Obligation Legal Definition

An obligation, in the legal context, refers to a binding duty or responsibility that one party has towards another. It is a legal requirement that must be fulfilled, and failure to do so can result in legal consequences. Obligations can arise from various sources, such as contracts, laws, or social norms.
There are different types of obligations in finance, including:
- Debt obligations: These are financial obligations that arise from borrowing money, such as loans or bonds. The borrower has an obligation to repay the borrowed amount, along with any agreed-upon interest or fees, within a specified period.
- Contractual obligations: These are obligations that arise from a legally binding agreement between two or more parties. The terms and conditions of the contract outline the obligations of each party, such as making payments, delivering goods, or providing services.
- Legal obligations: These are obligations that arise from laws and regulations. For example, businesses have legal obligations to pay taxes, comply with labor laws, and follow industry-specific regulations.
It is important to understand and fulfill obligations in finance to maintain trust and integrity in business relationships. Failure to meet financial obligations can result in legal action, damage to reputation, and financial penalties.
In finance, the legal concept of obligation refers to a binding agreement or duty that one party has towards another party. It is a legal responsibility that must be fulfilled, and failure to do so can result in legal consequences.
Obligations in finance can take various forms, such as contractual obligations, legal obligations, or moral obligations. Contractual obligations are typically outlined in a written agreement between two parties, specifying the terms and conditions that must be met. Legal obligations, on the other hand, are imposed by law and require compliance to avoid legal penalties.
Individuals also have financial obligations, such as paying taxes, mortgages, or loans. These obligations are legally binding and failure to fulfill them can result in penalties, fines, or even legal action.
Furthermore, obligations in finance play a significant role in investment and lending activities. Investors have an obligation to act in the best interest of their clients and to provide accurate and timely information. Lenders have an obligation to assess the creditworthiness of borrowers and to ensure that loans are repaid according to the agreed terms.
Obligation Examples in Finance
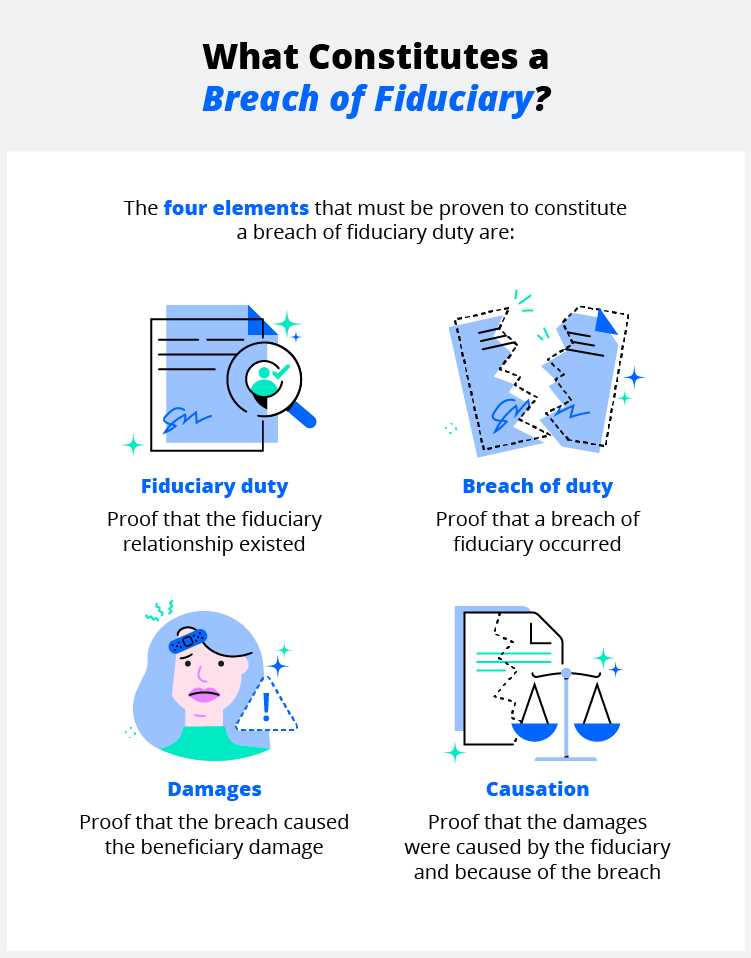
In finance, obligations refer to the legal or moral responsibilities that individuals or entities have to fulfill. These obligations can arise from various financial transactions and agreements. Here are some examples of obligations in finance:
1. Loan Repayment Obligations
When individuals or businesses borrow money from a bank or financial institution, they have an obligation to repay the loan amount along with any interest accrued. Failure to meet these repayment obligations can result in penalties, damage credit scores, and even legal action.
2. Bond Issuance Obligations
When a company or government issues bonds to raise capital, they have an obligation to make regular interest payments to bondholders and repay the principal amount at maturity. These obligations are legally binding and failure to meet them can lead to default.
3. Lease Obligations
When individuals or businesses lease assets such as property, equipment, or vehicles, they have an obligation to make regular lease payments as per the terms of the lease agreement. Failure to meet these obligations can result in eviction or repossession of the leased assets.
4. Payment Obligations
Payment obligations can arise from various financial transactions, such as invoices, contracts, or purchase orders. Individuals or businesses have an obligation to make timely payments for goods or services received. Failure to meet these payment obligations can damage business relationships and result in legal disputes.
5. Pension Obligations
Companies or governments that offer pension plans to their employees have an obligation to make regular contributions to the pension fund. These contributions are used to provide retirement benefits to employees. Failure to meet these obligations can lead to financial instability and legal consequences.
Overall, obligations in finance play a crucial role in maintaining trust, stability, and legal compliance in financial transactions and agreements. It is important for individuals and entities to understand and fulfill their obligations to ensure smooth financial operations.
Real-Life Scenarios Demonstrating Obligations in the Financial Industry
In the financial industry, obligations play a crucial role in various real-life scenarios. Here are some examples that demonstrate how obligations are encountered and managed:
1. Loan Repayment
When individuals or businesses take out a loan from a bank or financial institution, they enter into an obligation to repay the borrowed amount along with any interest within a specified period. Failure to meet this obligation can result in penalties, legal actions, and damage to the borrower’s credit score.
2. Bond Issuance
When a company or government issues bonds to raise capital, they are creating an obligation to repay the bondholders the principal amount plus interest over a predetermined period. Bondholders have the legal right to receive these payments, and the issuer must fulfill this obligation to maintain investor confidence and access to future funding.
3. Insurance Contracts
Insurance policies create obligations for both the insurer and the policyholder. The insurer is obligated to provide coverage and compensate the policyholder in the event of a covered loss or damage. On the other hand, the policyholder is obligated to pay the agreed-upon premiums regularly. Failure to meet these obligations can result in the termination of coverage or denial of claims.
4. Derivatives Trading
In derivative markets, traders enter into various obligations based on their trading positions. For example, a futures contract obligates the buyer to purchase the underlying asset at a specified price and the seller to deliver it. Options contracts create obligations for the buyer to exercise the option or let it expire worthless and the seller to fulfill the terms if the buyer chooses to exercise.
5. Merchant Agreements
When businesses enter into agreements with payment processors or credit card companies, they assume obligations to comply with the terms and conditions set by these entities. This includes obligations such as accepting certain payment methods, maintaining data security standards, and paying transaction fees. Non-compliance with these obligations can result in penalties, termination of services, and reputational damage.
Business Essentials: Obligation
What is an Obligation?
An obligation can be defined as a legal or moral responsibility to fulfill a certain duty or perform a specific action. In finance, obligations often refer to financial commitments or liabilities that an individual or organization is bound to fulfill. These obligations can arise from various sources, such as contracts, agreements, laws, or regulations.
It is important to note that obligations are not limited to monetary transactions. They can also include non-financial responsibilities, such as providing certain services, delivering goods, or meeting legal requirements.
Examples of Obligations in Finance
There are numerous examples of obligations in the financial industry. Some common examples include:
- Payment of debts: When an individual or organization borrows money, they have an obligation to repay the borrowed amount along with any agreed-upon interest.
- Compliance with regulations: Financial institutions have an obligation to comply with various regulations and laws, such as anti-money laundering laws, to ensure the integrity of the financial system.
- Providing accurate financial statements: Companies have an obligation to provide accurate and transparent financial statements to their stakeholders, including shareholders, investors, and regulators.
- Meeting contractual obligations: When two parties enter into a contract, they have mutual obligations to fulfill the terms and conditions specified in the agreement.
Real-Life Scenarios Demonstrating Obligations in the Financial Industry
Scenario 1: A company enters into a loan agreement with a bank to finance its expansion. The company has an obligation to make regular loan repayments according to the agreed-upon schedule.
Scenario 2: An investment firm manages a portfolio on behalf of its clients. The firm has an obligation to act in the best interests of its clients, make informed investment decisions, and provide regular updates on the performance of the portfolio.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
