What is a Balance Sheet?
A balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It is one of the three main financial statements used by businesses, along with the income statement and cash flow statement.
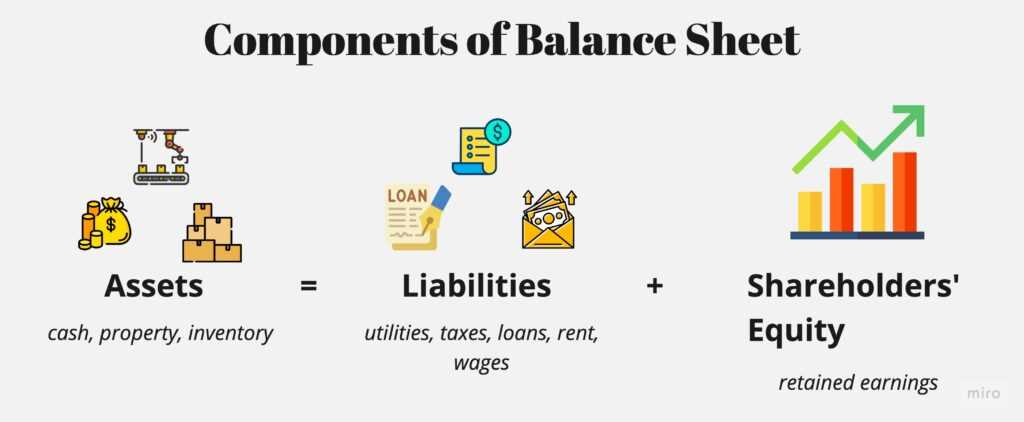
Components of a Balance Sheet
A balance sheet is divided into three main sections: assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity.
| Assets | Liabilities | Shareholders’ Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Current Assets | Current Liabilities | Common Stock |
| Long-Term Assets | Long-Term Liabilities | Retained Earnings |
| Property, Plant, and Equipment | Other Liabilities | Treasury Stock |
| Intangible Assets |
Assets represent what a company owns and include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and property. Liabilities represent what a company owes and include accounts payable, loans, and other debts. Shareholders’ equity represents the residual interest in the assets of the company after deducting liabilities and reflects the owners’ investment in the business.
The balance sheet equation is: Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity. This equation must always balance, hence the name “balance sheet.”
By analyzing a balance sheet, investors, creditors, and other stakeholders can assess a company’s financial health, liquidity, and solvency. It provides valuable information about a company’s ability to meet its short-term and long-term obligations, its overall financial stability, and the value of its shareholders’ investment.
Components of a Balance Sheet
A balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It is divided into three main components: assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity.
1. Assets
Assets are resources that a company owns or controls and that have economic value. They can be classified into two categories: current assets and non-current assets.
Current assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and short-term investments. These are assets that are expected to be converted into cash or used up within one year.
2. Liabilities

Liabilities are obligations that a company owes to external parties. They can also be classified into two categories: current liabilities and non-current liabilities.
Current liabilities include accounts payable, short-term debt, and accrued expenses. These are obligations that are expected to be settled within one year.
3. Shareholders’ Equity

Shareholders’ equity represents the residual interest in the assets of a company after deducting liabilities. It can be further divided into two components: contributed capital and retained earnings.
Contributed capital is the amount of money that shareholders have invested in the company by purchasing shares. Retained earnings, on the other hand, are the accumulated profits that the company has retained and reinvested in the business.
By analyzing the components of a balance sheet, investors and analysts can assess a company’s financial health and its ability to meet its obligations. It provides valuable information about a company’s liquidity, solvency, and overall financial stability.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
