Laggard: Definition, Functionality, and Potential Risks
A laggard, in the context of investing, refers to a stock or investment that has underperformed compared to its peers or the overall market. It is often used to describe companies or assets that have not kept up with the growth and performance of other similar investments.
Definition
Laggards are often identified by comparing their performance to a benchmark index or similar investments. If a stock consistently underperforms its benchmark over a certain period of time, it may be considered a laggard.
Functionality
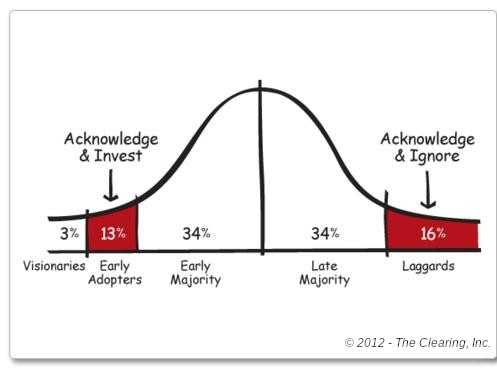
Investors may choose to invest in laggards for various reasons. Some investors believe that underperforming stocks have the potential to rebound and generate significant returns in the future. They may see an opportunity to buy these stocks at a lower price and benefit from their potential recovery.
Additionally, investors may use laggards as a diversification strategy. By including underperforming stocks in their portfolio, investors can reduce their overall risk and potentially benefit from the eventual recovery of these investments.
However, it is important to note that investing in laggards can be risky. There is no guarantee that underperforming stocks will recover or generate positive returns in the future. It requires careful analysis and research to identify laggards with the potential for improvement.
Potential Risks
Investing in laggards carries certain risks that investors should be aware of. One of the main risks is the possibility of further decline in value. Laggards may continue to underperform or experience additional challenges that can lead to further losses.
Another risk is the potential for a lack of recovery. While some laggards may eventually bounce back and generate positive returns, others may continue to struggle or even face bankruptcy. It is important for investors to carefully assess the underlying reasons for a stock’s underperformance and evaluate its potential for improvement.
Furthermore, investing in laggards may require a longer time horizon. It can take time for underperforming stocks to turn around and start generating positive returns. Investors need to be patient and willing to hold onto their investments for an extended period of time.
The laggard investment strategy is a popular approach used by investors to identify and invest in underperforming stocks or assets with the expectation that they will eventually catch up to their peers or the overall market. This strategy is based on the belief that these laggards have the potential to deliver higher returns in the future.
When implementing the laggard investment strategy, investors typically look for stocks or assets that have been consistently underperforming relative to their industry or market benchmarks. These laggards may have faced temporary setbacks or may have been overlooked by other investors, creating an opportunity for those who believe in their potential for future growth.
One of the main advantages of the laggard investment strategy is the potential for significant gains. By investing in underperforming stocks or assets, investors can buy them at a lower price, which increases the potential for higher returns when the market recognizes their value and they start to outperform their peers.
Another risk associated with the laggard investment strategy is the potential for missed opportunities. While investors focus on underperforming stocks or assets, they may miss out on other investment opportunities that are performing well or have a higher growth potential.
To mitigate these risks, it is important for investors to conduct thorough research and analysis before implementing the laggard investment strategy. They should carefully evaluate the reasons behind the underperformance of the stocks or assets and assess their potential for future growth. It is also advisable to diversify the portfolio by including a mix of laggards and outperforming assets to spread the risk.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
