What is Brand Extension?
Brand extension is a marketing strategy in which a company uses its existing brand name to launch a new product or enter a new market segment. It involves leveraging the brand equity and recognition that the company has already established to introduce a new offering to consumers.
Brand extension allows companies to capitalize on the positive associations and reputation that consumers have with their existing brand. By extending the brand into new product categories or markets, companies can potentially increase their market share and revenue without having to build a brand from scratch.
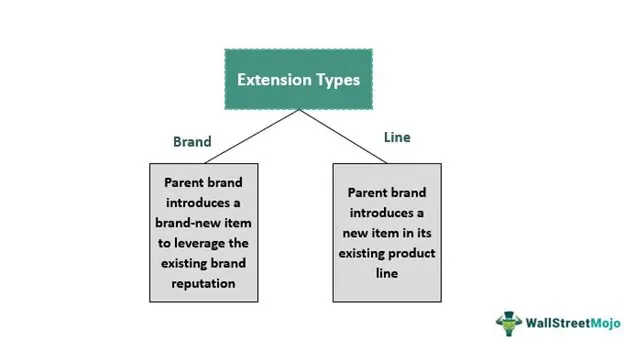
There are two main types of brand extension: line extension and category extension. Line extension involves introducing new products within the same product category, while category extension involves entering a completely different product category.
When done successfully, brand extension can be a powerful tool for companies to expand their business and reach new customers. However, it is important for companies to carefully consider the fit between the new product or market and their existing brand. If the connection is not clear or if the new offering does not align with the brand’s values and positioning, brand extension can be risky and potentially damage the brand’s reputation.
Definition and Explanation
Brand extension is a marketing strategy in which a company uses its existing brand name and equity to introduce a new product or service in a different market or category. It involves leveraging the positive associations and reputation of an established brand to create awareness and acceptance for the new offering.
The goal of brand extension is to capitalize on the existing brand’s recognition, loyalty, and customer base to generate additional revenue streams and expand market presence. By associating the new product or service with the established brand, companies aim to transfer the positive attributes and perceived value of the original brand to the extension.
Brand extension can take various forms, including line extensions, category extensions, and brand stretching. Line extensions involve introducing new variants or flavors of an existing product, while category extensions involve entering a new product category that is related to the existing brand. Brand stretching, on the other hand, involves entering a completely unrelated market or category.
Key Factors for Successful Brand Extension
While brand extension can be a powerful strategy, it is important for companies to carefully consider certain factors to ensure its success:
- Relevance: The new product or service should be relevant and aligned with the core values and positioning of the existing brand. It should make sense to consumers and fit within the brand’s overall identity.
- Brand Equity: The existing brand should have strong positive associations and a loyal customer base. This will help transfer the brand’s reputation and perceived value to the extension.
- Market Research: Companies should conduct thorough market research to understand consumer preferences, needs, and expectations in the new market or category. This will help identify opportunities and potential challenges for the brand extension.
- Marketing and Communication: Effective marketing and communication strategies are crucial for the success of a brand extension. Companies should clearly communicate the benefits and value proposition of the new offering, while also emphasizing its connection to the established brand.
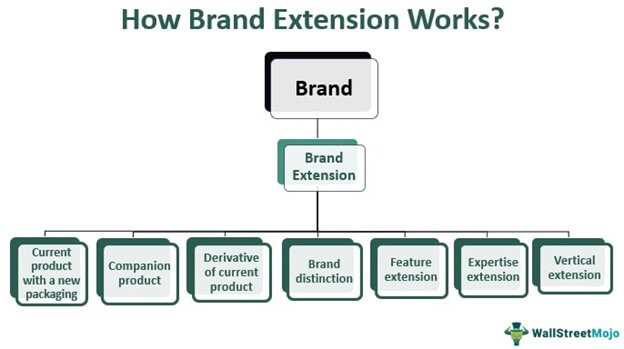
How Brand Extension Works
Brand extension is a marketing strategy that involves using an established brand name to introduce a new product or enter a new market segment. It works by leveraging the existing brand equity and recognition to create a sense of familiarity and trust with consumers.
1. Leveraging Brand Equity
One of the key ways brand extension works is by leveraging the brand equity that has been built up over time. Brand equity refers to the value and perception that consumers have of a particular brand. By using an established brand name, companies can tap into the positive associations and reputation that consumers already have with the brand.
For example, when Apple introduced the iPhone, they were able to leverage the strong brand equity they had built with products like the iPod and Mac computers. Consumers already trusted the Apple brand and were more willing to try out the new iPhone because of this existing positive perception.
2. Creating Familiarity and Trust
Another way brand extension works is by creating a sense of familiarity and trust with consumers. When a company introduces a new product under an existing brand name, consumers are more likely to perceive the new product as reliable and of high quality.
For instance, when Coca-Cola introduced Diet Coke, they were able to capitalize on the trust and familiarity that consumers had with the original Coca-Cola brand. Consumers were more willing to try the new diet version because they trusted the brand and believed that the new product would meet their expectations.
3. Expanding Market Reach
Brand extension also works by allowing companies to expand their market reach and enter new market segments. By introducing new products under an established brand name, companies can target different consumer groups and cater to their specific needs and preferences.
For example, when Nike introduced their line of athletic apparel, they were able to expand their market reach beyond just footwear. By leveraging the strong brand name and association with sports and athleticism, Nike was able to successfully enter the apparel market and capture a new segment of consumers.
Example of Brand Extension
One of the most successful examples of brand extension is the company Apple. Originally known for its Mac computers, Apple has successfully extended its brand into various other product categories.
One notable example is the introduction of the iPod in 2001. The iPod was a portable music player that revolutionized the way people listened to music. With its sleek design and user-friendly interface, the iPod quickly became a must-have device for music lovers.
Building on the success of the iPod, Apple further extended its brand with the launch of the iTunes Store in 2003. This online music store allowed users to legally purchase and download music directly to their iPods. The iTunes Store quickly became the largest music retailer in the world, solidifying Apple’s position as a leader in the digital music industry.
Apple continued to expand its brand with the introduction of the iPhone in 2007. The iPhone combined the functionality of a mobile phone, an iPod, and an internet communication device into one sleek device. This brand extension allowed Apple to tap into the growing smartphone market and establish itself as a major player in the industry.
Another successful brand extension by Apple is the Apple Watch. Launched in 2015, the Apple Watch combines the features of a fitness tracker, a smartwatch, and a fashion accessory. With its stylish design and advanced health tracking capabilities, the Apple Watch has become a popular choice among consumers.
These examples demonstrate how Apple has successfully extended its brand from computers to music players, online music stores, smartphones, and smartwatches. By maintaining a consistent brand image and delivering innovative products, Apple has been able to leverage its brand equity and capture market share in various industries.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
