Tick Size Definition
In the world of trading, tick size refers to the minimum price increment at which a security can be traded. It is the smallest possible price movement that can occur in a particular market. Tick size is an important concept for traders to understand, as it can have a significant impact on their trading strategies and profitability.
The tick size determines the minimum profit or loss that can be realized from a trade. For example, if the tick size for a particular stock is $0.01, then the minimum price movement is $0.01. If a trader buys a stock at $10.00 and the price increases to $10.01, they would realize a profit of $0.01. Similarly, if the price decreases to $9.99, they would realize a loss of $0.01.
Importance of Tick Size

Tick size is important for several reasons. Firstly, it affects the liquidity of a market. A smaller tick size generally leads to greater liquidity, as it allows for more precise pricing and smaller spreads between bid and ask prices. This can make it easier for traders to enter and exit positions at desired prices.
Secondly, tick size can impact trading costs. A smaller tick size may result in higher trading costs, as traders may need to pay more in commissions or fees for each trade. On the other hand, a larger tick size may result in lower trading costs, as traders may be able to execute larger trades without incurring additional fees.
What is Tick Size in Trading?
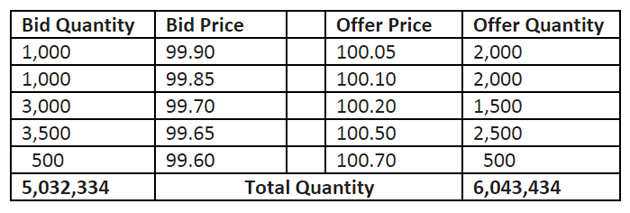
In trading, tick size refers to the minimum price increment at which a security can be traded. It represents the smallest possible movement in the price of a security. Tick size is an important concept in trading as it affects the liquidity and volatility of a security.
The tick size of a security is determined by the exchange on which it is traded. Different exchanges may have different tick sizes for the same security. For example, a stock listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) may have a tick size of $0.01, while the same stock listed on the Nasdaq may have a tick size of $0.05.
The tick size is important for traders as it determines the minimum price increment at which they can buy or sell a security. It also affects the bid-ask spread, which is the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept. A smaller tick size generally leads to tighter bid-ask spreads, which can benefit traders by reducing their transaction costs.
Tick size can also impact the volatility of a security. A smaller tick size allows for more precise price movements, which can increase the frequency and magnitude of price changes. This can create more opportunities for traders to profit from short-term price fluctuations.
Trading Requirements Examples

Stocks
For stocks, tick size requirements can vary depending on the price of the stock. Generally, stocks with a higher price have a larger tick size, while stocks with a lower price have a smaller tick size. For example, a stock with a price of $100 may have a tick size of $0.01, while a stock with a price of $10 may have a tick size of $0.001.
Traders need to be aware of these tick size requirements when placing orders for stocks. If a trader wants to buy or sell a stock, they need to ensure that their order meets the minimum tick size requirement. For example, if the tick size for a stock is $0.01, a trader cannot place an order for $10.05, as it does not meet the tick size requirement.
Options
Tick size requirements for options are different from stocks. Options have a tick size based on the price of the option contract. For example, an option with a price of $1 may have a tick size of $0.05, while an option with a price of $10 may have a tick size of $0.10.
Traders who trade options need to be aware of these tick size requirements when placing orders. They need to ensure that their order meets the minimum tick size requirement for the specific option contract they are trading. Failure to meet the tick size requirement may result in the order being rejected or executed at a different price than expected.
Futures
Futures contracts also have tick size requirements. The tick size for futures contracts is determined by the exchange on which the contract is traded. Different futures contracts have different tick sizes, and traders need to be aware of these requirements when trading futures.
For example, a futures contract for crude oil may have a tick size of $0.01, while a futures contract for gold may have a tick size of $0.10. Traders need to ensure that their orders for futures contracts meet the minimum tick size requirement set by the exchange.
Examples of Tick Size Requirements in Trading
Tick size refers to the minimum price increment at which a security can be traded. Different financial markets and instruments have different tick size requirements, which are set by the exchange or regulatory authorities. Here are some examples of tick size requirements in trading:
1. Stocks
In stock trading, tick size requirements vary depending on the price of the stock. For example, a stock priced below $1 may have a tick size of $0.0001, while a stock priced between $1 and $10 may have a tick size of $0.01. Stocks priced above $10 may have a tick size of $0.05 or higher.
2. Futures
In futures trading, tick size requirements also vary depending on the contract. For example, the tick size for the E-mini S&P 500 futures contract is 0.25 index points, while the tick size for the 10-year Treasury note futures contract is 0.015625 points.
3. Options
Options contracts have their own tick size requirements, which are usually based on the underlying stock or index. For example, an options contract based on a stock with a tick size of $0.01 will also have a tick size of $0.01.
4. Forex
In the forex market, tick size requirements vary depending on the currency pair. For example, the tick size for the EUR/USD currency pair is usually 0.0001, while the tick size for the USD/JPY currency pair is usually 0.01.
5. Cryptocurrencies

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
