Interest Coverage Ratio Formula
The interest coverage ratio is a financial ratio that measures a company’s ability to pay its interest expenses on outstanding debt. It is calculated by dividing a company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by its interest expenses. The formula for calculating the interest coverage ratio is as follows:
Interest Coverage Ratio Formula:
Interest Coverage Ratio = Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) / Interest Expenses
The interest coverage ratio is an important metric for investors and creditors as it indicates the company’s ability to meet its interest obligations. A higher interest coverage ratio suggests that the company is more capable of paying its interest expenses, while a lower ratio may indicate financial distress and a higher risk of defaulting on its debt.
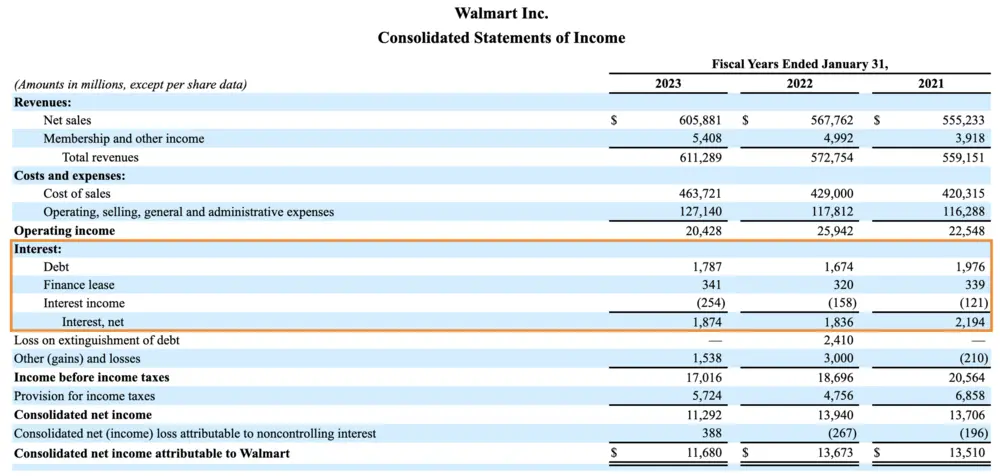
For example, let’s say Company XYZ has an EBIT of $500,000 and interest expenses of $100,000. Using the formula, we can calculate the interest coverage ratio as follows:
| EBIT | Interest Expenses | Interest Coverage Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| $500,000 | $100,000 | 5.0 |
Overall, the interest coverage ratio is a useful tool for investors and creditors to assess a company’s financial health and its ability to service its debt. It provides insight into the company’s profitability and risk profile, helping stakeholders make informed decisions about their investments or lending.
How It Works and Example
The interest coverage ratio is a financial metric that measures a company’s ability to pay its interest expenses on outstanding debt. It is calculated by dividing a company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by its interest expenses. The resulting ratio indicates the number of times a company can cover its interest expenses with its earnings.
A higher interest coverage ratio indicates that a company is more capable of meeting its interest obligations, as it has a larger buffer to cover its interest expenses. Conversely, a lower interest coverage ratio suggests that a company may have difficulty meeting its interest payments, which could be a sign of financial distress.
For example, let’s say Company A has an EBIT of $1,000,000 and interest expenses of $200,000. The interest coverage ratio would be calculated as follows:
Interest Coverage Ratio = EBIT / Interest Expenses
Interest Coverage Ratio = $1,000,000 / $200,000
Interest Coverage Ratio = 5
This means that Company A’s earnings are five times higher than its interest expenses. This indicates that the company is in a strong financial position and is likely able to comfortably meet its interest obligations.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
