Deposit: Definition, Meaning, Types, and Example

A deposit is a financial transaction in which money is placed into a bank account or other financial institution. It is a way for individuals and businesses to securely store their funds and earn interest on their savings. Deposits can also refer to the act of placing money or other valuable assets into a safe or vault for safekeeping.
There are several types of deposits, each with its own characteristics and benefits:
| Type of Deposit | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Savings Deposit | A deposit made into a savings account, typically earning interest. | John deposits $500 into his savings account at a bank. |
| Checking Deposit | A deposit made into a checking account, typically used for everyday transactions. | Sarah deposits her paycheck of $1,000 into her checking account. |
| Time Deposit | A deposit made for a fixed period of time, such as a certificate of deposit (CD). | Mark invests $10,000 in a 2-year CD with an interest rate of 3%. |
| Foreign Currency Deposit | A deposit made in a currency other than the local currency. | Emily deposits 1,000 euros into her foreign currency account. |
What is a Deposit?
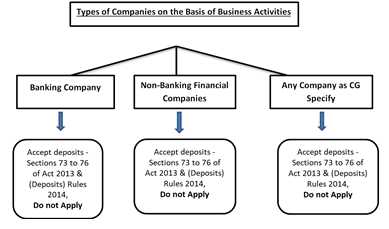
A deposit is a financial transaction in which money is placed into a bank account or held by a financial institution. It is a way for individuals and businesses to store their funds securely and earn interest on their savings.
Deposits can be made in various forms, such as cash, checks, or electronic transfers. When a deposit is made, the depositor becomes a creditor of the bank or financial institution and the funds are recorded as a liability on the institution’s balance sheet.
Types of Deposits

There are several types of deposits available to individuals and businesses:
1. Savings Deposits: These are accounts designed for individuals to save money over a period of time. They usually offer a lower interest rate compared to other types of deposits but provide easy access to funds.
3. Time Deposits: These are accounts with a fixed term, such as certificates of deposit (CDs). They offer higher interest rates than savings deposits but require the funds to be locked in for a specific period of time.
4. Money Market Deposits: These accounts combine features of both savings and checking deposits. They typically offer higher interest rates than savings accounts and provide limited check-writing privileges.
5. Negotiable Order of Withdrawal (NOW) Accounts: These are interest-bearing checking accounts typically offered to businesses. They allow for unlimited check-writing privileges while earning interest on the deposited funds.
Types of Deposits
Deposits are a fundamental aspect of banking and offer various options for individuals and businesses to store their money and earn interest. Here are some common types of deposits:
1. Savings Deposits:
Savings deposits are accounts designed for individuals to save money over time. These accounts typically offer a lower interest rate compared to other types of deposits but provide easy access to funds.
2. Current Deposits:
3. Fixed Deposits:
4. Recurring Deposits:
Recurring deposits allow individuals to deposit a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, usually monthly. These deposits are suitable for individuals who want to save a specific amount over a period of time and earn interest on their savings.
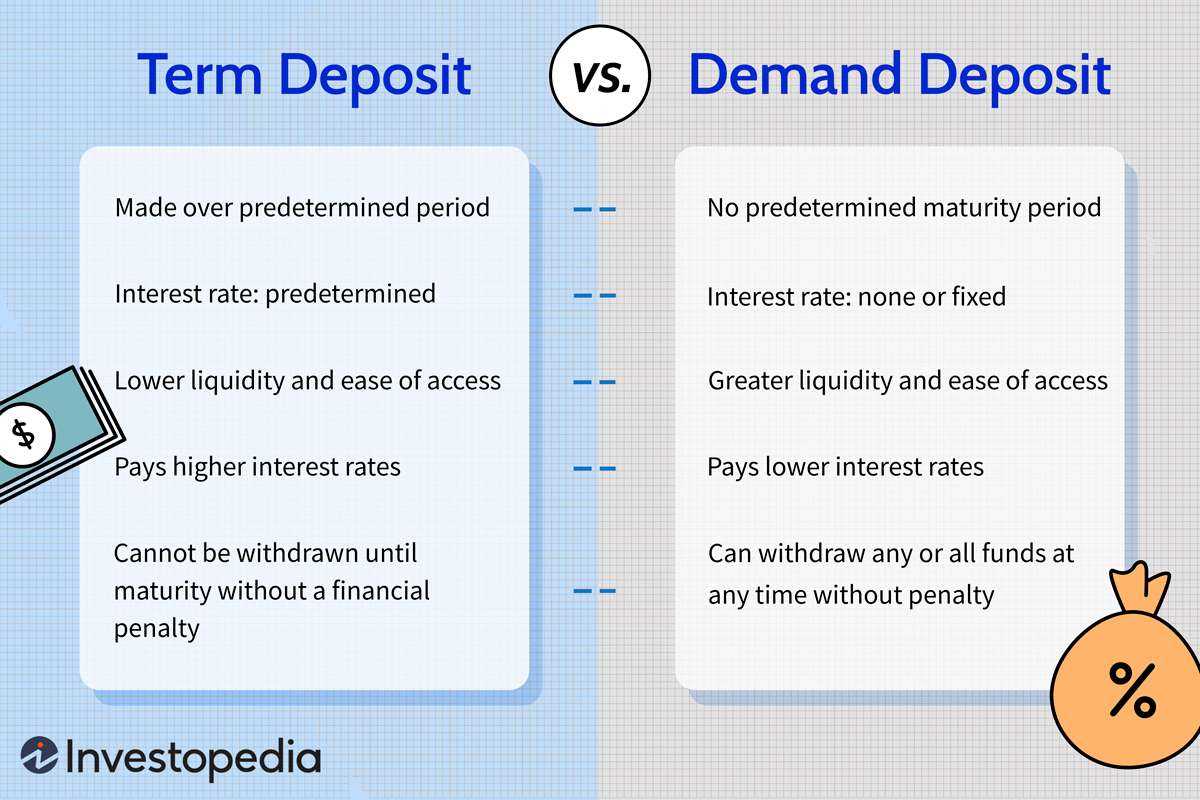
5. Term Deposits:
Term deposits are similar to fixed deposits but have a shorter maturity period. These deposits offer higher interest rates compared to savings accounts and provide flexibility in terms of the deposit amount and tenure.
6. Foreign Currency Deposits:
Foreign currency deposits allow individuals and businesses to hold their money in a foreign currency. These deposits are useful for individuals who frequently travel or engage in international transactions.
7. Demand Deposits:
It is important to carefully consider the features and terms of each type of deposit to choose the most suitable option based on individual financial goals and needs.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
