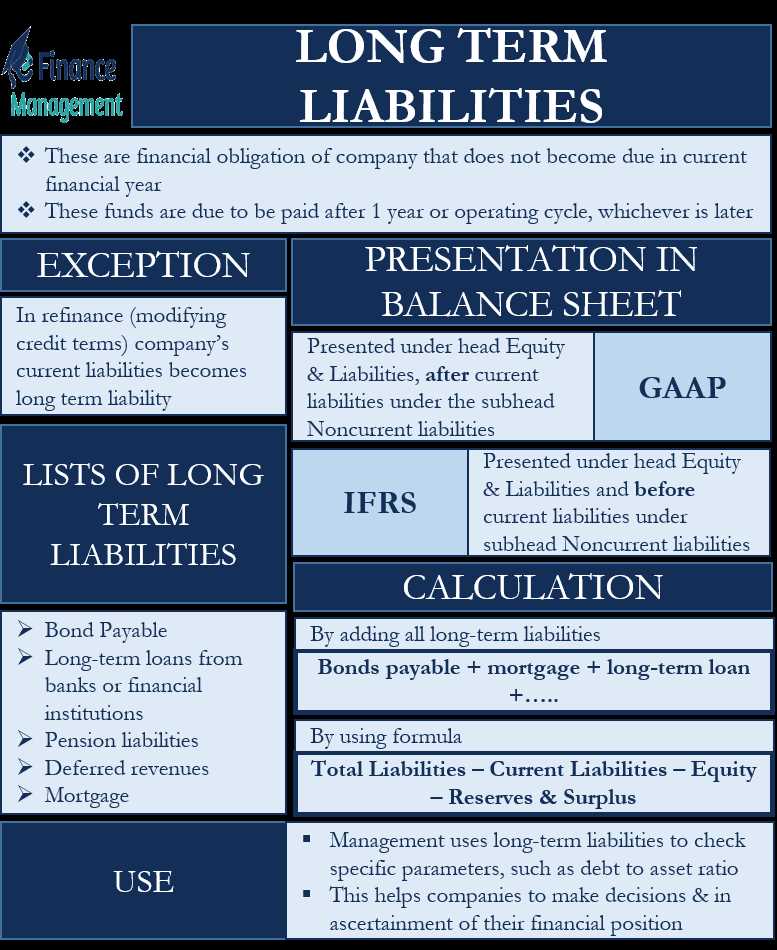
Meaning and Importance
Other long-term liabilities are an important component of a company’s financial structure. They represent obligations or debts that are not due within the next year. These liabilities can have a significant impact on a company’s financial health and ability to meet its long-term obligations.
Other long-term liabilities can include various types of debt, such as long-term loans, bonds, and leases. These obligations are typically repaid over a period of several years and may have specific terms and conditions attached to them.
Additionally, other long-term liabilities can also include deferred revenue, pension obligations, and other long-term contractual obligations. These liabilities can have a significant impact on a company’s financial statements and should be carefully managed and disclosed to stakeholders.
Overall, other long-term liabilities play a crucial role in a company’s financial management and should be carefully monitored and managed to ensure the company’s long-term financial stability and success.
Types of Other Long-Term Liabilities
Other long-term liabilities refer to the obligations that a company has to pay over a period of more than one year. These liabilities are not classified as current liabilities because they are not due within the next year. Instead, they are long-term in nature and are typically paid off over several years.
There are several types of other long-term liabilities that a company may have:
1. Long-Term Debt
Long-term debt is one of the most common types of other long-term liabilities. It refers to the money that a company borrows and is obligated to repay over a period of more than one year. This can include loans, bonds, and other forms of debt. Long-term debt is typically issued to finance large projects or investments.
2. Deferred Income Taxes
Deferred income taxes are another type of other long-term liability. They arise when a company’s taxable income is different from its financial income. The difference between the two creates a temporary tax liability that will be paid in future years. This liability is classified as other long-term because it is not due within the next year.
3. Pension Liabilities
4. Lease Obligations
Lease obligations are another type of other long-term liability. They arise when a company leases assets such as buildings, equipment, or vehicles. The company is obligated to make lease payments over the term of the lease, which can range from a few years to several decades. These lease obligations are considered other long-term liabilities because they are not due within the next year.
Example of Other Long-Term Liabilities
Other long-term liabilities are financial obligations that a company expects to settle over a period of more than one year. These liabilities are not classified as current liabilities because they are not expected to be settled within the next year.
One example of other long-term liabilities is long-term debt. This refers to any debt that a company owes and expects to repay over a period of more than one year. Long-term debt can include loans, bonds, and other forms of borrowing.
Another example of other long-term liabilities is pension obligations. Many companies offer pension plans to their employees, which provide retirement benefits. These pension obligations are considered long-term liabilities because the company expects to make payments to retired employees over a period of many years.
Other long-term liabilities can also include deferred taxes. When a company defers taxes, it means that it delays paying taxes on income that has been earned but not yet received. These deferred taxes are considered long-term liabilities because the company expects to pay them in future years.
Importance of Other Long-Term Liabilities

For example, if a company has a large amount of long-term debt, it may need to allocate a significant portion of its cash flow towards debt repayment. This can limit the company’s ability to invest in growth opportunities or make other necessary expenditures.
Similarly, pension obligations can be a significant financial burden for companies, especially if the pension plan is underfunded. Companies may need to contribute large amounts of money to their pension plans to ensure they can meet their obligations to retired employees.
Conclusion
Other long-term liabilities are an important aspect of a company’s financial structure. They represent financial obligations that extend beyond one year and can have a significant impact on a company’s financial health. By properly managing these liabilities, companies can ensure they have the necessary resources to meet their obligations and maintain a strong financial position.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
