The Origins of Taxation Without Representation

The concept of taxation without representation has its origins in the American Revolutionary period, specifically during the time leading up to the American Revolution in the 18th century. It refers to the idea that the American colonists were being taxed by the British government without having any say or representation in the decision-making process.
The colonists argued that they should not be subject to these taxes because they had no representation in the British Parliament, where the decisions regarding taxation were being made. This lack of representation was seen as a violation of their rights as British subjects and led to the famous slogan “No taxation without representation.”
The issue of taxation without representation became a rallying cry for the American colonists and played a significant role in the lead up to the American Revolution. It highlighted the growing tensions between the colonies and the British government and fueled the desire for independence.
The concept of taxation without representation not only played a crucial role in the American Revolution but also had a lasting impact on the development of democratic principles. It emphasized the importance of representation and the right of individuals to have a voice in the decisions that affect them.
Today, the phrase “taxation without representation” continues to be used to criticize situations where individuals or groups are taxed without having a say in the decision-making process. It serves as a reminder of the importance of democratic principles and the need for fair and equitable representation.
The Impact of Taxation Without Representation

Taxation without representation has had a profound impact throughout history, shaping the course of nations and sparking revolutions. The concept refers to the imposition of taxes on a population without their consent or the ability to influence the decision-making process. This lack of representation in taxation has often led to widespread discontent and resistance among the affected population.
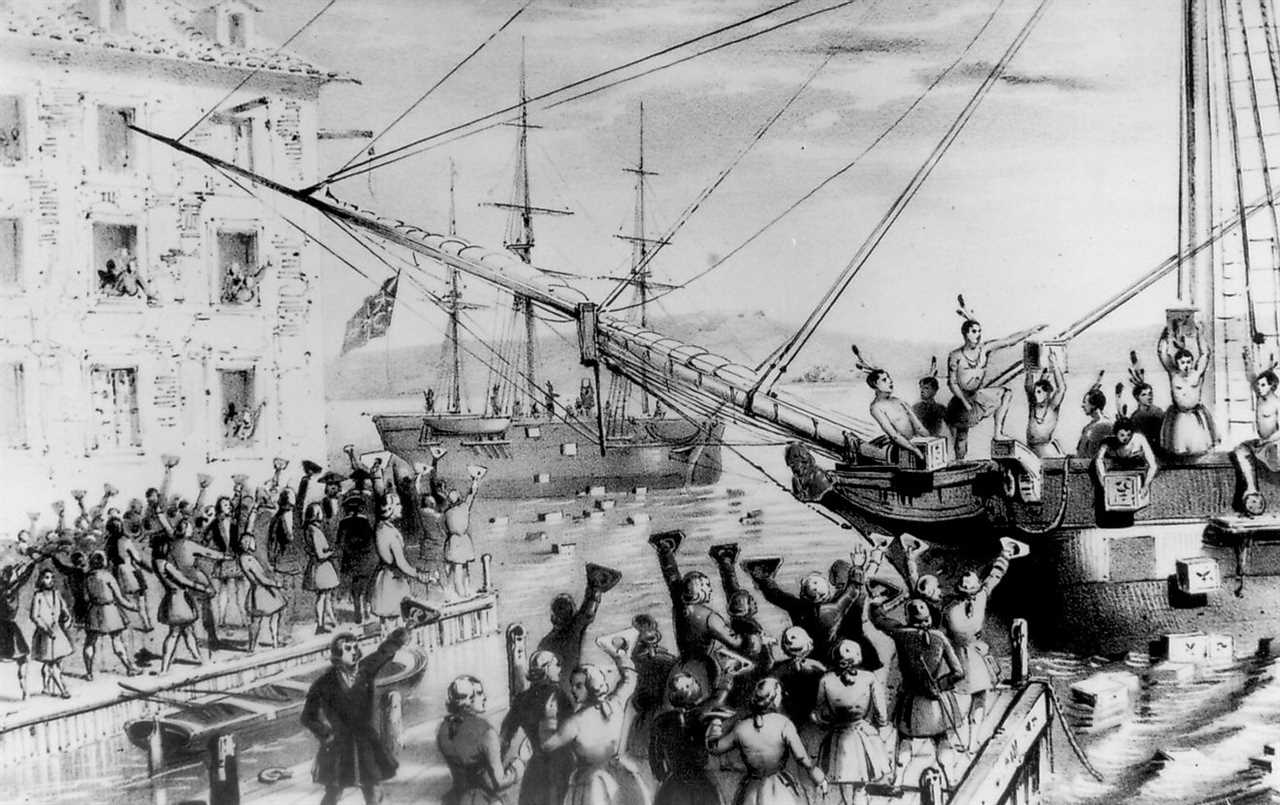
One of the most notable examples of the impact of taxation without representation is the American Revolution. The American colonists, who were subject to heavy taxation by the British government without having any representation in the British Parliament, grew increasingly frustrated with their lack of voice in decisions that directly affected their lives. This discontent eventually culminated in the Declaration of Independence and the subsequent Revolutionary War.
In addition to sparking revolutions, taxation without representation has also had significant economic consequences. When a population is burdened with excessive taxes without any say in the matter, it can lead to economic stagnation and decline. This is because individuals and businesses may be less motivated to work hard and invest in their communities if they feel that their efforts are not being fairly rewarded or if they have no influence over how their tax dollars are being spent.
Furthermore, taxation without representation can erode trust in government and undermine the social contract between rulers and the ruled. When people feel that their voices are not being heard and their interests are not being represented, it can lead to a breakdown in the relationship between the government and its citizens. This can result in social unrest, political instability, and a loss of faith in democratic institutions.
The impact of taxation without representation is not limited to historical contexts. Even in modern times, there are examples of populations feeling marginalized and disenfranchised due to unfair taxation practices. This can lead to protests, social movements, and calls for political reform.
Relevance of Taxation Without Representation Today
1. Government Accountability
Taxation without representation serves as a reminder of the importance of government accountability. When individuals are taxed without having a say in how those taxes are used or allocated, it can lead to feelings of frustration and disenfranchisement. This highlights the need for transparent and accountable governance, where citizens have a voice in decision-making processes.
2. Democratic Principles
The principle of representation lies at the core of democratic systems. Taxation without representation challenges this principle by denying individuals the right to participate in the decision-making process that directly affects their lives. This serves as a reminder of the importance of upholding democratic values and ensuring that all citizens have a voice in shaping their government.
3. Social and Economic Equality
Taxation without representation can also shed light on issues of social and economic inequality. When certain groups or individuals are excluded from the decision-making process, it can perpetuate existing disparities and hinder progress towards a more equitable society. By addressing the root causes of taxation without representation, societies can work towards creating a more inclusive and fair system.
4. Global Implications

Although taxation without representation originally emerged as a slogan during the American Revolution, its message has resonated with people around the world. Many countries continue to grapple with issues of governance, accountability, and representation. By examining the historical significance of taxation without representation, societies can learn from past mistakes and work towards building more inclusive and democratic systems.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
