Income Elasticity of Demand: Definition, Formula, and Types
The concept of income elasticity of demand is an important measure in economics that helps to understand how changes in income affect the demand for a particular good or service. It provides insights into the sensitivity of consumer demand to changes in income levels.
Definition:
Formula:
The formula to calculate income elasticity of demand is:
Income Elasticity of Demand = (% Change in Quantity Demanded) / (% Change in Income)
Types of Income Elasticity of Demand:
There are three types of income elasticity of demand:
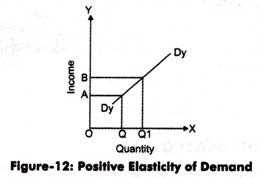
- Normal Goods: When the income elasticity of demand is positive, it indicates that the good is a normal good. This means that as income increases, the demand for the good also increases. Examples of normal goods include luxury items like cars, vacations, and designer clothing.
- Inferior Goods: When the income elasticity of demand is negative, it indicates that the good is an inferior good. This means that as income increases, the demand for the good decreases. Inferior goods are typically lower-quality or less desirable goods that consumers may switch to when their income decreases. Examples include generic brands, discount products, and used items.
- Luxury Goods: When the income elasticity of demand is greater than 1, it indicates that the good is a luxury good. This means that as income increases, the demand for the good increases at a greater rate. Luxury goods are typically high-end, expensive goods that are not necessary for survival. Examples include high-end electronics, designer handbags, and gourmet food products.
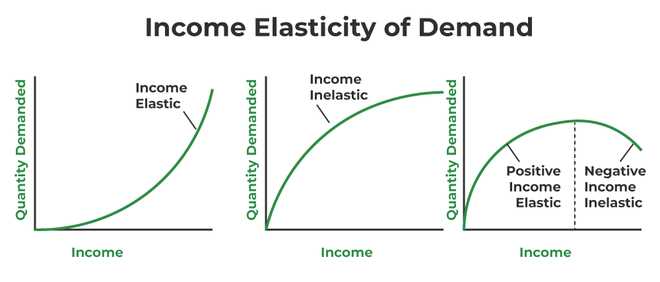
Income elasticity of demand is a concept that measures how sensitive the demand for a particular good or service is to changes in income. It is an important economic indicator that helps businesses and policymakers understand consumer behavior and market dynamics.
The magnitude of the income elasticity of demand also provides valuable insights. If the income elasticity of demand is greater than 1, it means that the good or service is income elastic, and the demand for it is highly sensitive to changes in income. This suggests that the good or service is a luxury item, and consumers are willing to spend a significant portion of their income on it. On the other hand, if the income elasticity of demand is less than 1, it means that the good or service is income inelastic, and the demand for it is not very sensitive to changes in income. This suggests that the good or service is a necessity, and consumers are less likely to cut back on it even when their income decreases.
Calculating Income Elasticity of Demand
The income elasticity of demand is a measure of how sensitive the quantity demanded of a good or service is to changes in income. It is calculated by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded by the percentage change in income.
To calculate the income elasticity of demand, you need to follow these steps:
Step 1: Determine the initial quantity demanded and income
Start by determining the initial quantity demanded of the good or service and the corresponding income level. This will serve as your baseline for comparison.
Step 2: Determine the new quantity demanded and income
Next, determine the new quantity demanded of the good or service and the corresponding income level. This will be the new data point that you will use to calculate the percentage change.
Step 3: Calculate the percentage change in quantity demanded
To calculate the percentage change in quantity demanded, subtract the initial quantity demanded from the new quantity demanded, and then divide the result by the initial quantity demanded. Multiply the answer by 100 to get the percentage change.
Step 4: Calculate the percentage change in income
Similarly, to calculate the percentage change in income, subtract the initial income level from the new income level, and then divide the result by the initial income level. Multiply the answer by 100 to get the percentage change.
Step 5: Divide the percentage change in quantity demanded by the percentage change in income
Finally, divide the percentage change in quantity demanded by the percentage change in income to calculate the income elasticity of demand. The result will be a numerical value that indicates the sensitivity of the quantity demanded to changes in income.
For example, if the income elasticity of demand is calculated to be 1.5, it means that a 1% increase in income will result in a 1.5% increase in the quantity demanded of the good or service. On the other hand, if the income elasticity of demand is calculated to be -0.8, it means that a 1% increase in income will result in a 0.8% decrease in the quantity demanded.
Calculating the income elasticity of demand allows businesses and economists to understand how changes in income will affect the demand for a particular good or service. This information can be used to make informed decisions regarding pricing, production, and marketing strategies.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
