What is an Electronic Communication Network (ECN)?
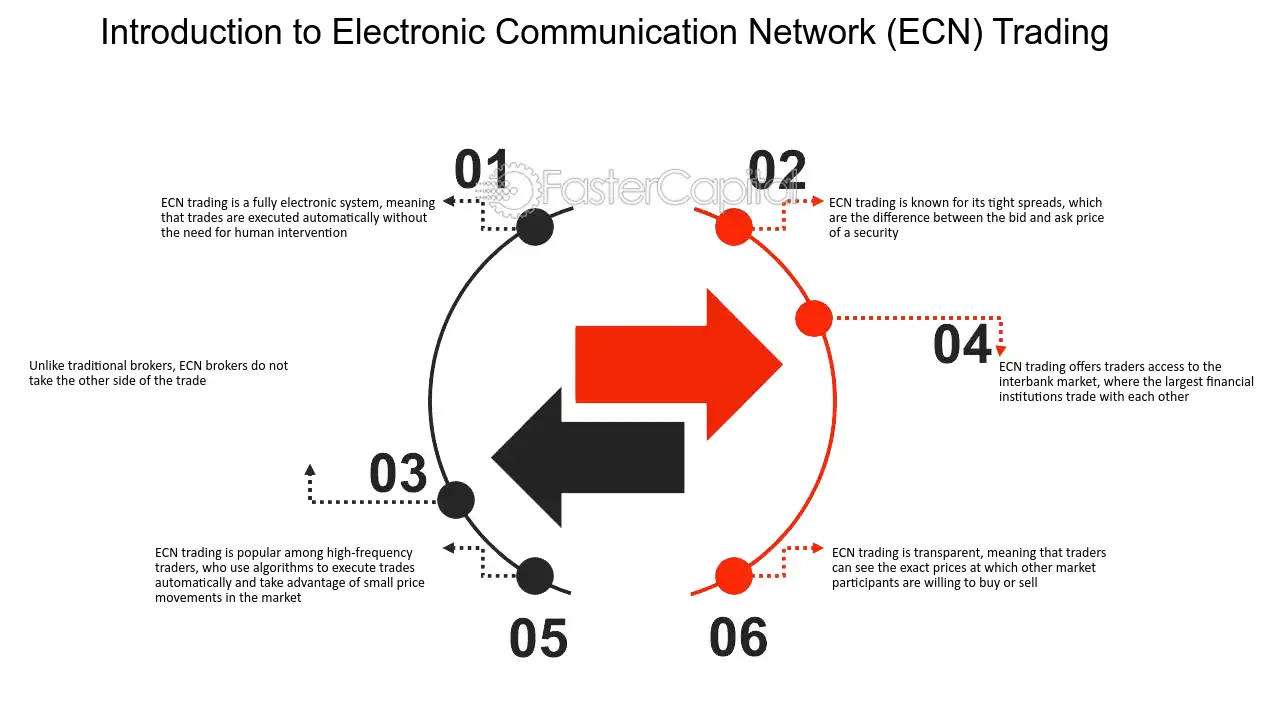
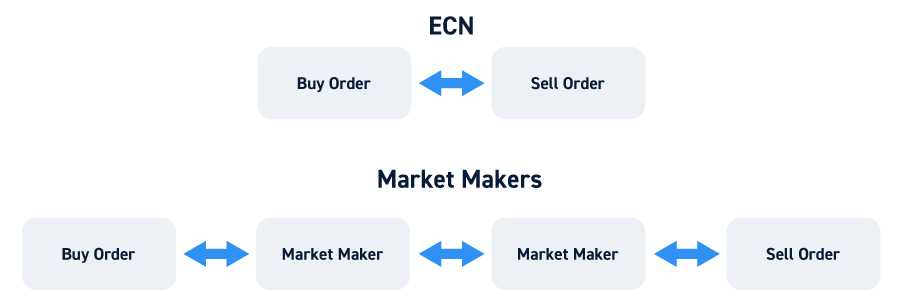
An Electronic Communication Network (ECN) is a type of trading network that allows for direct trading between market participants. It is a decentralized system that connects buyers and sellers in the financial markets, such as banks, financial institutions, and individual traders, without the need for intermediaries.
ECNs provide a transparent and efficient way to trade financial instruments, such as stocks, currencies, and commodities. They display the best available bid and ask prices from multiple market participants, allowing traders to see the depth of the market and make informed trading decisions.
How does an ECN work?
ECNs use computer-based systems to match buy and sell orders in real-time. When a trader submits an order to buy or sell a financial instrument, the ECN searches for a matching order from another participant. If a match is found, the trade is executed instantly, and both parties receive a confirmation of the transaction.
ECNs also provide access to market depth, which shows the number of buy and sell orders at different price levels. This information helps traders gauge the liquidity and potential price movements in the market.
Advantages of using an ECN
- Lower costs: ECNs often offer lower transaction costs compared to traditional trading platforms. They eliminate the need for intermediaries, such as brokers, and allow traders to access the market directly.
- Increased transparency: ECNs provide transparent pricing by displaying the best available bid and ask prices from multiple participants. This allows traders to see the true market conditions and make more informed trading decisions.
- Improved execution speed: ECNs offer fast and efficient trade execution, as orders are matched electronically in real-time. This reduces the risk of slippage and ensures that trades are executed at the best available prices.
- Access to liquidity: ECNs connect traders from around the world, providing access to a larger pool of liquidity. This increases the chances of finding a counterparty for a trade and reduces the impact of large orders on the market.
Examples of Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs)
Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs) are electronic systems that facilitate the trading of financial instruments, such as stocks, currencies, and commodities. They connect buyers and sellers directly, without the need for intermediaries like brokers or market makers. Here are some examples of popular ECNs:
1. NASDAQ
2. BATS Global Markets

BATS Global Markets is another well-known ECN that operates multiple stock exchanges in the United States and Europe. It is known for its low-cost trading and innovative technology. BATS offers trading in equities, options, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). It provides competitive pricing, efficient order routing, and a reliable trading infrastructure.
3. EBS (Electronic Broking Services)

EBS is a leading ECN in the foreign exchange (Forex) market. It is used by banks, financial institutions, and professional traders for trading currencies. EBS offers real-time pricing, deep liquidity, and anonymous trading. It is known for its robust trading platform and advanced order matching capabilities.
4. CME Globex
CME Globex is an electronic trading platform operated by the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME). It provides access to a wide range of financial products, including futures and options contracts. CME Globex offers global connectivity, 24-hour trading, and efficient order execution. It is used by traders around the world for hedging, speculation, and risk management.
These are just a few examples of the many ECNs that exist in the financial markets. Each ECN has its own unique features and advantages, but they all share the goal of providing efficient, transparent, and fair trading opportunities for market participants.
Benefits of Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs)
Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs) offer a range of benefits to traders and investors in the financial markets. These benefits include:
1. Direct Market Access
One of the key advantages of ECNs is that they provide direct market access to traders. This means that traders can interact directly with the liquidity providers, such as banks, hedge funds, and other traders, without the need for intermediaries. Direct market access allows for faster execution of trades and can result in better prices for traders.
2. Increased Transparency
ECNs offer increased transparency in the trading process. Unlike traditional trading platforms, where orders are routed through a central exchange, ECNs display the best bid and ask prices available from multiple liquidity providers. This transparency allows traders to see the true market depth and make more informed trading decisions.
3. Lower Costs
ECNs often offer lower trading costs compared to traditional trading platforms. Since ECNs connect traders directly to liquidity providers, there is no need for intermediaries, such as brokers, who may charge additional fees. Additionally, ECNs can provide access to tighter spreads, resulting in lower transaction costs for traders.
4. Faster Execution
5. Increased Liquidity
ECNs can provide access to a larger pool of liquidity compared to traditional trading platforms. By connecting traders from around the world, ECNs create a global marketplace where buyers and sellers can interact. This increased liquidity can result in tighter spreads and better order execution for traders.
6. Anonymity
ECNs offer traders the option to trade anonymously. This can be beneficial for traders who do not want their trading strategies or positions to be visible to other market participants. Anonymity can help prevent front-running and reduce the impact of large orders on the market.
7. Customization and Flexibility
ECNs often provide traders with customizable trading interfaces and advanced order types. Traders can tailor their trading platforms to suit their individual preferences and trading strategies. Additionally, ECNs offer flexibility in terms of trading hours, allowing traders to access the market outside of regular exchange hours.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
