The Concept of Demographic Dividend

Demographic dividend occurs when the proportion of the working-age population (15-64 years) increases relative to the dependent population (below 15 years and above 64 years). This demographic shift creates a window of opportunity for economic progress, as a larger working-age population can potentially contribute more to the country’s productivity and output.
There are several key factors that contribute to the realization of demographic dividend. Firstly, a decline in fertility rates leads to a decrease in the dependency ratio, meaning that there are fewer dependents to support for each working-age individual. This frees up resources that can be invested in productive sectors such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
Secondly, the increase in the working-age population can lead to a boost in labor supply, which can drive economic growth. With a larger pool of workers, businesses have access to a greater talent pool, which can enhance productivity and innovation. This can attract foreign direct investment and stimulate entrepreneurship, leading to job creation and higher incomes.
Furthermore, demographic dividend can also be realized through improvements in human capital. With a larger working-age population, there is a greater potential for investments in education and skills development. This can lead to a more skilled and productive workforce, which is essential for sustained economic growth and competitiveness in the global market.
However, it is important to note that demographic dividend is not automatic and requires supportive policies and investments. Governments need to implement effective strategies to harness the potential of the working-age population, such as providing quality education and healthcare, promoting job creation, and fostering an enabling business environment.
Conclusion
The concept of demographic dividend highlights the economic benefits that can be achieved through changes in population structure. By investing in human capital and creating a favorable environment for economic growth, countries can unlock the potential of their working-age population and experience sustained development. However, realizing demographic dividend requires proactive policies and investments to ensure that the demographic shift translates into tangible economic gains.
Economic Benefits of Demographic Dividend
The demographic dividend refers to the economic benefits that can be derived from changes in a country’s age structure, particularly when there is a decline in fertility rates and a subsequent increase in the working-age population. This demographic shift can lead to increased productivity, higher savings and investment rates, and overall economic growth.
Another economic benefit of the demographic dividend is increased savings and investment. With a larger working-age population, there is a greater potential for individuals to save and invest their income. Higher savings rates can lead to increased capital accumulation, which can then be used to finance productive investments. This can stimulate economic growth and development.
In addition to these direct economic benefits, the demographic dividend can also have positive spillover effects on other sectors of the economy. For example, increased labor supply can lead to increased demand for goods and services, which can stimulate business activity and job creation. This can further contribute to economic growth and development.
However, it is important to note that realizing the economic benefits of the demographic dividend requires appropriate policies and investments. Governments need to implement policies that promote education and skills development, create job opportunities, and ensure social protection for the growing working-age population. Additionally, investments in infrastructure, healthcare, and technology are necessary to support economic growth and development.
the demographic dividend offers significant economic benefits for countries experiencing changes in their age structure. Increased labor supply, higher savings and investment rates, improvements in human capital, and positive spillover effects are some of the key advantages. However, realizing these benefits requires effective policies and investments to support the growing working-age population and stimulate economic growth.
Mechanisms of Demographic Dividend
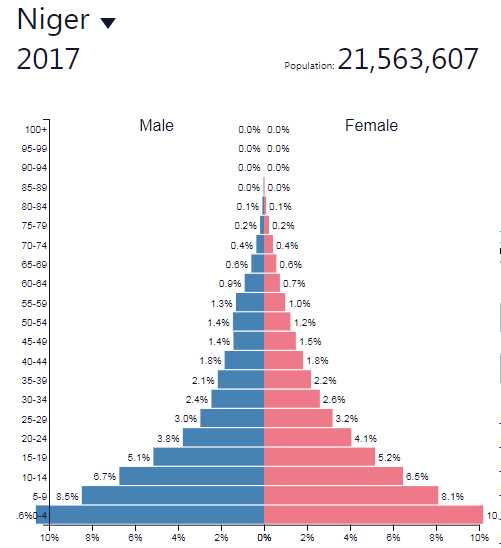
The demographic dividend refers to the economic growth potential that can be derived from changes in the age structure of a population. It occurs when the proportion of working-age individuals in a population increases relative to the dependent population (children and elderly). This demographic shift can lead to increased productivity, savings, and investment, which in turn can drive economic growth.
There are several key mechanisms through which the demographic dividend can be realized:
2. Human capital accumulation: With a larger working-age population, there is a greater potential for investment in education and skills development. This can lead to an increase in human capital, as individuals acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to participate in a modern economy. Higher levels of education and skills can enhance productivity and innovation, driving economic growth.
5. Demographic dividend multiplier effect: The demographic dividend can create a positive feedback loop, where economic growth leads to further demographic changes and vice versa. As economic growth occurs, living standards improve, leading to lower fertility rates and increased life expectancy. These demographic changes, in turn, can reinforce the demographic dividend by further shifting the age structure of the population in favor of working-age individuals.
Policy Implications and Challenges
Another important policy implication is the need for job creation. While a growing working-age population can provide a potential labor force, it is essential to create enough job opportunities to absorb this workforce. Governments should focus on promoting entrepreneurship, attracting foreign investments, and implementing policies that encourage the growth of industries that can generate employment.
Furthermore, addressing gender inequality is crucial for maximizing the benefits of demographic dividend. Women play a vital role in the economy, and empowering them through education, healthcare, and equal employment opportunities can contribute significantly to economic growth. Policies that promote gender equality and women’s empowerment should be a priority for governments.
However, harnessing the demographic dividend also comes with challenges. One of the main challenges is ensuring inclusive growth. While the demographic dividend can bring economic benefits, it is essential to ensure that these benefits are distributed equitably across different segments of society. Policies should be designed to address income inequality and reduce disparities in access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
