What is Proportional Tax?

Unlike progressive or regressive tax systems, which have varying tax rates based on income level, a proportional tax applies a consistent tax rate to all individuals. This means that if the tax rate is set at 10%, someone earning $10,000 would pay $1,000 in taxes, while someone earning $100,000 would pay $10,000 in taxes.
Advantages of Proportional Tax

One of the main advantages of a proportional tax system is its simplicity. With a flat tax rate, individuals and businesses can easily calculate their tax liability without the need for complex calculations or deductions. This can reduce the administrative burden and make the tax system more transparent.
Another advantage of a proportional tax is that it can promote fairness and equal treatment. Since everyone pays the same percentage of their income in taxes, regardless of their income level, it can be seen as a fair way to distribute the tax burden. This can help to reduce income inequality and ensure that everyone contributes to the funding of public services.
Disadvantages of Proportional Tax
One of the main criticisms of a proportional tax system is that it can be regressive in nature. While the tax rate remains the same for everyone, the impact of the tax burden may be greater on lower-income individuals. For example, someone earning $20,000 a year would pay $2,000 in taxes, which represents a larger percentage of their income compared to someone earning $200,000 a year.
How Does Proportional Tax Work?
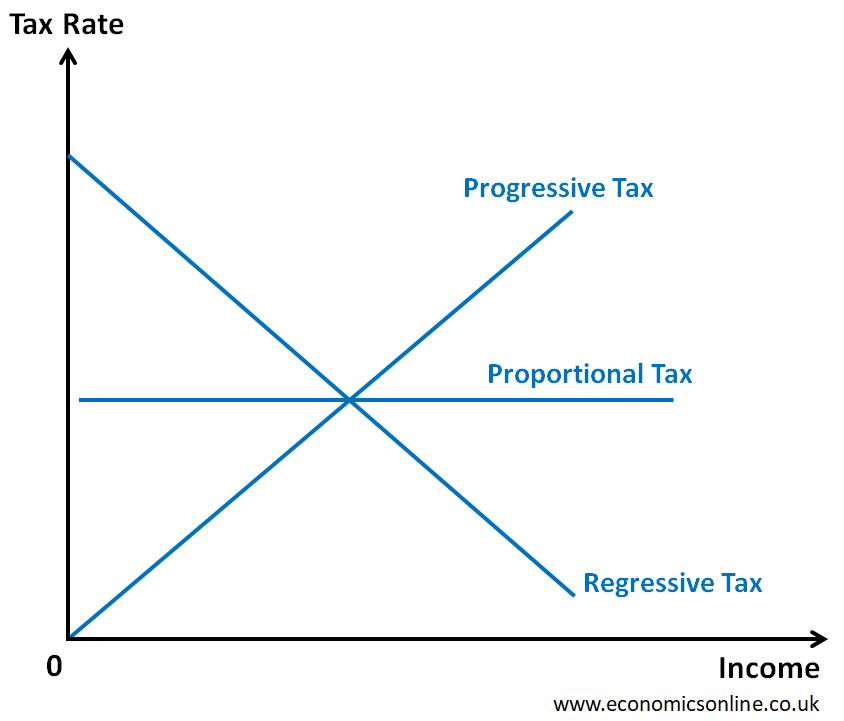
Unlike progressive or regressive tax systems, which have varying tax rates based on income or consumption, a proportional tax system applies a consistent tax rate to all individuals or businesses. For example, if the tax rate is set at 10%, someone earning $50,000 would pay $5,000 in taxes, while someone earning $100,000 would pay $10,000.
The concept behind a proportional tax system is that it is fairer and simpler than other tax systems. It ensures that everyone contributes to the government’s revenue based on their ability to pay, without placing a heavier burden on higher-income individuals or giving preferential treatment to lower-income individuals.
However, critics argue that a proportional tax system can be regressive in practice, as it may disproportionately affect lower-income individuals who rely on a larger portion of their income for basic necessities. For example, someone earning $20,000 would pay $2,000 in taxes, which may have a greater impact on their quality of life compared to someone earning $200,000 who pays $20,000 in taxes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Proportional Tax
Advantages:
1. Simplicity: One of the main advantages of a proportional tax system is its simplicity. With a flat tax rate applied to all income levels, taxpayers can easily calculate their tax liability without the need for complex calculations or extensive paperwork.
2. Fairness: Proponents of proportional tax argue that it promotes fairness by treating all taxpayers equally. Regardless of income level, everyone pays the same percentage of their income in taxes. This eliminates any perceived bias towards higher or lower income individuals.
3. Incentives for Economic Growth: Some economists believe that a proportional tax system can stimulate economic growth. By applying a flat tax rate, individuals and businesses have more disposable income, which can be reinvested into the economy through spending or investment activities.
Disadvantages:
1. Burden on Lower Income Individuals: Critics of proportional tax argue that it places a heavier burden on lower income individuals. Since everyone pays the same percentage of their income, those with lower incomes may struggle to meet their basic needs while still fulfilling their tax obligations.
3. Impact on Government Revenue: Depending on the specific tax rate set, a proportional tax system may impact government revenue. If the tax rate is too low, it may result in a decrease in revenue, potentially leading to budget deficits. On the other hand, if the tax rate is too high, it may discourage economic activity and hinder growth.
Overall, the advantages and disadvantages of a proportional tax system should be carefully considered when evaluating its effectiveness and fairness. While it offers simplicity and fairness, it may also place a heavier burden on lower income individuals and lack progressivity. Additionally, its impact on government revenue should be taken into account to ensure a balanced fiscal policy.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
