Labor Intensive Definition
Labor intensive industries rely heavily on human capital and physical labor rather than automated machinery or technology. The production process involves a large number of workers performing tasks that require physical effort, such as assembly line work, construction, agriculture, and hospitality.
These industries often have a high labor-to-capital ratio, meaning that the cost of labor is a significant portion of the overall production costs. This can make labor intensive industries more susceptible to fluctuations in labor costs and changes in labor regulations.
Examples of Labor Intensive Industries
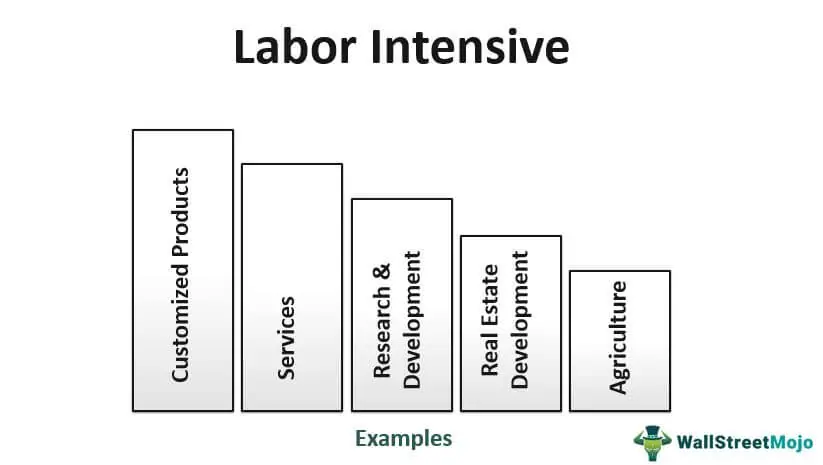
Some examples of labor intensive industries include:
- Manufacturing: Industries such as textile manufacturing, garment production, and furniture manufacturing often require a large number of workers to perform tasks like cutting, sewing, and assembling.
- Agriculture: Farming and agricultural activities, such as planting, harvesting, and livestock care, rely heavily on manual labor.
- Construction: Building and construction projects require a significant amount of physical labor for tasks like digging, lifting, and building structures.
- Hospitality: The hospitality industry, including hotels, restaurants, and tourism, relies on human labor for customer service, food preparation, and housekeeping.
- Healthcare: Many healthcare services, such as nursing, caregiving, and medical assistance, require a large workforce to provide patient care.
In labor intensive industries, the level of automation is relatively low, and tasks are performed manually by a large number of workers. This can include industries such as agriculture, construction, hospitality, and certain manufacturing sectors.
Characteristics of Labor Intensive Industries
There are several key characteristics that define labor intensive industries:
- Low capital investment: Labor intensive industries typically have lower levels of capital investment compared to capital intensive industries. This is because the focus is on employing a large workforce rather than investing in expensive machinery or technology.
- Reliance on manual labor: In labor intensive industries, tasks are performed manually by workers rather than automated machines. This can involve physical labor, repetitive tasks, and the need for skilled or specialized labor.
- High employment potential: Labor intensive industries have the potential to generate a significant number of jobs. This can be beneficial for economies with a large labor force, as it provides employment opportunities and income for a large number of people.
It is important to note that the level of labor intensity can vary within industries. Some industries may have a higher degree of automation and rely less on manual labor, while others may have a greater need for human workers.
Examples of Labor Intensive Industries
Labor intensive industries are those that require a high amount of manual labor to produce goods or provide services. These industries typically have a large number of employees and rely heavily on human resources to carry out their operations. Here are some examples of labor intensive industries:
- Manufacturing Industry: Industries such as textile production, garment manufacturing, and furniture making are labor intensive. These industries involve various manual processes, including cutting, sewing, assembling, and finishing, which require a significant amount of human labor.
- Construction: The construction industry is another labor intensive sector. Building structures, such as houses, commercial buildings, and infrastructure projects, require a significant amount of manual labor for tasks like excavation, bricklaying, carpentry, plumbing, and electrical work.
- Hospitality and Tourism: The hospitality and tourism industry heavily relies on human resources to provide services. Hotels, restaurants, resorts, and travel agencies require a large number of employees to provide customer service, housekeeping, cooking, and other related tasks.
- Healthcare: The healthcare industry is labor intensive due to the nature of medical services. Hospitals, clinics, and nursing homes require a large number of healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, technicians, and support staff, to provide patient care and support.
- Retail: Retail industry, especially in areas such as grocery stores, supermarkets, and department stores, is labor intensive. These businesses require employees for tasks like stocking shelves, assisting customers, operating cash registers, and maintaining the store’s cleanliness.
These are just a few examples of labor intensive industries. The common thread among them is the significant reliance on human labor to carry out their operations. These industries often require a large workforce and play a crucial role in providing employment opportunities in many countries.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
