Sovereign Wealth Fund: Definition, Examples, and Types
A sovereign wealth fund (SWF) is a state-owned investment fund that is typically funded by a country’s foreign exchange reserves or revenue from natural resources such as oil or gas. These funds are managed by the government and are used to invest in various assets, both domestically and internationally, with the goal of generating long-term returns and preserving wealth for future generations.
Definition
A sovereign wealth fund can be defined as a pool of money owned by a government that is separate from its regular budget. It is typically created to manage and invest the excess funds generated by the country’s budget surplus, trade surplus, or revenue from natural resources. The primary objective of an SWF is to maximize returns on investment while also serving as a strategic tool for economic development and stabilization.
Examples
Another example is the Abu Dhabi Investment Authority (ADIA), which is the sovereign wealth fund of the United Arab Emirates. ADIA was established in 1976 and is responsible for investing the country’s oil revenues. It is considered one of the world’s largest sovereign wealth funds, with estimated assets of over $800 billion.
Types
Sovereign wealth funds can be categorized into different types based on their objectives and sources of funding. Some common types include:
- Stabilization funds: These funds are created to stabilize the economy during periods of economic volatility or external shocks. They aim to mitigate the impact of fluctuations in commodity prices or other external factors on the country’s budget and economy.
- Development funds: These funds are established to promote economic development and diversification. They typically invest in infrastructure projects, education, healthcare, and other sectors that contribute to long-term economic growth.
- Reserve investment funds: These funds are designed to preserve and grow a country’s foreign exchange reserves. They focus on investing in low-risk assets, such as government bonds and highly rated corporate bonds, to ensure the stability and liquidity of the reserves.
Each type of sovereign wealth fund has its own investment strategy and objectives, depending on the specific needs and goals of the country.
What is a Sovereign Wealth Fund?
A sovereign wealth fund (SWF) is a state-owned investment fund that is typically created by a government to manage and invest the country’s surplus funds. These funds are often generated from revenues derived from natural resources, such as oil, gas, or minerals, or from other sources like foreign exchange reserves or budget surpluses.
The main purpose of a sovereign wealth fund is to preserve and grow the country’s wealth over the long term, ensuring financial stability and providing a source of funds for future generations. These funds are typically managed by professional investment managers and are invested in a diversified portfolio of assets, including stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments.
While sovereign wealth funds are primarily associated with governments, they operate independently from political influence and are managed with a focus on maximizing returns and minimizing risks. However, they are subject to regulations and oversight to ensure transparency and accountability.
Overall, sovereign wealth funds are an important tool for countries to manage their financial resources and generate returns for the benefit of their citizens. They can contribute to economic growth, stability, and long-term prosperity.
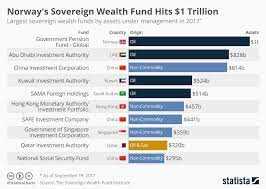
Examples of Sovereign Wealth Funds
A sovereign wealth fund is a state-owned investment fund that is typically created by a government to manage and invest the country’s surplus financial resources. These funds are usually established with the goal of generating long-term returns and preserving wealth for future generations. Here are some examples of sovereign wealth funds from around the world:
| Name | Country | Year Established | Assets Under Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Government Pension Fund Global | Norway | 1990 | $1.3 trillion |
| China Investment Corporation | China | 2007 | $941 billion |
| Abu Dhabi Investment Authority | United Arab Emirates | 1976 | $579 billion |
| Singapore Investment Corporation | Singapore | 1981 | $440 billion |
| Kuwait Investment Authority | Kuwait | 1953 | $592 billion |
These sovereign wealth funds vary in terms of their size, investment strategies, and objectives. Some funds, like the Government Pension Fund Global of Norway, focus on investing in a diversified portfolio of global assets, while others, like the China Investment Corporation, prioritize strategic investments in sectors that are of national interest.
Overall, sovereign wealth funds play a crucial role in managing a country’s financial resources and ensuring their long-term growth and stability. They provide a means for governments to invest surplus funds and generate returns that can be used for various purposes, such as funding social programs, infrastructure development, or supporting the economy during times of crisis.
Types of Sovereign Wealth Funds
Sovereign wealth funds can be categorized into different types based on their objectives, investment strategies, and sources of funding. Here are some of the common types of sovereign wealth funds:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Stabilization Funds | These funds are designed to stabilize a country’s economy by saving excess revenues during periods of high commodity prices and using them during periods of low prices. They act as a buffer against economic volatility and help maintain fiscal stability. |
| Reserve Investment Funds | These funds are created to manage a country’s foreign exchange reserves. They aim to generate returns on these reserves by investing in various asset classes such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments. |
| Development Funds | These funds are established to support economic development and promote long-term growth. They invest in domestic industries, infrastructure projects, and strategic sectors to stimulate economic activity and create employment opportunities. |
| Pension Reserve Funds | These funds are set up to meet future pension liabilities. They invest the contributions made by the government or public sector employees to ensure the availability of funds for pension payments in the future. |
| Infrastructure Funds | These funds focus on investing in infrastructure projects such as transportation, energy, telecommunications, and utilities. They aim to provide capital for the development of critical infrastructure assets that support economic growth and improve quality of life. |
Each type of sovereign wealth fund serves a specific purpose and operates according to its own investment guidelines and governance structure. The establishment of a sovereign wealth fund depends on a country’s economic conditions, financial goals, and political considerations.
It is important to note that sovereign wealth funds are subject to regulations and transparency requirements to ensure accountability and prevent misuse of funds. Governments often establish legal frameworks and oversight mechanisms to govern the operations of these funds and safeguard the interests of the country and its citizens.
Government Spending and Sovereign Wealth Funds
Sovereign Wealth Funds (SWFs) play a significant role in government spending and economic development. These funds are established by governments to manage and invest their countries’ surplus funds, typically derived from natural resources, trade surpluses, or budgetary surpluses.
SWFs are designed to generate wealth for future generations, stabilize the economy, and diversify the government’s revenue sources. They invest in various asset classes, including stocks, bonds, real estate, and infrastructure projects, both domestically and internationally.
The Impact of SWFs on Government Spending
SWFs can have a direct impact on government spending by providing a stable source of income. The returns generated by these funds can be used to finance public projects, social welfare programs, and infrastructure development. By investing in long-term assets, SWFs can generate steady income streams, reducing the reliance on volatile revenue sources such as taxes or oil prices.
Moreover, SWFs can act as countercyclical buffers during economic downturns. When faced with a recession or financial crisis, governments can tap into their SWFs to stimulate the economy, support struggling industries, or provide financial assistance to citizens. This flexibility in government spending can help mitigate the negative effects of economic shocks.
Transparency and Accountability
Transparency and accountability are crucial aspects of SWFs. Governments must ensure that these funds are managed in a responsible and transparent manner. This includes disclosing information about the fund’s investments, performance, and governance structure.
By promoting transparency, governments can build trust with their citizens and international investors. This, in turn, can attract foreign direct investment and foster economic growth. Additionally, transparency helps prevent corruption and mismanagement of public funds, ensuring that the wealth generated by SWFs benefits the entire society.
Some SWFs have established best practices and guidelines to enhance transparency and accountability. For example, the Santiago Principles, developed by the International Working Group of Sovereign Wealth Funds, provide a framework for responsible investment practices and governance.
Conclusion
Sovereign Wealth Funds are powerful tools for government spending and economic development. By effectively managing surplus funds, governments can ensure long-term financial stability, diversify revenue sources, and support economic growth. Transparency and accountability are essential in maintaining public trust and maximizing the benefits of SWFs for society as a whole.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
