Market Portfolio Definition
The market portfolio is a theoretical concept in portfolio management that represents a diversified investment portfolio that includes all available assets in the market. It is often used as a benchmark for evaluating the performance of individual portfolios and investment strategies.
The market portfolio is constructed by weighting each asset in the market according to its market value. This means that assets with higher market values will have a larger weight in the market portfolio. The goal is to create a portfolio that represents the overall market and captures the average return of all investors in the market.
The concept of the market portfolio is based on the efficient market hypothesis, which assumes that all available information is already reflected in the prices of assets. Therefore, the market portfolio is considered to be the optimal portfolio in terms of risk and return. It is often used as a starting point for constructing efficient portfolios using various asset allocation strategies.
Investors can use the market portfolio as a reference point to evaluate the performance of their own portfolios. If an investor’s portfolio outperforms the market portfolio, it is considered to have generated alpha, which indicates superior performance. On the other hand, if an investor’s portfolio underperforms the market portfolio, it is considered to have generated negative alpha, indicating poor performance.
It is important to note that the market portfolio is a theoretical concept and cannot be directly invested in. However, investors can use market index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that aim to replicate the performance of the market portfolio.
Theory
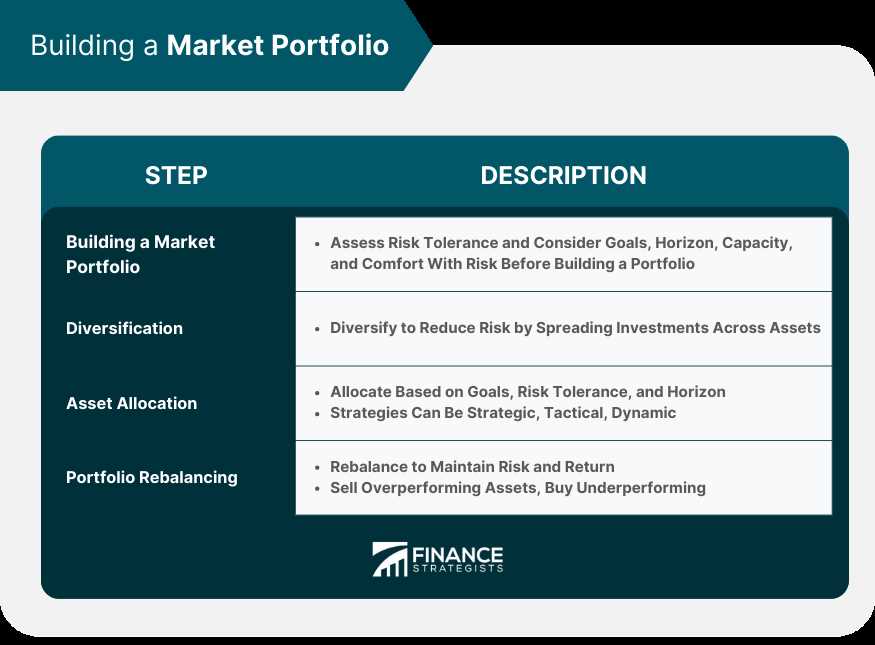
The concept of the market portfolio is a fundamental concept in portfolio management. It is based on the idea that an investor should hold a diversified portfolio that represents the entire market. The market portfolio is a theoretical construct that includes all available investments in the market, weighted according to their market values.
The market portfolio is often used as a benchmark for evaluating the performance of investment portfolios. It represents the average return of all investments in the market and serves as a reference point for comparing the returns of individual portfolios. If a portfolio outperforms the market portfolio, it is considered to have generated positive alpha, indicating skillful management or superior investment selection.
The concept of the market portfolio is closely related to the efficient market hypothesis (EMH), which states that financial markets are efficient and all available information is already reflected in the prices of securities. According to the EMH, it is not possible to consistently outperform the market portfolio through active management or stock picking. Instead, investors should aim to replicate the market portfolio through passive strategies such as index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
One of the key benefits of investing in the market portfolio is diversification. By holding a diversified portfolio that represents the entire market, investors can reduce their exposure to specific risks associated with individual securities or sectors. Diversification helps to spread risk and can improve the risk-return profile of a portfolio.
However, constructing a true market portfolio is practically impossible, as it would require owning a proportionate share of every investment in the market. Instead, market proxies such as broad-based stock market indices are often used to represent the market portfolio. Examples of market proxies include the S&P 500, Dow Jones Industrial Average, and Russell 2000.
Examples of Market Portfolio Definition in Portfolio Management
- S&P 500 Index: The S&P 500 index is a widely recognized market portfolio that represents the performance of 500 large-cap U.S. companies. It includes companies from various sectors, such as technology, finance, healthcare, and consumer goods. Investors often compare the performance of their portfolios to the S&P 500 index to assess their investment returns.
- MSCI World Index: The MSCI World index is another example of a market portfolio that represents the performance of large and mid-cap stocks from developed countries around the world. It covers approximately 85% of the global equity market. Many global investors use the MSCI World index as a benchmark to evaluate their international portfolios.
- Global Bond Index: In addition to equity market portfolios, there are also market portfolios for fixed-income securities. The global bond index represents a diversified portfolio of government and corporate bonds from various countries and regions. It provides investors with a benchmark to assess the performance of their bond portfolios.
These examples demonstrate how market portfolio definition is applied in portfolio management. By comparing the performance of their portfolios to these market portfolios, investors can gain insights into the effectiveness of their investment strategies and make informed decisions to optimize their portfolios.
Portfolio Management
What is the Market Portfolio?
The market portfolio is a theoretical construct that represents a diversified investment portfolio that includes all available assets in the market. It is often used as a benchmark for evaluating the performance of other portfolios. The market portfolio is considered to be efficient because it offers the highest expected return for a given level of risk.
Theory behind the Market Portfolio
The concept of the market portfolio is based on the modern portfolio theory (MPT) developed by Harry Markowitz. According to MPT, investors should focus on creating a diversified portfolio that maximizes returns while minimizing risk. The market portfolio is the result of combining all available assets in the market in proportion to their market values.
MPT suggests that by investing in the market portfolio, investors can achieve the optimal balance between risk and return. This is because the market portfolio represents the collective wisdom of all market participants and reflects the overall market sentiment.
Examples of the Market Portfolio
Investors can also create their own market portfolio by investing in a diversified mix of assets that closely resembles the market composition. This can be achieved through the use of exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or mutual funds that track a specific market index.
| Advantages of the Market Portfolio | Disadvantages of the Market Portfolio |
|---|---|
| 1. Provides diversification | 1. Limited customization |
| 2. Reflects overall market sentiment | 2. May not align with individual goals |
| 3. Offers high expected return | 3. Can be influenced by market fluctuations |
Overall, the market portfolio is an important concept in portfolio management. It serves as a benchmark for evaluating the performance of other portfolios and provides a foundation for constructing well-diversified investment strategies.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
