Glide Path Definition
It is important to note that the specific glide path used may vary depending on the investment strategy and risk tolerance of the investor. Some glide paths may be more aggressive, with a slower reduction in stock allocation, while others may be more conservative, with a faster shift towards bonds.
What is Glide Path?
How Does Glide Path Work?
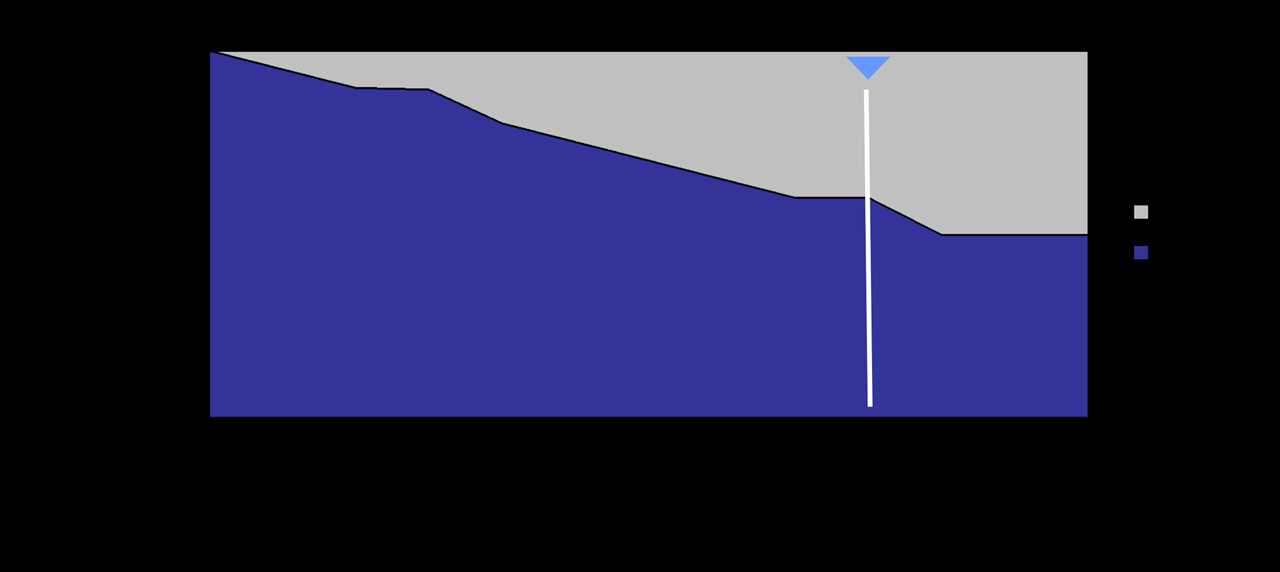
Here’s a simplified example of how glide path works:
Suppose an investor has a target retirement date of 2050. They start investing in 2020 and have a moderate risk tolerance. The glide path strategy may involve gradually reducing the allocation to equities and increasing the allocation to fixed income investments over time.
By following a glide path strategy, investors can manage risk and potentially increase the likelihood of achieving their long-term financial goals.
Importance in Investing
The glide path is an essential concept in portfolio management as it helps investors achieve their financial goals by adjusting the asset allocation over time. It provides a strategic framework for managing investments and allows for a systematic approach to risk management.
One of the key reasons why the glide path is important in investing is its ability to balance risk and return. As investors approach their retirement age or a specific target date, they generally have a lower risk tolerance. The glide path helps to gradually reduce the exposure to riskier assets, such as stocks, and increase the allocation to more conservative assets, such as bonds or cash. This gradual shift in asset allocation helps to protect the portfolio from potential market downturns and volatility.
Another important aspect of the glide path is its ability to provide a disciplined investment strategy. By following a predetermined glide path, investors are less likely to make emotional or impulsive investment decisions based on short-term market fluctuations. This helps to maintain a long-term perspective and stay focused on the overall investment objectives.
The glide path also plays a crucial role in managing the sequence of returns risk. This risk refers to the order in which investment returns are realized. A negative sequence of returns, especially in the early years of retirement, can significantly impact the sustainability of a portfolio. By gradually reducing the exposure to volatile assets, the glide path helps to mitigate the impact of a negative sequence of returns and provides a more predictable income stream during retirement.
Furthermore, the glide path allows investors to align their investments with their changing financial needs and goals. As investors progress through different life stages, their investment objectives may change. The glide path provides a framework for adjusting the asset allocation to reflect these changing needs, whether it’s saving for retirement, funding education expenses, or preserving wealth for future generations.
Conclusion
The glide path is a critical component of portfolio management, offering a systematic approach to risk management, disciplined investment strategy, and the ability to align investments with changing financial needs. By gradually adjusting the asset allocation over time, investors can better navigate market volatility, protect their portfolio, and achieve their long-term financial goals.
Types of Glide Paths in Portfolio Management
1. Target Date Glide Path

2. Risk-Based Glide Path
The risk-based glide path takes into account an investor’s risk tolerance and adjusts the asset allocation accordingly. This type of glide path is based on the idea that different investors have different risk preferences, and their portfolios should be tailored to their individual needs. The asset allocation may shift based on market conditions and the investor’s changing risk tolerance over time.
3. Constant Glide Path
The constant glide path maintains a fixed asset allocation throughout the investment horizon. This means that the portfolio remains balanced between different asset classes, regardless of market conditions or the investor’s age. This type of glide path is often used by investors who have a long-term investment horizon and are comfortable with a consistent level of risk exposure.
4. Dynamic Glide Path
The dynamic glide path is a more flexible approach that adjusts the asset allocation based on market conditions and other factors. This type of glide path allows for more active management of the portfolio and can be used to take advantage of investment opportunities or mitigate potential risks. The asset allocation may change based on market trends, economic indicators, or the investment manager’s discretion.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
