Importance of Statistical Significance in Financial Analysis
Statistical significance plays a crucial role in financial analysis. It provides a way to determine whether the observed results in a study or analysis are due to chance or if they are truly significant. This is important because it allows analysts and investors to make informed decisions based on reliable data.
When conducting financial analysis, it is essential to ensure that the results obtained are not simply random fluctuations. Statistical significance helps to establish the validity and reliability of the findings, providing confidence in the conclusions drawn from the analysis.
Statistical significance is a measure of the probability that the observed results are not due to chance. It is typically represented by a p-value, which indicates the likelihood of obtaining the observed results if the null hypothesis is true. A p-value of less than 0.05 is commonly used to determine statistical significance.
By determining statistical significance, financial analysts can differentiate between random fluctuations and meaningful patterns or relationships in the data. This allows them to identify trends, make predictions, and draw conclusions that are more likely to be accurate and reliable.
Application in Financial Analysis
In financial analysis, statistical significance is crucial when analyzing various factors such as stock returns, interest rates, economic indicators, and market trends. It helps analysts identify significant relationships or patterns that can inform investment decisions.
For example, if a study finds a statistically significant relationship between a company’s earnings and its stock price, it suggests that changes in earnings can have a significant impact on the stock price. This information can be valuable for investors looking to make informed decisions about buying or selling stocks.
Statistical significance also helps in comparing different investment strategies or evaluating the effectiveness of financial models. By determining whether the observed differences in returns or performance are statistically significant, analysts can assess the reliability and effectiveness of various investment approaches.
Examples of Statistical Significance in Financial Analysis

1. Stock Market Analysis
Statistical significance is often used in stock market analysis to determine the effectiveness of investment strategies. For example, an analyst may want to test whether a particular trading strategy consistently outperforms the market. By comparing the returns of the strategy to a benchmark index using statistical tests such as t-tests or regression analysis, the analyst can determine whether the strategy’s performance is statistically significant.
Additionally, statistical significance can be used to identify patterns or anomalies in stock price movements. For instance, an analyst may want to investigate whether there is a significant relationship between a company’s earnings announcements and its stock price. By conducting a statistical analysis, the analyst can determine whether the observed relationship is statistically significant, indicating a potential trading opportunity.
2. Risk Management
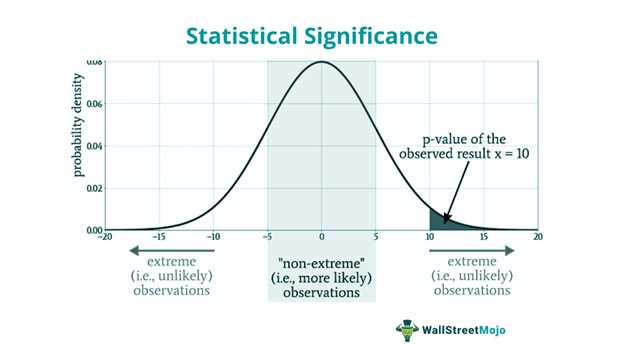
Statistical significance is also important in risk management, particularly in determining the likelihood of extreme events or outliers. Financial institutions, such as banks and insurance companies, rely on statistical models to assess and manage various risks, including credit risk, market risk, and operational risk.
For example, in credit risk analysis, statistical significance can be used to determine the probability of default for a borrower. By analyzing historical data and applying statistical techniques, such as logistic regression or survival analysis, analysts can estimate the likelihood of a borrower defaulting on their loan. This information is crucial for setting appropriate interest rates, determining credit limits, and making lending decisions.
3. Portfolio Management

In portfolio management, statistical significance is used to evaluate the performance of investment portfolios and make informed asset allocation decisions. By comparing the returns of different asset classes or investment strategies using statistical tests, analysts can determine whether the differences in performance are statistically significant.
For example, an analyst may want to compare the returns of a portfolio invested in stocks versus a portfolio invested in bonds. By conducting a statistical analysis, the analyst can determine whether the difference in returns is statistically significant, indicating a potential advantage of one asset class over the other. This information can guide portfolio managers in rebalancing their portfolios and optimizing their asset allocation strategies.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
