and allocates resources efficiently through market mechanisms.
One of the key concepts in neoclassical economics is the theory of marginal utility. According to this theory, individuals derive satisfaction or utility from consuming additional units of a good or service. The marginal utility of a good decreases as more units are consumed, leading to the law of diminishing marginal utility.
Neoclassical economics also incorporates the concept of opportunity cost, which refers to the value of the next best alternative that is forgone when making a decision. This concept helps explain how individuals and firms make choices in a world of scarcity.
Neoclassical economics has been influential in shaping economic policy and has been used to analyze a wide range of economic phenomena, from individual consumer behavior to macroeconomic issues such as inflation and unemployment. However, it has also been criticized for its assumptions of rationality and its focus on market mechanisms, which some argue may not accurately reflect real-world economic behavior.
The Significance of Neoclassical Economics in Modern Society
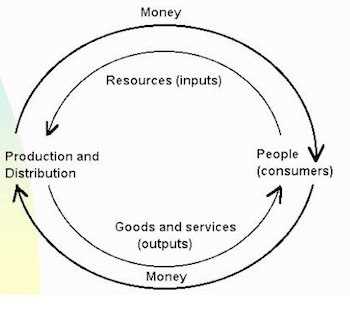
Neoclassical economics also informs policy decisions by providing a framework for evaluating the costs and benefits of different interventions. By analyzing the potential impacts of policies on consumer welfare, producer surplus, and overall social welfare, neoclassical economics helps policymakers make informed choices about how to address market failures and promote economic growth.
Moreover, neoclassical economics has influenced other fields of study, such as finance, international trade, and development economics. Its concepts and methodologies have been applied to analyze financial markets, understand patterns of trade, and design strategies for economic development.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
