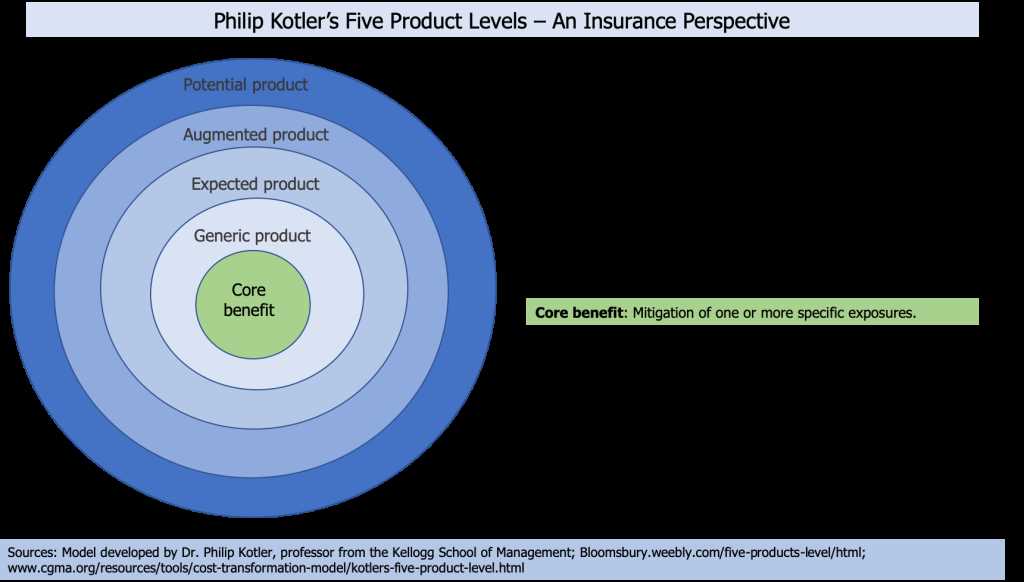
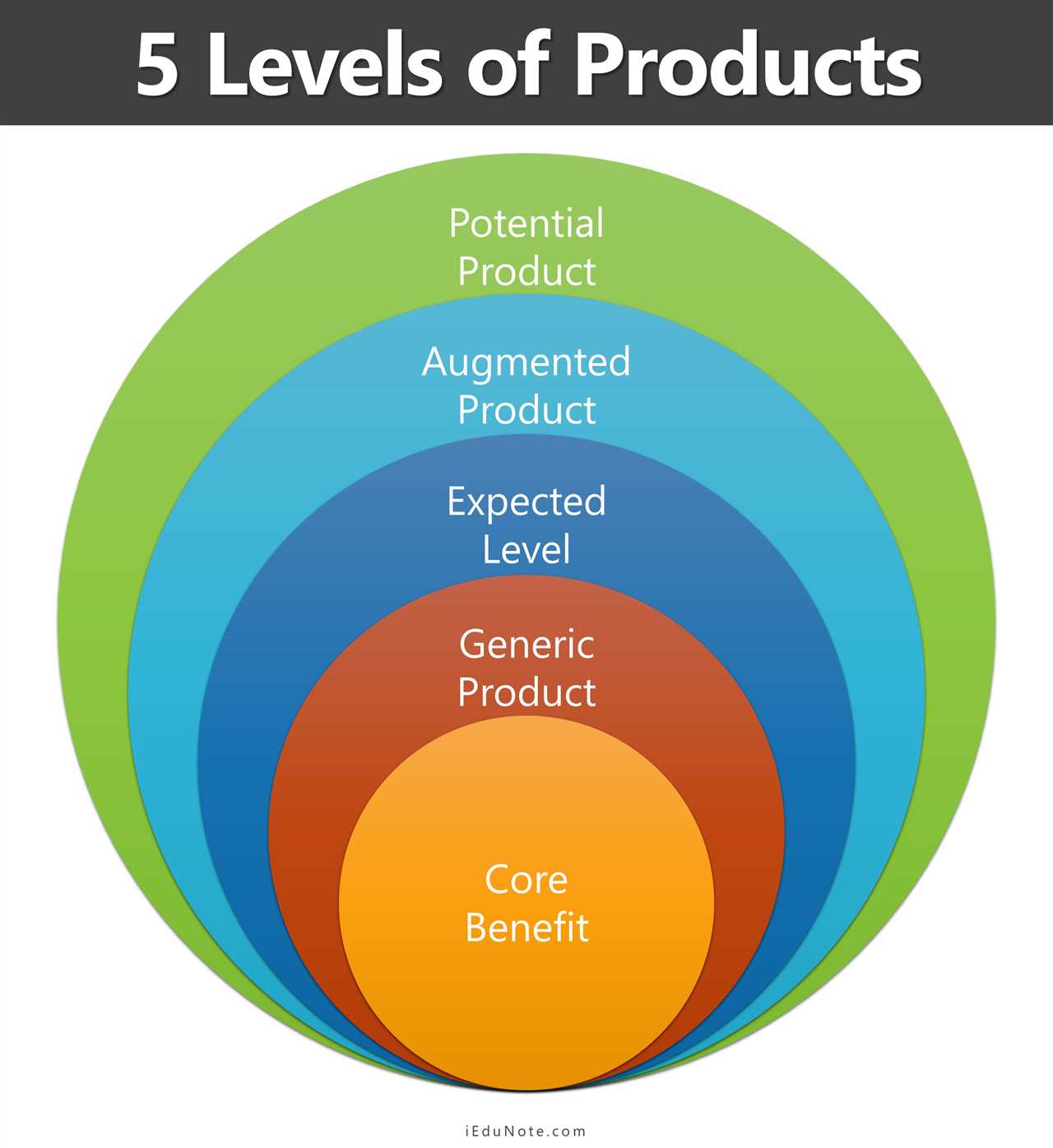
Augmented Product: Definition
An augmented product is a concept in marketing that refers to the additional features or services that accompany a core product to enhance its value and meet customer needs and expectations. It goes beyond the basic features of a product and provides additional benefits that differentiate it from competitors.
The concept of augmented product stems from the idea that customers are not only interested in the core features of a product but also in the overall experience and value it provides. By adding extra features or services, companies can create a unique selling proposition and attract more customers.
Working Mechanism of Augmented Product
The working mechanism of augmented product involves identifying customer needs and preferences and then adding features or services that fulfill those needs. This can be done through market research, customer feedback, and analysis of competitors’ offerings.
Once the additional features or services are identified, they are integrated into the core product to create the augmented product. This can be done through product design, packaging, or through the use of technology such as software or apps.
Companies also need to ensure that the augmented product is effectively communicated to customers. This can be done through marketing and advertising campaigns that highlight the added benefits and value of the product.
Examples of Augmented Product
There are numerous examples of augmented product in various industries. For example, in the automotive industry, car manufacturers often offer extended warranties, roadside assistance, and free maintenance services as part of the purchase. These additional services enhance the value of the car and provide peace of mind to the customers.
In the technology industry, companies often provide software updates, customer support, and online resources to accompany their products. These additional services ensure that customers have the latest features and can easily troubleshoot any issues they may encounter.
Another example is the hospitality industry, where hotels offer amenities such as spa services, complimentary breakfast, and concierge services to enhance the overall guest experience.
Overall, augmented product plays a crucial role in meeting customer needs and creating a competitive advantage. By adding extra features or services, companies can differentiate themselves and provide a superior customer experience.
The concept of augmented product refers to the additional features and benefits that are added to a core product to enhance its value and meet the evolving needs and expectations of customers. It goes beyond the basic features and functionalities of a product to provide added value and a unique selling proposition.
The importance of augmented product lies in its ability to differentiate a brand or product from competitors in the market. By offering additional features, services, or experiences, companies can create a competitive advantage and attract more customers. Augmented product also plays a crucial role in customer satisfaction and loyalty, as it provides enhanced benefits and meets the specific requirements of individual customers.
Benefits of Augmented Product
There are several benefits of incorporating augmented product into a marketing strategy:
- Competitive Advantage: By offering unique and valuable additional features, companies can differentiate themselves from competitors and gain a competitive edge in the market.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Augmented product provides customers with enhanced benefits and experiences, leading to higher levels of satisfaction and loyalty.
- Expanded Market Reach: By catering to the specific needs and preferences of different customer segments, augmented product allows companies to tap into new markets and attract a wider customer base.
- Brand Differentiation: Augmented product helps to establish a distinct brand identity by offering unique features and benefits that are not easily replicated by competitors.
- Improved Profitability: By adding value to the core product, companies can justify higher price points, leading to increased profitability and revenue.
Examples of Augmented Product
There are numerous examples of augmented product across various industries:
- In the automotive industry, augmented product can include features such as advanced safety systems, in-car entertainment systems, and navigation systems.
- In the technology industry, augmented product can include additional software, warranties, and customer support services.
- In the hospitality industry, augmented product can include amenities such as spa services, complimentary breakfast, and personalized concierge services.
- In the fashion industry, augmented product can include personalized styling services, alterations, and exclusive access to limited edition collections.
Working Mechanism of Augmented Product
The working mechanism of augmented products involves the integration of technology and additional features to enhance the functionality and user experience of a product. Augmented products go beyond the basic features and benefits offered by a standard product, providing added value to customers.
One of the key components of the working mechanism is the use of augmented reality (AR) technology. AR overlays digital information onto the real-world environment, creating an interactive and immersive experience for users. This technology can be integrated into various products, such as smartphones, wearable devices, and even household appliances.
Augmented products utilize sensors, cameras, and other hardware components to capture and interpret the user’s environment. The data collected is then processed by software algorithms to generate virtual objects or information that can be displayed to the user in real-time. This allows users to interact with digital content while still being aware of their physical surroundings.
For example, in the context of a smartphone, an augmented product can offer features like AR navigation, where users can see virtual directions overlaid on the real-world view through their device’s camera. This can be particularly useful for exploring unfamiliar areas or finding specific points of interest.
Another working mechanism of augmented products is the integration of additional sensors and connectivity options. For instance, a fitness tracker can be augmented with heart rate monitoring, sleep tracking, and GPS capabilities, providing users with a comprehensive health and fitness monitoring solution.
Furthermore, augmented products often leverage cloud computing and internet connectivity to enhance their functionality. This allows for real-time updates, data synchronization, and remote control capabilities. For example, a smart home system can be augmented with cloud-based services, enabling users to control their lights, thermostat, and security system from anywhere using their smartphone or voice commands.
Exploring the Technology and Implementation of Augmented Product
Augmented product is a concept that combines physical products with digital technology to enhance the overall user experience. This technology has gained significant popularity in recent years, as it offers a wide range of possibilities for businesses to engage with their customers in innovative ways.
The technology behind augmented product involves the use of computer-generated sensory inputs, such as sound, video, graphics, or GPS data, to enhance the perception of reality. By overlaying digital information onto the physical world, augmented product creates an immersive and interactive experience for users.
There are several technologies that are commonly used in the implementation of augmented product:
- Computer Vision: This technology enables computers to understand and interpret visual information from the real world. It is often used in augmented reality applications to recognize and track objects or markers in the physical environment.
- Gesture Recognition: This technology allows users to interact with augmented product through gestures, such as waving their hands or pointing their fingers. It is commonly used in gaming and virtual reality applications.
- Location-Based Services: This technology uses GPS or other positioning systems to provide information or services based on the user’s location. It is often used in augmented reality applications to display relevant information about nearby points of interest.
- Wearable Devices: These devices, such as smart glasses or smartwatches, are equipped with sensors and displays that enable users to interact with augmented product in a hands-free manner.
Implementing Augmented Product
Implementing augmented product requires a combination of hardware, software, and content development. Businesses need to invest in the necessary technology infrastructure and collaborate with developers and designers to create compelling augmented reality experiences.
Here are the key steps involved in implementing augmented product:
- Define Objectives: Clearly define the objectives and goals of the augmented product implementation. Determine how it will add value to the user experience and align with the overall business strategy.
- Choose the Right Technology: Select the appropriate technology platform or framework for developing the augmented product. Consider factors such as compatibility, scalability, and ease of use.
- Develop Content: Create engaging and interactive content that will be overlaid onto the physical world. This may include 3D models, animations, videos, or interactive games.
- Test and Iterate: Conduct thorough testing of the augmented product to ensure its functionality, usability, and performance. Gather user feedback and make necessary improvements.
- Launch and Promote: Once the augmented product is ready, launch it and promote it to the target audience. Use various marketing channels, such as social media, websites, or mobile apps, to create awareness and generate interest.
- Monitor and Analyze: Continuously monitor the performance of the augmented product and analyze user engagement and feedback. Use this data to make data-driven decisions and improve the user experience.
Overall, implementing augmented product requires a strategic approach and collaboration between different stakeholders, including business leaders, developers, designers, and marketers. By leveraging the power of augmented reality technology, businesses can create unique and immersive experiences that differentiate their products and services in the market.
Examples of Augmented Product
Augmented reality has become increasingly popular in various industries, and its applications are expanding rapidly. Here are some examples of how augmented product is being implemented:
1. Retail
In the retail industry, augmented product is being used to enhance the shopping experience for customers. For example, some clothing brands have developed augmented reality apps that allow customers to virtually try on clothes before making a purchase. This not only saves time and effort but also helps customers make more informed buying decisions.
2. Education
In the field of education, augmented product is being utilized to create interactive and engaging learning experiences. For instance, some textbooks now come with augmented reality features that allow students to access additional content, such as 3D models or interactive quizzes, by scanning specific pages with a smartphone or tablet. This makes learning more immersive and helps students better understand complex concepts.
3. Healthcare
In healthcare, augmented product is being used to improve patient care and medical training. Surgeons, for example, can use augmented reality to overlay digital information, such as medical images or real-time patient data, onto their field of view during surgeries. This helps them make more precise decisions and enhances their overall performance. Additionally, augmented reality is being used in medical training to simulate realistic scenarios and allow students to practice procedures in a safe and controlled environment.
4. Tourism

5. Gaming
Gaming is one of the industries that has fully embraced augmented product. Augmented reality games, such as Pokémon Go, have gained immense popularity worldwide. These games blend the real world with virtual elements, allowing players to interact with virtual characters and objects in their physical surroundings. Augmented reality gaming provides a unique and immersive gaming experience that appeals to a wide range of players.
These examples demonstrate the diverse applications of augmented product across various industries. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative uses of augmented reality in the future.
Showcasing Real-life Applications

The concept of augmented product has found numerous real-life applications across various industries. Here are some examples:
1. Retail: In the retail industry, augmented product is used to enhance the shopping experience for customers. For example, some clothing stores offer virtual fitting rooms where customers can try on clothes virtually before making a purchase. This not only saves time but also helps customers make more informed decisions.
2. Education: Augmented product has also made its way into the education sector. Teachers can use augmented reality to create interactive learning experiences for students. For instance, they can use augmented reality apps to bring historical events to life or to demonstrate complex scientific concepts in a more engaging way.
5. Gaming: The gaming industry has fully embraced augmented product. Augmented reality games, such as Pokemon Go, have gained immense popularity. These games allow players to interact with virtual characters and objects in the real world, creating a unique and immersive gaming experience.
6. Architecture and Design: Architects and designers can use augmented reality to visualize and present their projects. They can create virtual models of buildings and interiors, allowing clients to experience and make changes to the designs before construction begins. This helps in better communication and decision-making.
7. Marketing and Advertising: Augmented product has opened up new possibilities in marketing and advertising. Brands can use augmented reality to create interactive and engaging campaigns. For example, they can create AR ads that allow customers to virtually try on products or see how furniture would look in their homes.
These are just a few examples of how augmented product is being implemented in various industries. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of augmented reality in the future.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
