Business Exit Strategy: Definition, Examples, Best Types
An exit strategy is a plan that outlines how a business owner or investor intends to exit their investment in a company. It is a crucial aspect of any business plan as it provides a roadmap for the future and helps ensure a smooth transition when the time comes to exit the business.
Definition
A business exit strategy is a plan that outlines the methods and timeline for an entrepreneur or investor to exit their investment in a company. It is a strategic plan that helps business owners maximize their returns and minimize risks when exiting their business.
Examples
There are several examples of business exit strategies that entrepreneurs and investors can consider:
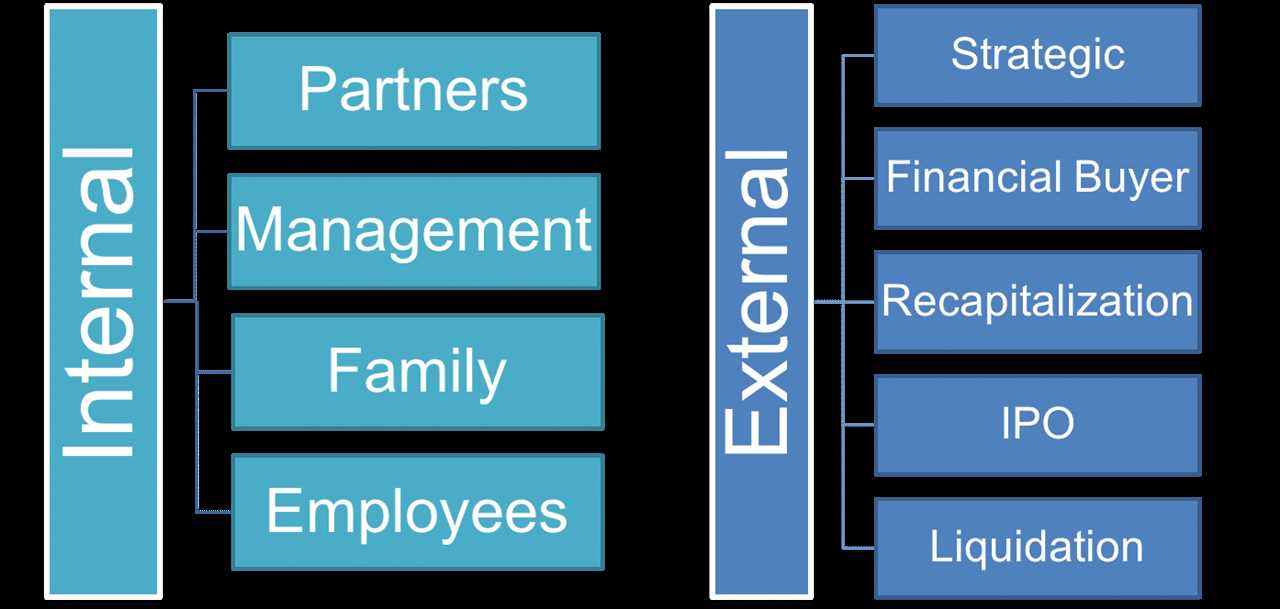
- IPO (Initial Public Offering): This is when a company decides to go public and sell its shares on the stock market. It allows the business owner to exit their investment by selling their shares to the public.
- Merger or Acquisition: This is when a company merges with or is acquired by another company. The business owner can exit their investment by selling their shares to the acquiring company.
- Sale to a Private Equity Firm: This is when a private equity firm buys a majority stake in a company. The business owner can exit their investment by selling their shares to the private equity firm.
- Management Buyout: This is when the existing management team of a company buys out the business owner’s shares. It allows the business owner to exit their investment while ensuring continuity of the business.
Best Types
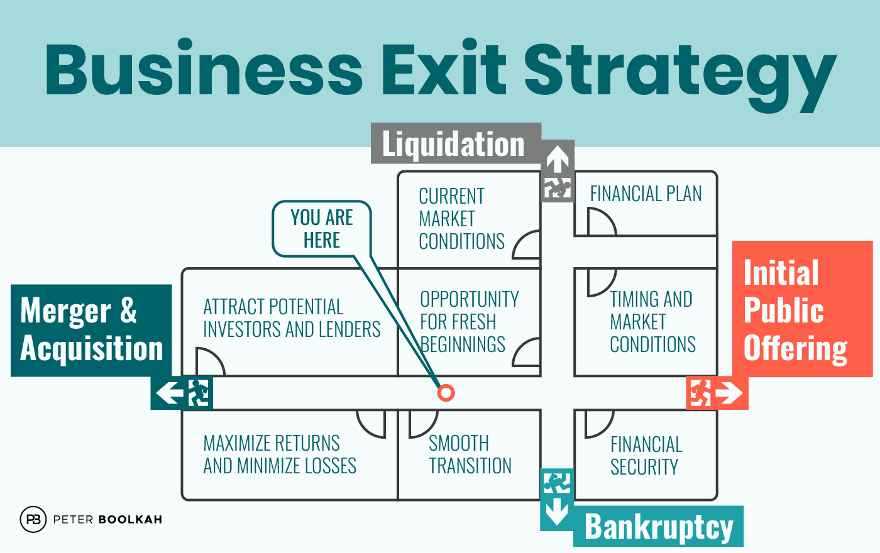
- IPO (Initial Public Offering): This is often considered the best exit strategy as it allows the business owner to sell their shares to the public at a potentially high valuation.
- Merger or Acquisition: This can be a good exit strategy if there is a strong demand for the company’s products or services and if the owner can negotiate a favorable deal.
- Sale to a Strategic Buyer: Selling the business to a strategic buyer, such as a competitor or a company in a related industry, can be a good exit strategy as it can result in synergies and a higher valuation.
What is a Business Exit Strategy?
A business exit strategy is a plan that outlines how a business owner or investor intends to exit their investment in a company. It is a strategic plan that is put in place to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the value of the business when the owner or investor decides to exit.
Why is a Business Exit Strategy Important?
Having a well-defined exit strategy is crucial for any business owner or investor. It provides a roadmap for the future and helps to mitigate risks. Here are a few reasons why a business exit strategy is important:
- Maximizing Value: A well-executed exit strategy can help maximize the value of the business, ensuring that the owner or investor gets the highest possible return on their investment.
- Planning for the Future: An exit strategy allows the owner or investor to plan for the future and make informed decisions about the direction of the business.
- Risk Mitigation: By having a clear exit strategy in place, the owner or investor can mitigate risks and avoid potential pitfalls that may arise during the exit process.
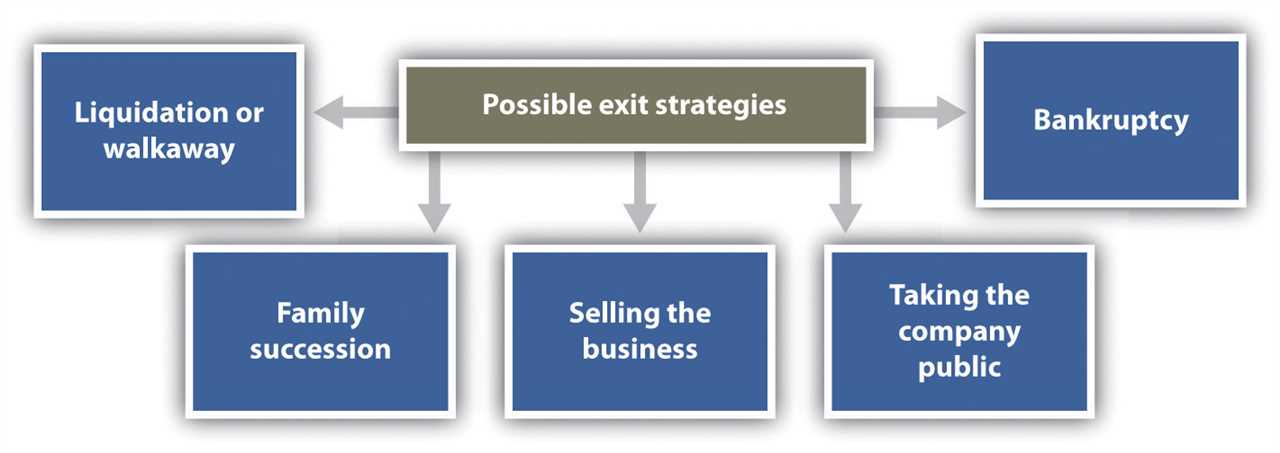
Types of Business Exit Strategies

There are several types of business exit strategies that a business owner or investor can consider:
- Selling the Business: This is the most common type of exit strategy, where the owner or investor sells the business to a third party.
- Initial Public Offering (IPO): An IPO is when a private company goes public by offering shares to the public for the first time.
- Management Buyout: In a management buyout, the existing management team of the company purchases the business from the owner or investor.
- Passing on to Family: Some business owners choose to pass on their business to family members, ensuring that it remains within the family.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
