What is a Trailing Stop?
Definition and Explanation
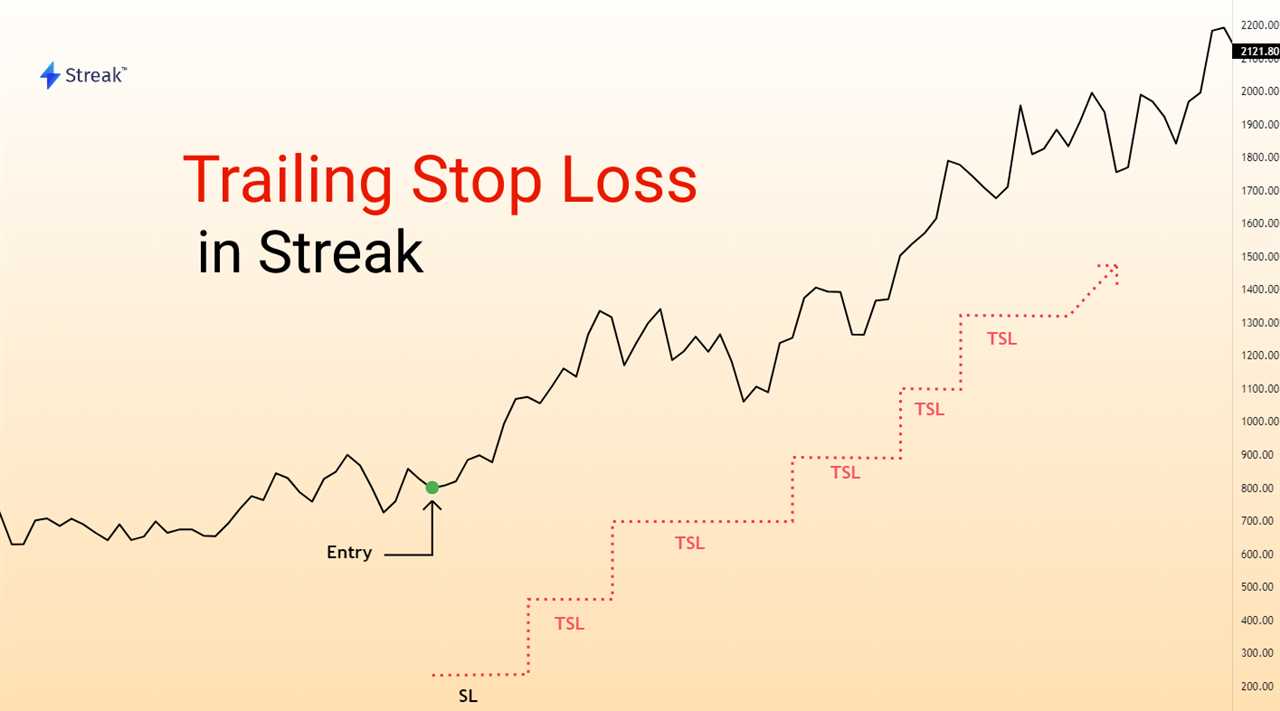
A trailing stop is a risk management tool used by traders to protect their profits and limit potential losses. It is especially useful in volatile markets where prices can fluctuate rapidly.
For example, let’s say a trader buys a stock at $50 and sets a trailing stop of 10%. If the price of the stock increases to $55, the trailing stop will adjust to $49.50 (10% below the current market price). If the price then continues to rise to $60, the trailing stop will adjust to $54 (10% below the new market price).
Example of a Trailing Stop
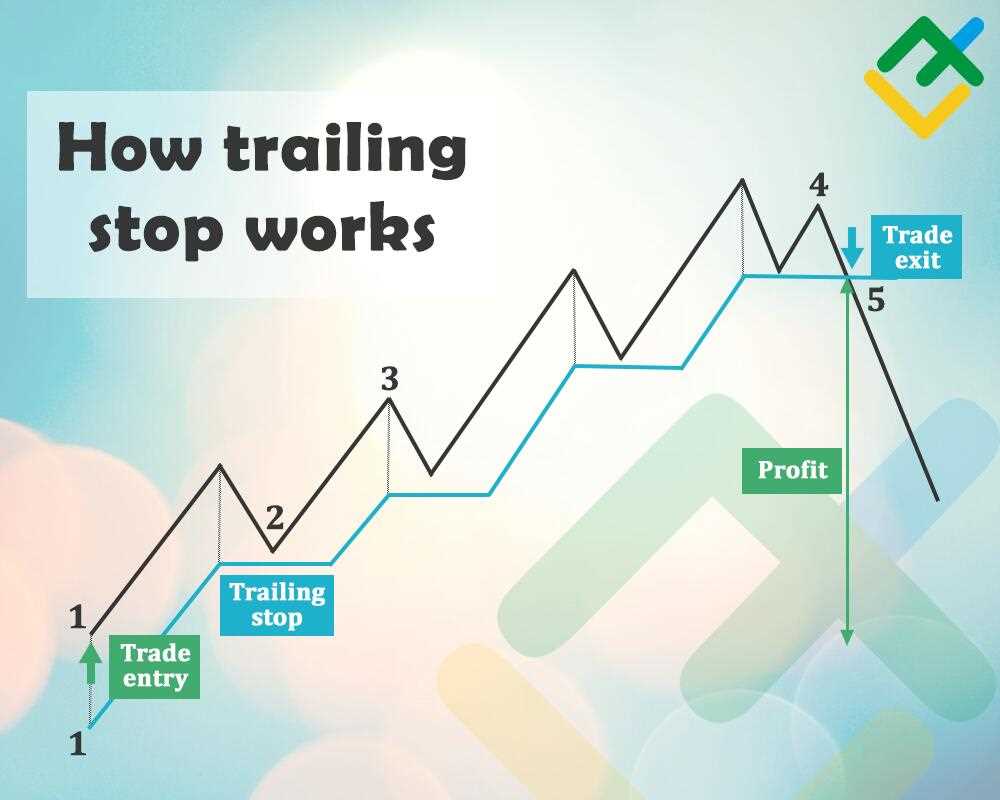
Suppose a trader purchases shares of a company at $100 per share. They set a trailing stop of 5%. If the price of the stock increases to $110, the trailing stop will adjust to $104.50 (5% below the current market price). If the price then drops to $105, the trailing stop will remain at $104.50. However, if the price continues to rise to $120, the trailing stop will adjust to $114 (5% below the new market price).
How to Use a Trailing Stop
To use a trailing stop, a trader must first determine the desired percentage or dollar amount for the trailing stop distance. This will depend on the trader’s risk tolerance and trading strategy.
It is important to note that a trailing stop is not guaranteed to protect against all losses. In fast-moving markets or during periods of extreme volatility, the price may gap past the trailing stop level, resulting in a larger loss than anticipated.
Traders should also consider the potential for false triggers with trailing stops. If the price briefly dips below the trailing stop level before rebounding, the stop order may be triggered prematurely, resulting in missed profits.
Step-by-Step Guide
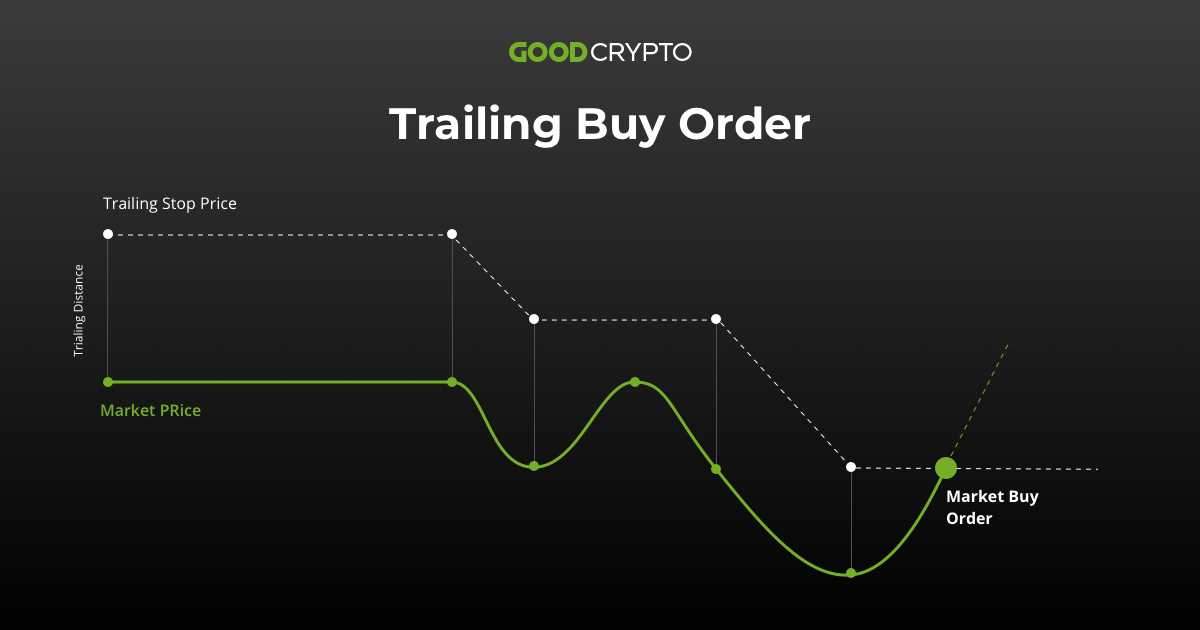
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use a trailing stop:
- Determine the desired trailing stop distance (percentage or dollar amount).
- Place a trailing stop order with your broker.
- Monitor the price movement of the asset.
- If the price increases, the trailing stop will adjust accordingly.
- If the price decreases and reaches the trailing stop level, the stop order will be triggered and the trade will be closed.
By following these steps, traders can effectively use trailing stops to protect their profits and manage their risk in the market.
Definition and Explanation
For example, let’s say a trader buys a stock at $50 and sets a trailing stop order at 10% below the highest price reached after the purchase. If the stock price rises to $60, the trailing stop order would adjust to $54 (10% below $60). If the stock price then drops to $53, the trailing stop order would adjust to $48.60 (10% below $54). If the stock price continues to decline and reaches $48.60, the trailing stop order would be triggered and the trade would be automatically closed.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| – Allows traders to capture more profit in a trending market | – Can result in premature exits if the price reverses temporarily |
| – Helps to protect profits and limit potential losses | – May not be suitable for all trading strategies |
| – Provides a more flexible and dynamic approach to stop loss orders | – Requires active monitoring and adjustment of stop loss levels |
Example of a Trailing Stop
Let’s say you have purchased a stock at $50 per share and you want to protect your profits in case the price starts to decline. You decide to use a trailing stop order to automatically sell the stock if it drops by a certain percentage.
For example, you set a trailing stop order with a 10% trailing stop value. This means that if the stock price increases to $55 per share, the trailing stop order will be triggered and a sell order will be placed at $49.50 per share (10% below the highest price of $55).
Now, let’s suppose the stock price continues to rise and reaches $60 per share. The trailing stop order will adjust accordingly and the sell order will be placed at $54 per share (10% below the new highest price of $60).
On the other hand, if the stock price starts to decline after reaching $55 per share, the trailing stop order will be triggered and a sell order will be placed at the current market price. This allows you to protect your profits and limit your potential losses.
Advantages of Using a Trailing Stop
Using a trailing stop order has several advantages:
- It helps protect your profits by automatically selling the stock if the price starts to decline.
- It helps limit your potential losses by selling the stock at the current market price if the price starts to decline.
Disadvantages of Using a Trailing Stop
While a trailing stop order can be beneficial, it also has some disadvantages:
- If the stock price experiences a sudden and significant decline, the trailing stop order may not be able to sell the stock at the desired price, resulting in larger losses.
- If the stock price fluctuates frequently, the trailing stop order may be triggered multiple times, resulting in frequent buying and selling of the stock and potentially higher transaction costs.
- The trailing stop order relies on the availability of buyers in the market, so if there is low liquidity or a lack of buyers, the sell order may not be executed at the desired price.
Overall, a trailing stop order can be a useful tool for managing risk and protecting profits in trading. However, it is important to consider the potential disadvantages and carefully monitor the market conditions when using this order type.
How to Use a Trailing Stop
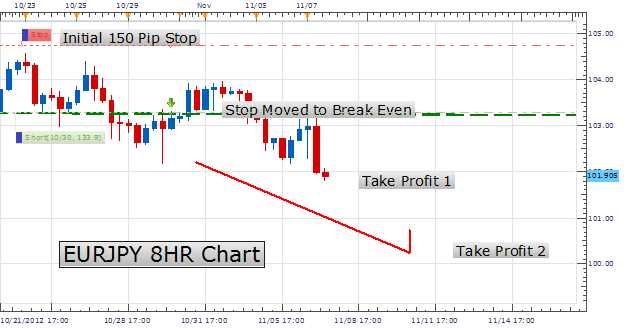
Using a trailing stop can be a useful strategy for managing risk and maximizing profits in trading. Here are the steps to effectively use a trailing stop:
- Monitor the trade: After placing the trailing stop order, it is essential to monitor the trade closely. Traders should keep an eye on the market price and the trailing stop price to ensure that the order is being executed correctly.
- Adjust the trailing stop: If the market price continues to move in the trader’s favor, they can consider adjusting the trailing stop to lock in profits. This can be done by manually moving the trailing stop price closer to the current market price.
- Exit the trade: If the market price reverses and hits the trailing stop price, the trailing stop order will be triggered, and the trade will be automatically closed. This helps to protect profits and limit potential losses.
Step-by-Step Guide
Using a trailing stop can be a valuable tool for traders looking to protect their profits and limit their losses. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use a trailing stop:
| Step 1: | Open your trading platform and select the position you want to apply a trailing stop to. |
| Step 2: | Locate the option to set a trailing stop. This can usually be found in the order entry window or in the settings of your trading platform. |
| Step 3: | Choose the percentage or price level at which you want the trailing stop to start. This is the point at which the stop loss will begin to move with the price. |
| Step 4: | Decide on the trailing stop distance. This is the number of pips or points away from the current price that you want the stop loss to trail behind. |
| Step 5: | |
| Step 6: | Monitor the trade and adjust the trailing stop as necessary. If the price continues to move in your favor, you can tighten the trailing stop to lock in more profits. If the price reverses and hits the trailing stop, the trade will be closed automatically. |
By following this step-by-step guide, you can effectively use a trailing stop to protect your profits and minimize your losses in the dynamic world of trading.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
