Definition and Purpose of a Bicameral System
A bicameral system refers to a governmental structure that consists of two separate chambers or houses. This system is commonly found in democratic countries, including the United States, where it plays a crucial role in the legislative process.
The purpose of a bicameral system is to provide a system of checks and balances within the government. By having two separate chambers, each with its own unique characteristics and functions, the system ensures that no single entity has absolute power. This helps prevent the concentration of power in the hands of a few individuals or groups.
One of the key features of a bicameral system is the division of powers and responsibilities between the two chambers. Typically, one chamber represents the interests of the people, while the other represents the interests of the states or regions. This division helps ensure that both the majority and minority interests are taken into account during the decision-making process.
Another important purpose of a bicameral system is to provide a forum for debate and discussion. The two chambers allow for different perspectives and ideas to be presented and considered. This helps in the formulation of well-rounded policies and laws that reflect the diverse needs and opinions of the population.
Furthermore, a bicameral system can also serve as a safeguard against hasty decision-making. The requirement for both chambers to agree on a proposed law or policy before it can be enacted helps ensure that decisions are carefully considered and thoroughly debated. This can help prevent the passage of laws that may have negative consequences or that do not have broad support.
Historical Significance of the Bicameral System in the U.S.

The bicameral system has played a crucial role in the history of the United States, shaping its government and ensuring a balance of power. The concept of a bicameral legislature was derived from the British Parliament, which had a House of Commons and a House of Lords.
When the Founding Fathers were drafting the United States Constitution, they debated the structure of the legislative branch. They ultimately decided to adopt a bicameral system, with a House of Representatives and a Senate. This decision was influenced by several factors.
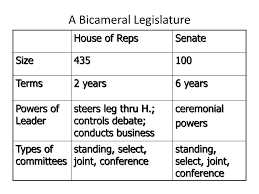
First, the Founding Fathers wanted to ensure that both large and small states had representation in the legislative process. The House of Representatives was designed to represent the population, with each state allocated a number of representatives based on its population. This ensured that larger states had more influence in the legislative process.
On the other hand, the Senate was designed to give equal representation to each state, regardless of population. Each state is represented by two senators, providing smaller states with a voice in the legislative process. This was a compromise between the large and small states, ensuring that both had a say in the decision-making process.
Second, the bicameral system was seen as a way to prevent the concentration of power in the hands of a few individuals or groups. By dividing the legislative branch into two chambers, each with its own powers and responsibilities, the Founding Fathers sought to create a system of checks and balances. This system would prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful and ensure that decisions were made through a process of negotiation and compromise.
Finally, the bicameral system was also influenced by the historical context of the time. The Founding Fathers were familiar with the British system of government and wanted to adopt a similar structure that had proven to be effective. They believed that a bicameral legislature would provide stability and prevent radical changes in government.
Over the years, the bicameral system has played a crucial role in the functioning of the U.S. government. It has provided a platform for debate and discussion, allowing different perspectives to be heard and considered. It has also served as a mechanism for accountability, with each chamber of Congress providing oversight and scrutiny of the other.
Role of the Bicameral System in Government and Policy Making

The bicameral system plays a crucial role in the functioning of government and the policy-making process. It provides a system of checks and balances that helps ensure the fair and effective representation of the people’s interests.
One of the main benefits of a bicameral system is that it allows for a diversity of perspectives and opinions to be represented in the legislative process. The two chambers, typically the Senate and the House of Representatives, provide different perspectives and priorities, which can lead to more comprehensive and well-thought-out legislation.
The bicameral system also helps to prevent the concentration of power in one branch of government. By dividing the legislative power between two chambers, it ensures that no single group or individual can dominate the decision-making process. This helps to safeguard against the potential abuse of power and promotes a more balanced and democratic system of governance.
Furthermore, the bicameral system serves as a mechanism for compromise and negotiation. The two chambers often have different political compositions and priorities, which can lead to disagreements and conflicts. However, through the process of negotiation and compromise, lawmakers are able to reach consensus and pass legislation that reflects the interests of a broader range of constituents.
The bicameral system also provides a system of checks and balances within the legislative branch itself. Each chamber has its own set of rules and procedures, which helps to ensure that legislation is thoroughly reviewed and debated. This helps to prevent hasty decision-making and allows for a more thorough examination of proposed policies.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
