Degree of Financial Leverage Definition and Formula
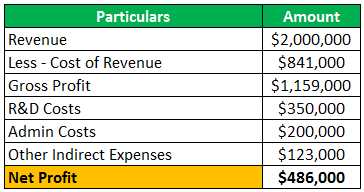
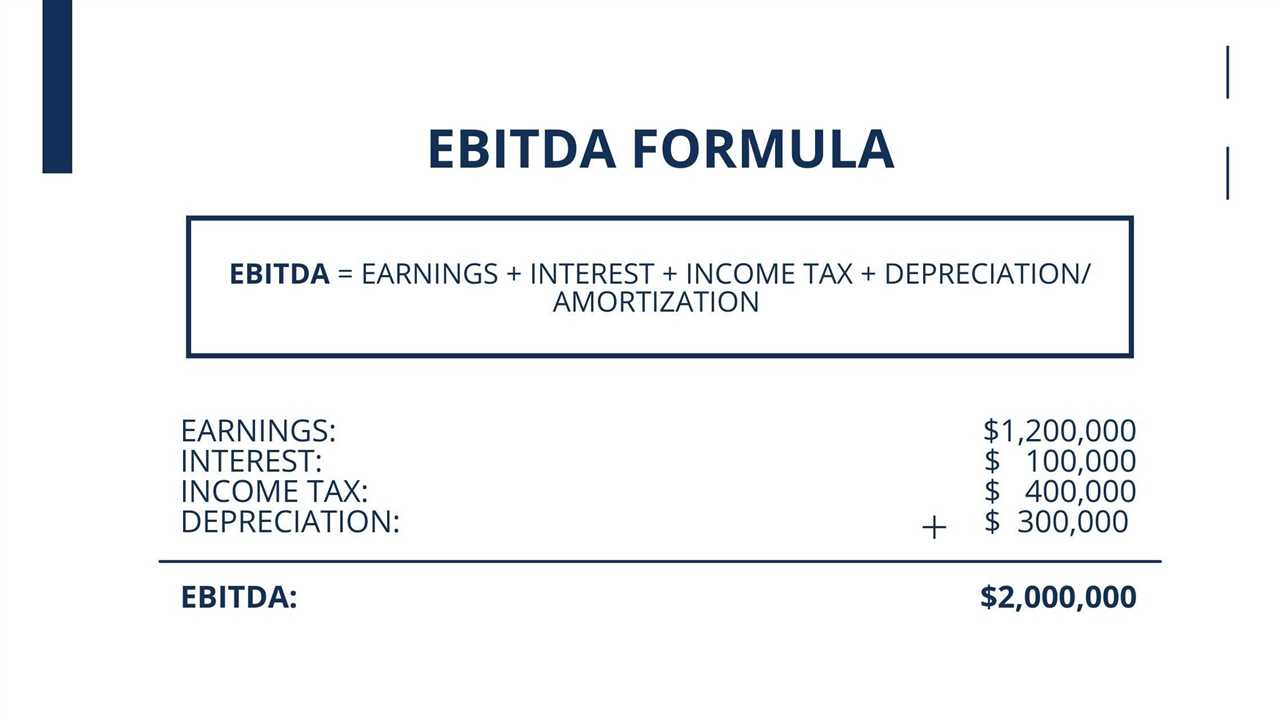
Degree of Financial Leverage Definition The degree of financial leverage (DFL) is a financial ratio that measures the sensitivity of a company’s earnings per share (EPS) to changes in its operating income. It indicates the impact of changes in operating income on the company’s profitability and risk. The degree of … …