Defining Economic Justice
Economic justice is a concept that refers to the fair distribution of economic resources and opportunities within a society. It is based on the principles of equality, fairness, and social justice. Economic justice aims to ensure that all individuals have access to basic necessities, such as food, housing, healthcare, education, and employment, and that they have the opportunity to improve their economic well-being.
At its core, economic justice seeks to address the inequalities and disparities that exist in society, particularly in relation to wealth and income distribution. It recognizes that certain groups, such as marginalized communities, women, and people of color, often face systemic barriers that prevent them from accessing economic opportunities and achieving economic security.
Key Principles of Economic Justice
There are several key principles that underpin the concept of economic justice:
- Equity: Economic justice emphasizes the importance of fairness and equal treatment. It advocates for policies and practices that promote equal access to resources and opportunities, regardless of an individual’s background or circumstances.
- Redistribution: Economic justice recognizes the need to redistribute wealth and resources in order to address existing inequalities. This may involve implementing progressive taxation policies, providing social safety nets, and investing in programs that promote economic mobility.
- Human Dignity: Economic justice recognizes that every individual has inherent worth and dignity, and that their economic well-being is essential for their overall well-being. It seeks to ensure that all individuals are able to live with dignity and have their basic needs met.
- Sustainability: Economic justice takes into account the long-term sustainability of economic systems. It advocates for practices that promote environmental sustainability and ensure that future generations have access to the same economic opportunities and resources.
Challenges in Achieving Economic Justice

While economic justice is a noble goal, there are several challenges that need to be addressed in order to achieve it:
- Inequality: Economic inequality is a major obstacle to economic justice. The concentration of wealth and power in the hands of a few can perpetuate systemic injustices and limit opportunities for others.
- Discrimination: Discrimination based on factors such as race, gender, and socioeconomic status can prevent individuals from accessing economic opportunities and achieving economic security.
- Lack of access: Limited access to education, healthcare, and financial services can hinder economic mobility and perpetuate economic disparities.
Despite these challenges, efforts to achieve economic justice continue to be made at various levels, including through policy reforms, grassroots movements, and international cooperation. By addressing the root causes of economic inequality and promoting inclusive economic systems, it is possible to create a more just and equitable society for all.
Importance of Economic Justice
Economic justice plays a crucial role in creating a fair and equitable society. It ensures that every individual has equal opportunities to access resources, participate in economic activities, and benefit from the overall economic growth. Here are some reasons why economic justice is important:
1. Reducing inequality:
Economic justice helps in reducing income and wealth inequality within a society. It ensures that the benefits of economic growth are distributed more evenly, allowing marginalized and disadvantaged groups to have a fair share of resources and opportunities. This leads to a more balanced and inclusive society.
2. Promoting social stability:
When there is a lack of economic justice, it often leads to social unrest and instability. Unequal distribution of resources and opportunities can create resentment and frustration among the disadvantaged groups, which can result in social conflicts. By promoting economic justice, societies can maintain social harmony and stability.
3. Enhancing economic efficiency:
Economic justice is not only a matter of fairness but also contributes to the overall economic efficiency. When resources and opportunities are distributed more equitably, it allows for the full utilization of human potential and talent. This leads to increased productivity, innovation, and economic growth.
4. Ensuring equal access to basic needs:
Economic justice ensures that everyone has access to basic needs such as food, shelter, healthcare, and education. It prevents the creation of a society where some individuals are deprived of these essential requirements, while others have an abundance. This promotes social cohesion and improves the overall well-being of the population.
5. Fostering social mobility:
Economic justice creates a level playing field for individuals to improve their economic status and social mobility. It provides equal opportunities for education, training, and employment, allowing individuals to break free from the cycle of poverty and achieve upward mobility. This not only benefits individuals but also contributes to the overall development of society.
Examples of Achieving Economic Justice
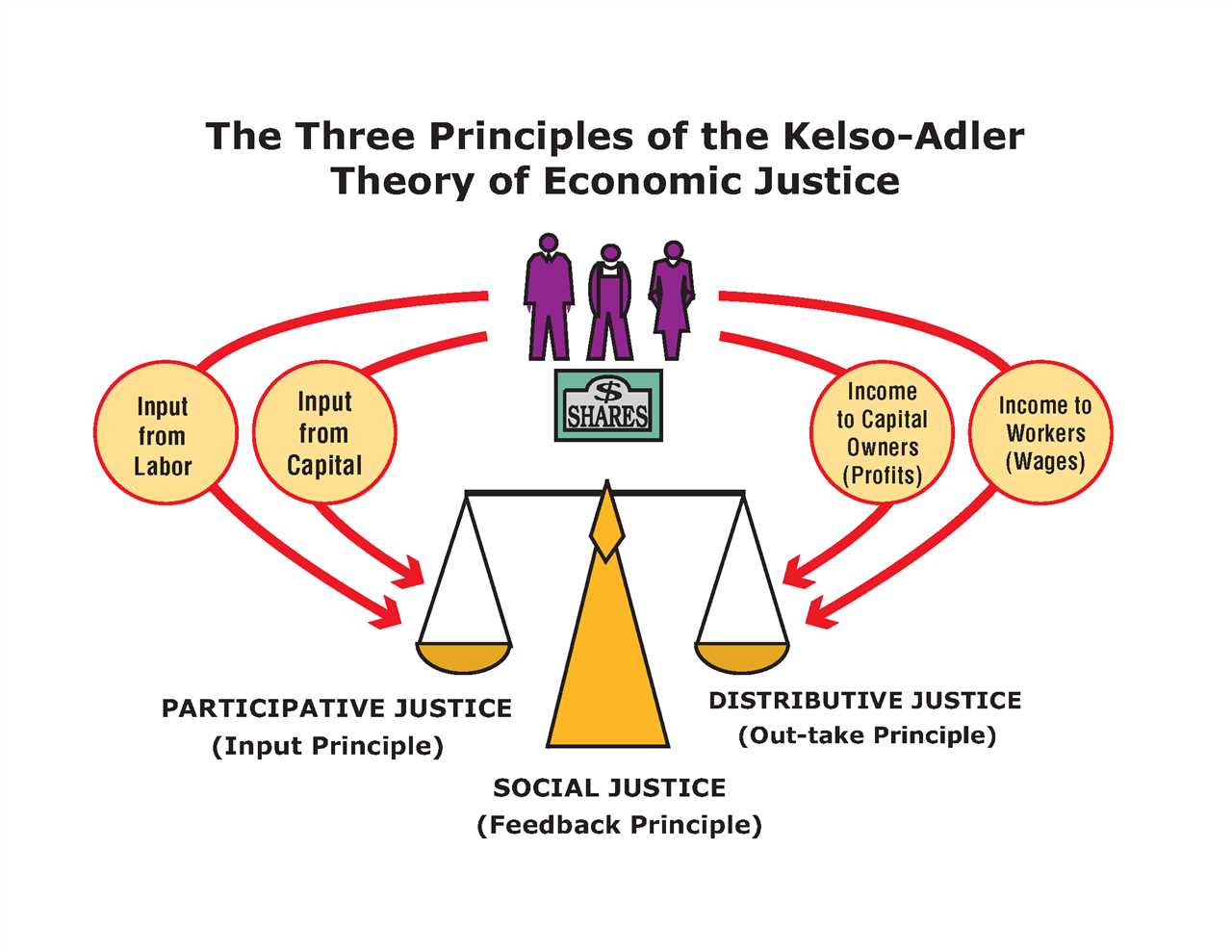
Economic justice is a concept that aims to create a fair and equitable distribution of resources and opportunities within a society. It seeks to address the inequalities and disparities that exist in the economic system, ensuring that everyone has access to basic needs and opportunities for growth and development.
There are various examples of how economic justice can be achieved:
1. Progressive Taxation: One way to achieve economic justice is through progressive taxation. This means that individuals with higher incomes are taxed at a higher rate, while those with lower incomes are taxed at a lower rate. This helps to redistribute wealth and reduce income inequality.
2. Minimum Wage Laws: Another example is the implementation of minimum wage laws. These laws set a minimum wage that employers must pay their workers, ensuring that they receive a fair and livable wage. This helps to reduce poverty and ensure that workers are not exploited.
3. Social Safety Nets: Social safety nets, such as unemployment benefits, welfare programs, and healthcare coverage, are also examples of achieving economic justice. These programs provide a safety net for individuals and families who are struggling financially, helping to alleviate poverty and ensure basic needs are met.
4. Access to Education: Ensuring equal access to quality education is another important aspect of economic justice. Education is a key driver of social mobility and economic opportunity. By providing equal access to education, regardless of socioeconomic background, individuals have a better chance of breaking the cycle of poverty and achieving economic success.
5. Fair Trade Practices: Promoting fair trade practices is another example of achieving economic justice. Fair trade ensures that producers in developing countries receive fair prices for their goods and are not exploited by multinational corporations. This helps to create more equitable trading relationships and improve the economic conditions of marginalized communities.
6. Wealth Redistribution: Wealth redistribution policies, such as inheritance taxes and wealth taxes, can also contribute to economic justice. These policies aim to reduce wealth concentration among the rich and redistribute resources to those in need, helping to create a more equitable society.
7. Gender and Racial Equality: Addressing gender and racial inequalities is crucial for achieving economic justice. This involves promoting equal pay for equal work, eliminating discriminatory practices in hiring and promotion, and providing equal opportunities for advancement. By addressing these inequalities, we can create a more inclusive and just economic system.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
