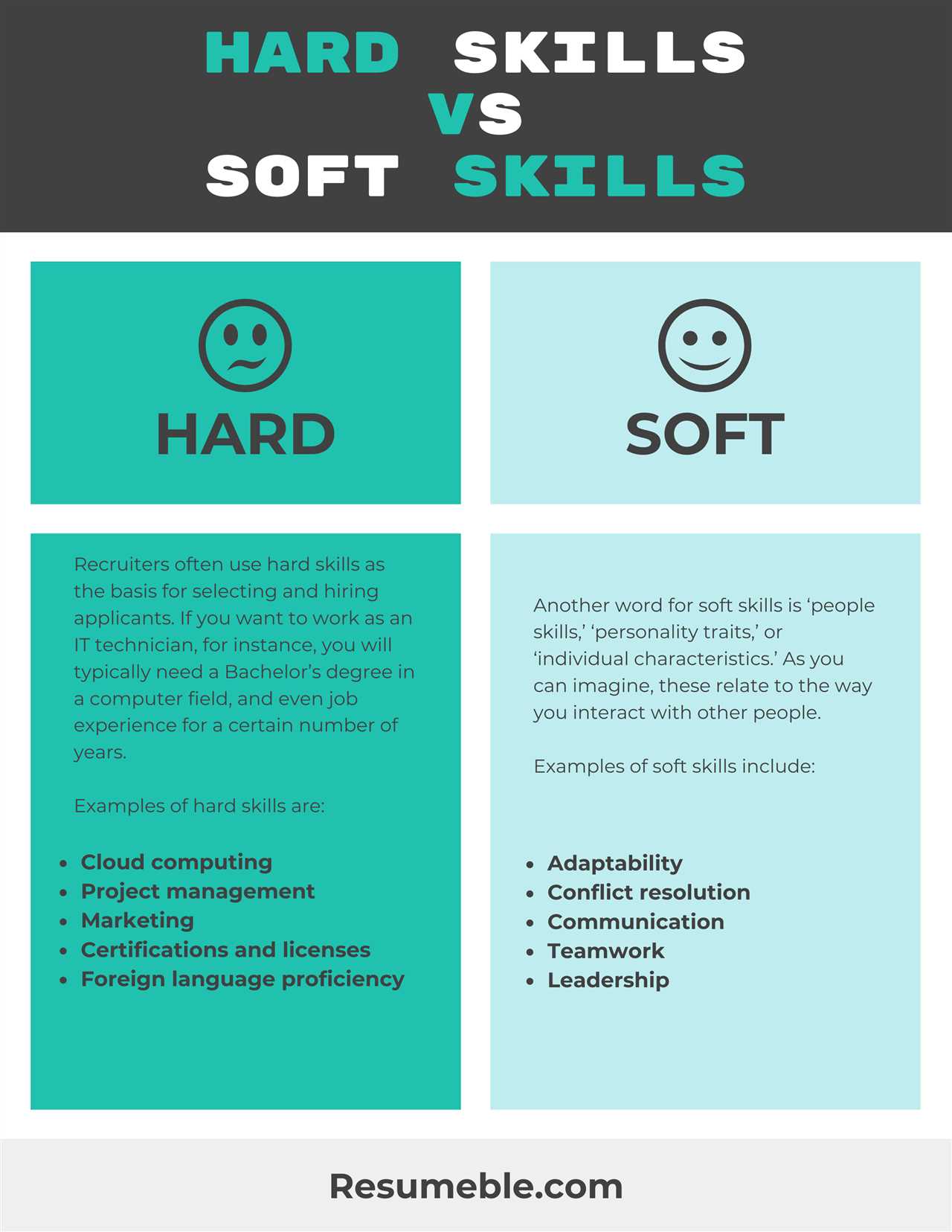
What are Hard Skills?
Hard skills refer to the specific knowledge and abilities that are acquired through education, training, and experience. These skills are typically measurable and can be easily demonstrated or tested. They are often technical in nature and are specific to a particular job or industry.
Importance of Hard Skills
Hard skills are essential for performing specific tasks and duties in a professional setting. They provide individuals with the necessary expertise to excel in their chosen field. Employers often prioritize hard skills when hiring because they directly contribute to an employee’s ability to perform job-related tasks effectively and efficiently.
Having a strong set of hard skills can also enhance career prospects and open up opportunities for advancement. Employers value individuals who possess the technical skills required for a particular role, as it reduces the need for extensive training and ensures that the individual can contribute to the organization from day one.
Examples of Hard Skills
Hard skills can vary depending on the industry and job role. Some common examples of hard skills include:
- Programming languages (e.g., Java, Python, C++)
- Data analysis and interpretation
- Project management
- Graphic design
- Financial analysis
- Foreign language proficiency
- Technical writing
- Computer literacy
These are just a few examples, and there are countless other hard skills that may be relevant to specific professions or industries.
Comparison of Hard Skills and Soft Skills
While hard skills are technical in nature and specific to a job or industry, soft skills are more general and relate to an individual’s interpersonal and communication abilities. Hard skills are typically easier to quantify and measure, while soft skills are often more subjective and difficult to assess.
Both hard skills and soft skills are important in the workplace, and a combination of both is often desired by employers. While hard skills may get an individual hired, it is often the soft skills that determine their success and ability to work well with others.
Overall, hard skills provide individuals with the necessary expertise to perform specific tasks, while soft skills contribute to their overall effectiveness and ability to work in a team environment.
Definition and Importance of Hard Skills
Hard skills are specific, teachable abilities that can be measured and quantified. They are typically acquired through formal education, training programs, or on-the-job experience. These skills are often technical in nature and are related to a specific job or industry.
Hard skills are essential for performing tasks and duties related to a particular job. They provide individuals with the necessary knowledge and expertise to carry out their responsibilities effectively. Without these skills, it would be challenging to excel in a specific field or profession.
Employers value hard skills because they are tangible and can be easily assessed. These skills are often listed as requirements in job postings and are used as criteria for evaluating candidates during the hiring process. Having the right hard skills can increase an individual’s chances of securing a job and advancing in their career.
Hard skills are constantly evolving due to advancements in technology and changes in industries. It is crucial for individuals to stay updated with the latest developments in their field and continuously acquire new hard skills to remain competitive in the job market.
| Benefits of Hard Skills | Importance of Hard Skills |
|---|---|
| 1. Enhance job performance | 1. Essential for job-specific tasks |
| 2. Increase employability | 2. Employers value and require them |
| 3. Enable career advancement | 3. Increase chances of professional growth |
| 4. Adaptability to industry changes | 4. Constantly evolving and updating |
Examples of Hard Skills
Hard skills are specific, teachable abilities that can be measured and quantified. They are often acquired through formal education, training programs, or on-the-job experience. Here are some examples of hard skills:
Technical Skills
Technical skills refer to the knowledge and proficiency in using specific tools, software, or equipment. Examples of technical skills include:
| Technical Skills | Examples |
|---|---|
| Programming | Java, Python, C++ |
| Web Development | HTML, CSS, JavaScript |
| Data Analysis | SQL, Excel, Tableau |
| Graphic Design | Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator |
Analytical Skills
Analytical skills involve the ability to gather and interpret data, solve problems, and make informed decisions. Examples of analytical skills include:
- Critical thinking
- Data analysis
- Statistical analysis
- Research
- Problem-solving
Communication Skills
Communication skills are essential in various professional settings. Examples of communication skills include:
- Verbal communication
- Written communication
- Presentation skills
- Public speaking
- Active listening
Project Management Skills
Project management skills involve the ability to plan, organize, and execute projects effectively. Examples of project management skills include:
- Leadership
- Time management
- Budgeting
- Resource allocation
- Risk management
Comparison of Hard Skills and Soft Skills
Definition:
Hard skills refer to the specific technical knowledge and abilities that are required to perform a certain job. These skills are typically learned through formal education, training programs, or on-the-job experience. Examples of hard skills include proficiency in a programming language, knowledge of accounting principles, or the ability to operate heavy machinery.
Soft skills, on the other hand, are the personal attributes and qualities that enable individuals to work well with others and effectively navigate the workplace. These skills are often more difficult to quantify and are typically developed through experience and personal growth. Examples of soft skills include communication, teamwork, problem-solving, and leadership.
Importance:
Both hard skills and soft skills are important for career success, but they play different roles in the workplace. Hard skills are often necessary to meet the technical requirements of a job and are typically listed as qualifications in job postings. Employers rely on hard skills to ensure that employees can perform the specific tasks and responsibilities of a position.
Soft skills, on the other hand, are essential for building strong relationships, collaborating with others, and adapting to changing work environments. These skills are often considered transferable and can be valuable in a variety of roles and industries. Employers look for candidates with strong soft skills because they indicate the ability to work well with others and contribute to a positive work culture.
Comparison:
While both hard skills and soft skills are important, there are some key differences between the two:
1. Tangibility: Hard skills are tangible and can be measured or demonstrated through specific tasks or certifications. Soft skills, on the other hand, are more intangible and are often assessed through behavioral observations and interpersonal interactions.
2. Teachability: Hard skills are typically taught and learned through formal education or training programs. Soft skills, on the other hand, are often developed through experience and personal growth, making them more difficult to teach or learn in a traditional classroom setting.
3. Transferability: Hard skills are often specific to a particular job or industry and may not be easily transferable to other roles. Soft skills, on the other hand, are often considered transferable and can be valuable in a variety of roles and industries.
4. Evolution: Hard skills are more likely to change and evolve over time due to advancements in technology and industry standards. Soft skills, on the other hand, are often considered timeless and can be valuable throughout a person’s career.
Differences Between Hard Skills and Soft Skills
While both hard skills and soft skills are important for success in the workplace, there are some key differences between the two.
Definition
Hard skills refer to specific technical knowledge or abilities that are acquired through education, training, or experience. These skills are typically measurable and can be easily demonstrated or tested.
Soft skills, on the other hand, are more subjective and relate to a person’s interpersonal skills, emotional intelligence, and communication abilities. These skills are often more difficult to quantify or assess.
Acquisition
Hard skills are typically acquired through formal education, vocational training, or on-the-job experience. They can be learned and developed over time through practice and repetition.
Soft skills, on the other hand, are often developed through personal experiences, interactions with others, and self-reflection. While some individuals may naturally possess certain soft skills, they can also be cultivated and improved through conscious effort and self-awareness.
Transferability
Hard skills are often specific to a particular job or industry and may not be easily transferable to other roles. For example, a software developer may have expertise in a specific programming language that may not be applicable in a different field.
Soft skills, on the other hand, are generally transferable and can be valuable in various professional and personal contexts. Skills such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving can be applied in different roles and industries.
Importance
Both hard skills and soft skills are important for career success, but their relative importance may vary depending on the job or industry. Hard skills are often essential for performing specific tasks or functions, while soft skills are crucial for building relationships, collaborating with others, and adapting to changing circumstances.
In some industries, such as technology or engineering, hard skills may be prioritized, while in others, such as customer service or leadership roles, soft skills may be more valued.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
