Lower of Cost or Market Method: Why It’s Used and Application

The lower of cost or market method is a widely used accounting principle that helps businesses determine the value of their inventory. This method is used to ensure that inventory is not overstated on the financial statements, which can lead to misleading information about a company’s financial health.
Why is the lower of cost or market method used?

The lower of cost or market method is used to account for potential losses in the value of inventory. It helps businesses to accurately report the value of their inventory on the balance sheet by taking into consideration any declines in the market value of the inventory. This method ensures that the inventory is reported at the lower of its cost or its market value, whichever is lower.
By using the lower of cost or market method, businesses can avoid overstating the value of their inventory, which can lead to inaccurate financial statements. This method provides a conservative approach to valuing inventory, as it takes into account any potential decreases in market value.
Application of the lower of cost or market method
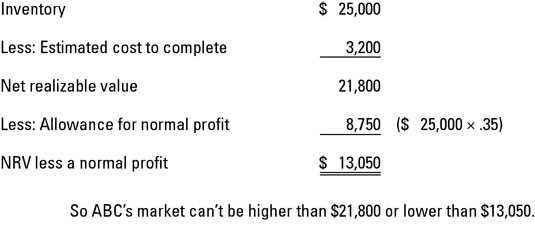
The lower of cost or market method is typically applied to each individual item in a company’s inventory. The cost of each item is compared to its market value, and the lower value is then used to determine the value of the inventory as a whole.
The Lower of Cost or Market (LCM) method is an accounting technique used to value inventory. It is based on the principle of conservatism, which states that assets should not be overstated and liabilities should not be understated. The LCM method ensures that inventory is valued at the lower of its cost or its market value.
How does the LCM method work?
For example, if a company has inventory that cost $10,000 but its market value has decreased to $8,000, the LCM method would require the company to record the inventory at $8,000 on the financial statements. This ensures that the inventory is not overstated and reflects its true economic value.
When is the LCM method used?
The LCM method is typically used when the market value of inventory has declined below its cost. This can occur due to factors such as changes in market demand, technological advancements, or obsolescence of the inventory. By valuing inventory at the lower of cost or market, the LCM method provides a more conservative and realistic representation of the company’s financial position.
The LCM method is particularly important for industries with volatile markets or perishable goods, where the market value of inventory can fluctuate significantly. It helps prevent overvaluation of inventory and ensures that the financial statements accurately reflect the company’s ability to generate profits.
Application of the LCM method
The LCM method is applied to each individual item of inventory, rather than the inventory as a whole. This means that if a company has multiple units of the same item, each unit is evaluated separately to determine its cost and market value. The LCM method is also applied consistently from one accounting period to another to ensure comparability of financial statements.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
