Funds Transfer Pricing (FTP) Calculation
Funds Transfer Pricing (FTP) is a financial management technique used by banks and other financial institutions to allocate the cost of funds to different business units and products. It helps in determining the profitability of different activities and ensures that each business unit is accountable for the cost of funds it uses.
Importance of Funds Transfer Pricing
Funds Transfer Pricing is important for several reasons:
- Profitability Analysis: FTP helps in analyzing the profitability of different business units and products. It provides insights into which activities are generating more revenue and which ones are not performing well.
- Performance Evaluation: FTP allows for the evaluation of the performance of individual business units. It helps in identifying areas of improvement and making informed decisions regarding resource allocation.
- Risk Management: FTP helps in assessing the risk associated with different activities. It allows for the identification of high-risk activities and the implementation of risk mitigation strategies.
- Cost Allocation: FTP ensures that each business unit is accountable for the cost of funds it uses. It promotes transparency and fairness in resource allocation.
Factors Affecting Funds Transfer Pricing Calculation
The calculation of Funds Transfer Pricing depends on several factors:
- Cost of Funds: The cost of funds is a key factor in FTP calculation. It includes the interest paid on deposits, borrowing costs, and other funding expenses.
- Market Conditions: Market conditions, such as interest rates and liquidity, can impact the cost of funds and, consequently, the FTP calculation.
Explanation of Funds Transfer Pricing (FTP)
Funds Transfer Pricing (FTP) is a mechanism used by financial institutions to allocate the cost of funds to different business units and products. It involves assigning a cost to each source of funds (liabilities) and determining the revenue generated by each use of funds (assets).
The FTP calculation takes into account the interest rates, market conditions, and the risk associated with different activities. It helps in determining the profitability of each business unit and product, facilitating performance evaluation and resource allocation decisions.
How Funds Transfer Pricing Works
The Funds Transfer Pricing process involves the following steps:
- Identification of Funding Sources: The first step is to identify the various sources of funds, such as deposits, borrowings, and equity.
- Assigning Costs to Funding Sources: Each funding source is assigned a cost based on the interest rates and other funding expenses associated with it.
- Allocation of Funds to Business Units and Products: The allocated funds are then assigned to different business units and products based on their funding requirements.
- Calculating Revenue Generated: The revenue generated by each business unit and product is calculated based on their interest income and other revenue sources.
- Profitability Analysis: Finally, the profitability of each business unit and product is analyzed by comparing the revenue generated with the cost of funds allocated.
The Funds Transfer Pricing process helps in determining the profitability of different activities and ensures that each business unit is accountable for the cost of funds it uses. It is an essential tool for financial institutions to manage their resources effectively and make informed decisions.
Funds Transfer Pricing (FTP) is a crucial concept in the financial industry that helps banks and other financial institutions determine the profitability of their various business units and products. It is a method used to allocate the cost of funds and measure the profitability of assets and liabilities within an organization.
The importance of Funds Transfer Pricing lies in its ability to provide a transparent and accurate assessment of the profitability of different business lines and products. It allows financial institutions to make informed decisions regarding pricing, risk management, and resource allocation.
Why is Funds Transfer Pricing important?
1. Profitability Analysis: Funds Transfer Pricing enables financial institutions to evaluate the profitability of individual business units, products, and customer segments. By assigning costs and revenues to specific assets and liabilities, FTP helps identify areas of strength and weakness within the organization.
2. Pricing Decisions: FTP plays a crucial role in determining the pricing of various financial products and services. It helps banks set interest rates on loans and deposits by considering the cost of funds and the risk associated with different assets. This ensures that pricing decisions are based on accurate cost information and align with the institution’s profitability objectives.
3. Risk Management: Funds Transfer Pricing aids in assessing the risk associated with different assets and liabilities. By assigning a cost to funds, financial institutions can measure the risk-adjusted return on their investments and identify potential areas of risk concentration. This information enables banks to make informed decisions regarding risk mitigation and portfolio diversification.
4. Resource Allocation: FTP assists in allocating resources effectively within an organization. By analyzing the profitability of different business lines and products, financial institutions can allocate capital, liquidity, and human resources to areas that generate the highest return. This ensures optimal utilization of resources and enhances overall profitability.
Conclusion
Factors Affecting Funds Transfer Pricing Calculation
1. Market Interest Rates: The prevailing market interest rates play a vital role in FTP calculation. Financial institutions need to consider the cost of borrowing funds from the market when determining the pricing for internal transfers. Changes in market interest rates can directly impact the cost of funds and, consequently, the FTP calculation.
2. Liquidity Risk: Liquidity risk refers to the potential difficulty of converting assets into cash quickly without significant loss. Financial institutions need to account for liquidity risk when calculating FTP. Higher liquidity risk may result in higher FTP rates to compensate for the potential loss of liquidity.
3. Credit Risk: Credit risk is the risk of default by borrowers or counterparties. It is crucial to consider credit risk when determining FTP, as higher credit risk may require higher FTP rates to cover potential losses in case of default. Financial institutions need to assess the creditworthiness of borrowers and counterparties to accurately calculate FTP.
4. Funding Costs: The cost of funds for financial institutions can vary depending on the source of funding. For example, funds obtained through deposits may have a different cost compared to funds borrowed from other financial institutions. It is essential to consider the funding costs when calculating FTP to ensure accurate pricing decisions.
6. Regulatory Requirements: Regulatory requirements imposed by governing bodies can also impact FTP calculation. Financial institutions need to comply with regulations related to capital adequacy, liquidity, and risk management. Failure to consider regulatory requirements in FTP calculation can result in penalties and reputational damage.
By considering these factors, financial institutions can accurately calculate FTP and make informed pricing decisions. Effective FTP calculation helps ensure the profitability and stability of the institution while aligning with market conditions and regulatory requirements.
Explanation of Funds Transfer Pricing (FTP)
Funds Transfer Pricing (FTP) is a financial tool used by banks and other financial institutions to allocate the cost of funds and measure the profitability of different business units or products. It is an internal mechanism that helps banks determine the interest rates they charge and pay for funds transferred between different departments or entities within the organization.
FTP calculations involve several steps. First, the bank needs to determine the cost of funds for each source of funds, such as deposits, loans, or borrowings. This is done by considering factors such as interest rates, market conditions, and the creditworthiness of the borrower or depositor.
Once the FTP rates are assigned, the bank can calculate the profitability of each unit or product by comparing the interest income generated with the allocated cost of funds. This allows the bank to identify the most profitable units or products and make informed decisions regarding pricing, resource allocation, and risk management.
Overall, Funds Transfer Pricing is a crucial tool for banks to effectively manage their funds and measure the profitability of their operations. It provides valuable insights into the cost of funds and helps banks make informed decisions regarding pricing, risk management, and resource allocation.
How Funds Transfer Pricing Works
Funds Transfer Pricing (FTP) is a mechanism used by financial institutions to determine the cost of funds and allocate them to various business units and products. It is an essential tool for managing profitability and risk within an organization.
FTP works by assigning a cost to each source of funds, such as deposits, borrowings, and equity. This cost is based on factors such as market rates, credit risk, and liquidity. The assigned cost is then used to determine the interest rates charged to borrowers and paid to depositors.
Allocation of Costs
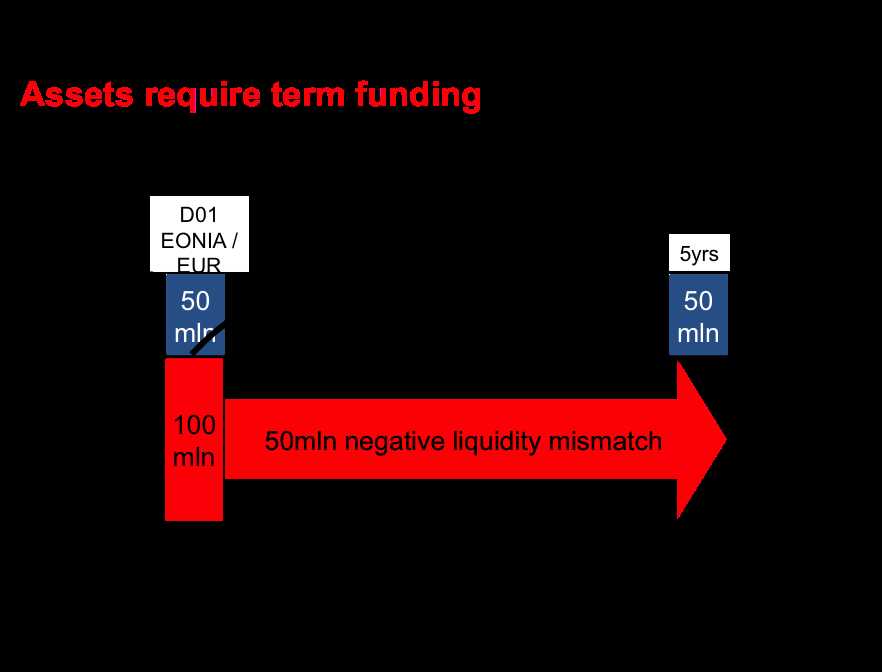
The allocation of costs allows the organization to understand the profitability of each business unit and product. It helps identify areas that are generating excess profits and areas that may be operating at a loss. This information can then be used to make strategic decisions, such as adjusting pricing or reallocating resources.
Managing Risk and Profitability

Funds Transfer Pricing also plays a crucial role in managing risk and profitability. By assigning a cost to each source of funds, it encourages business units to use funds efficiently and manage their risk exposure. Units that generate higher profits or have lower risk profiles are rewarded with lower funding costs, while units that underperform or have higher risk profiles face higher funding costs.
This incentivizes business units to make decisions that are aligned with the organization’s overall objectives. It helps ensure that resources are allocated to activities that generate the highest return and that risk is managed effectively.
Monitoring and Adjusting FTP
Monitoring and adjusting FTP is an ongoing process. Market conditions, interest rates, and risk profiles change over time, and it is essential to regularly review and update the FTP framework. This allows the organization to adapt to changing circumstances and ensure that the allocation of costs remains fair and accurate.
Regular monitoring also helps identify any anomalies or inconsistencies in the FTP calculations. This allows for timely corrections and ensures the integrity of the FTP system.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
