High Deductible Health Plan Definition
A high deductible health plan (HDHP) is a type of health insurance plan that has a higher deductible compared to traditional health insurance plans. The deductible is the amount of money that an individual or family must pay out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in.
HDHPs are designed to lower monthly premiums but require individuals to pay more for their healthcare expenses upfront. This means that individuals are responsible for paying for most of their medical costs until they reach the deductible amount.
HDHPs are often paired with health savings accounts (HSAs), which allow individuals to save pre-tax money to pay for qualified medical expenses. The funds in an HSA can be used to cover the deductible and other out-of-pocket costs.
| Criteria for an HDHP | 2021 Limits for Self-only Coverage | 2021 Limits for Family Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Deductible | $1,400 | $2,800 |
| Maximum Out-of-Pocket Expenses | $7,000 | $14,000 |
HDHPs can be a good option for individuals who are generally healthy and don’t anticipate needing frequent medical care. They provide a way to save on monthly premiums and take control of their healthcare expenses.
Overall, HDHPs offer a balance between lower monthly premiums and higher out-of-pocket costs. They can be a cost-effective option for individuals who are willing to take on more financial responsibility for their healthcare expenses.
Coverage and Costs
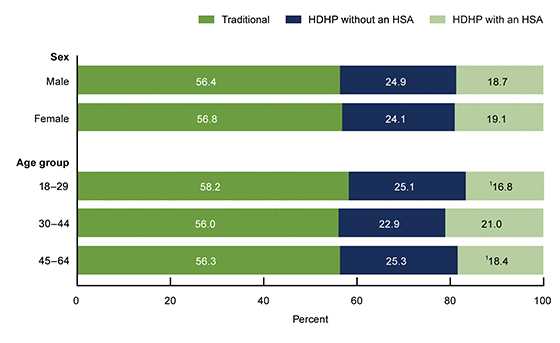
Advantages of HDHP

One of the main advantages of an HDHP is the lower monthly premium compared to traditional health insurance plans. This can be especially beneficial for individuals or families who are generally healthy and do not require frequent medical care.
Another advantage is the ability to open a Health Savings Account (HSA). An HSA is a tax-advantaged savings account that allows you to save money specifically for medical expenses. Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, and the funds can be used to pay for qualified medical expenses tax-free.
Additionally, HDHPs typically offer preventive care services at no cost to the insured. This means that routine check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings are covered without requiring you to meet your deductible.
Disadvantages of HDHP
While HDHPs have their advantages, there are also some disadvantages to consider. The main drawback is the high deductible that must be met before the plan starts covering most medical expenses. This means that you will have to pay a significant amount out-of-pocket before your insurance kicks in.
Another disadvantage is the potential for higher out-of-pocket costs. Once you meet your deductible, you will still be responsible for paying a percentage of the costs until you reach your out-of-pocket maximum. This can be a significant financial burden, especially if you require extensive medical care.
Lastly, HDHPs may not be the best option for individuals with chronic health conditions or those who require regular medical treatments. The high out-of-pocket costs and limited coverage for ongoing care may make it more difficult to manage their healthcare expenses.
Comparing Costs
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Lower monthly premiums | High deductible |
| Ability to open an HSA | Potential for higher out-of-pocket costs |
| No-cost preventive care | May not be suitable for chronic health conditions |
By carefully considering the coverage and costs of an HDHP, you can make an informed decision about whether it is the right choice for you and your healthcare needs.
In the context of high deductible health plans, the term “catname” refers to a specific category or classification of medical services or procedures. This categorization is used by insurance companies to determine the level of coverage and costs associated with different types of medical treatments.
Categories
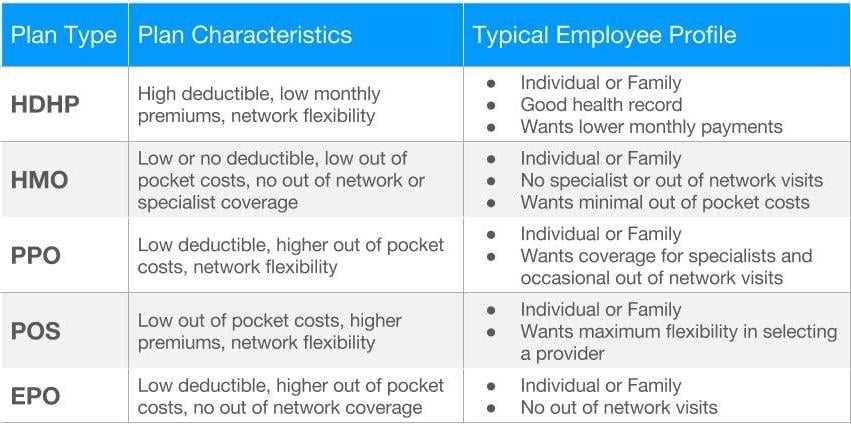
High deductible health plans typically divide medical services into various categories, each with its own level of coverage and cost-sharing requirements. These categories can include:
- Preventive care: This category includes routine check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings that are designed to prevent or detect health issues early on. In many high deductible health plans, preventive care is covered in full, meaning that policyholders do not have to pay any out-of-pocket costs for these services.
- Primary care: Primary care services, such as visits to a general practitioner or family doctor, are often covered at a higher level than other types of medical services. Policyholders may be required to pay a copayment or coinsurance for primary care visits, but the overall cost is typically lower compared to specialist care.
- Specialist care: Specialist care refers to medical services provided by healthcare professionals who have expertise in a specific area, such as cardiologists, dermatologists, or orthopedic surgeons. These services may have a higher cost-sharing requirement, such as a higher deductible or coinsurance percentage.
- Diagnostic tests and imaging: This category includes laboratory tests, X-rays, MRIs, and other imaging procedures used to diagnose medical conditions. The coverage and cost-sharing for these tests can vary depending on the specific high deductible health plan.
- Emergency care: Emergency care services, such as visits to the emergency room or ambulance transportation, are typically covered at a high level to ensure that policyholders have access to necessary medical treatment in urgent situations. However, policyholders may still be responsible for a portion of the costs, such as a copayment or coinsurance.
Costs
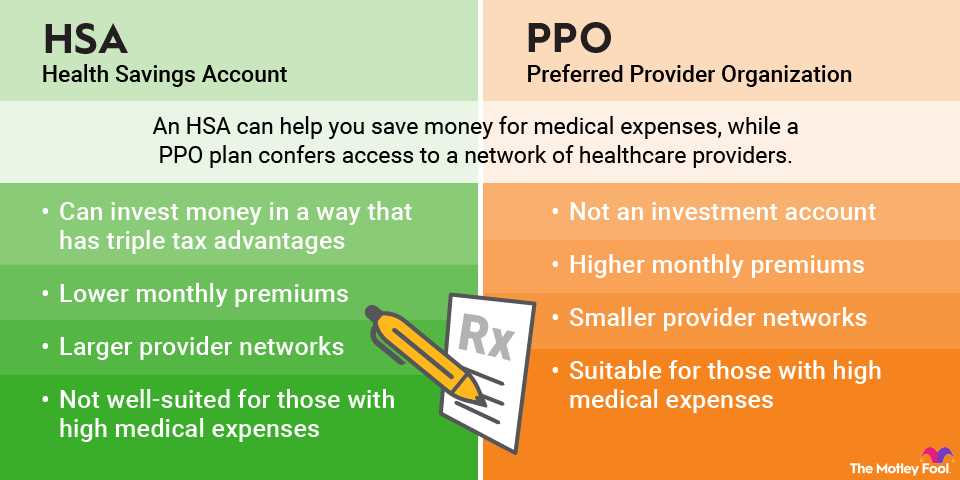
High deductible health plans are characterized by their high deductibles, which are the amount that policyholders must pay out-of-pocket for medical services before the insurance coverage kicks in. The deductibles for high deductible health plans can vary widely, ranging from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars.
In addition to the deductible, policyholders may also be responsible for coinsurance or copayments for certain medical services. Coinsurance refers to a percentage of the cost of a service that the policyholder must pay, while copayments are fixed amounts that policyholders must pay for each visit or service.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
