What is Comparable Company Analysis (CCA)?
The basic idea behind CCA is that the value of a company can be estimated by looking at the financial performance and valuation multiples of similar companies. By comparing key financial metrics such as revenue, earnings, and cash flow, as well as valuation multiples such as price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio and price-to-sales (P/S) ratio, analysts can assess the relative value of a company.
CCA is commonly used in the financial industry for various purposes, including investment decision-making, mergers and acquisitions, and initial public offerings (IPOs). It helps investors and analysts gain insights into the market value of a company and make informed investment decisions.
To perform a CCA, analysts typically gather financial data and other relevant information about the target company and its comparable peers. They then calculate and compare various financial ratios and multiples to identify any significant differences or similarities. This analysis provides a basis for estimating the value of the target company.
Comparable Company Analysis (CCA) is a powerful tool used in investment analysis to determine the value of a company by comparing it to similar companies in the same industry. This analysis helps investors make informed decisions about whether to buy, sell, or hold a particular stock.
How Does CCA Work?
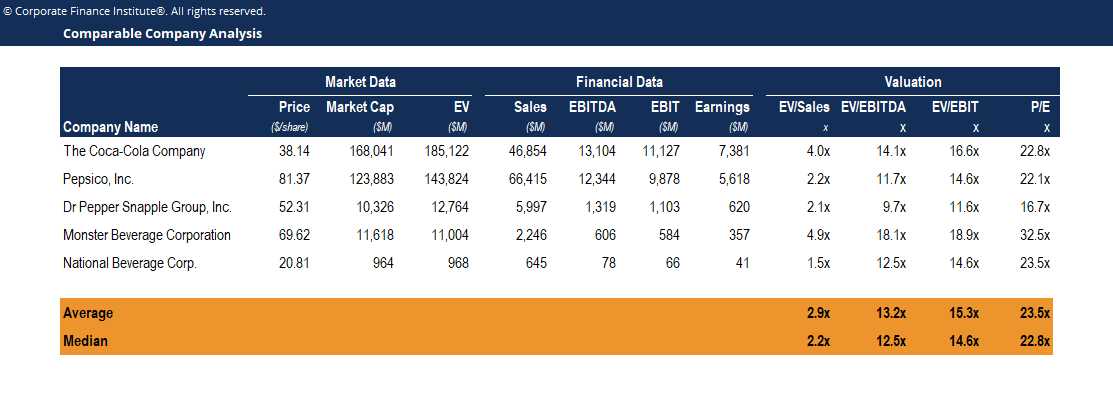
CCA works by comparing key financial metrics of a company, such as revenue, earnings, and valuation multiples, to those of its peers. By analyzing these metrics, investors can gain insights into the relative performance and valuation of the company in question.
First, a list of comparable companies is selected based on factors such as industry, size, and business model. These companies should be similar in terms of their operations and market dynamics. The financial data of these companies is then collected and analyzed.
Next, the financial metrics of the target company are compared to those of its peers. This comparison helps identify any strengths or weaknesses in the target company’s financial performance and valuation. For example, if the target company has a higher price-to-earnings ratio compared to its peers, it may indicate that the market has higher expectations for its future growth.
CCA also allows investors to identify potential investment opportunities by uncovering undervalued or overvalued companies. If a company is trading at a lower valuation multiple compared to its peers, it may be considered undervalued and present a buying opportunity. Conversely, if a company is trading at a higher valuation multiple, it may be overvalued and warrant caution.
The Benefits of CCA
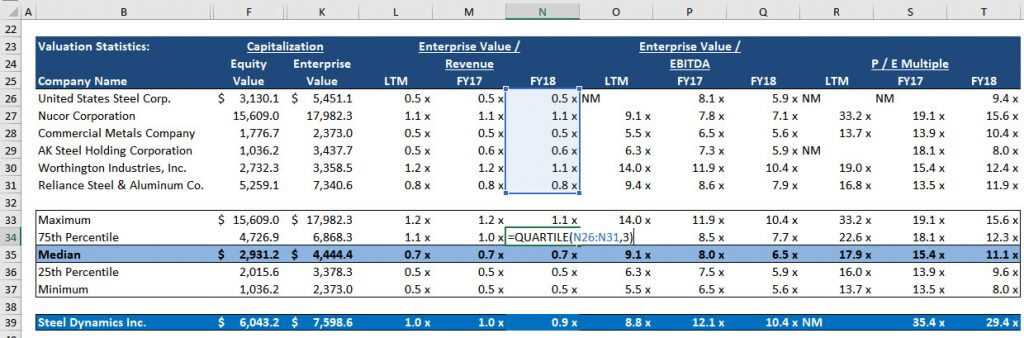
There are several benefits to using CCA in investment analysis:
- Objective Comparison: CCA provides an objective way to compare a company to its peers, eliminating biases and subjective opinions.
- Identifying Trends: By analyzing the financial metrics of multiple companies, CCA can help identify industry trends and patterns.
- Valuation Insights: CCA helps investors gain insights into the valuation of a company, allowing them to make more informed investment decisions.
- Risk Assessment: By comparing a company’s financial metrics to those of its peers, CCA can help assess the risk associated with investing in the company.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
