Meaning and Importance of APEC
APEC (Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation) is an intergovernmental forum that promotes economic cooperation and trade among its member economies in the Asia-Pacific region. It was established in 1989 with the goal of fostering sustainable economic growth and prosperity in the region.
APEC provides a forum for member economies to discuss and address common economic challenges, such as trade barriers, investment facilitation, and regional economic integration. Through dialogue and cooperation, APEC aims to create a more open and integrated regional economy, which can benefit all member economies.
APEC also plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable development in the region. It recognizes the importance of balancing economic growth with environmental protection and social development. APEC member economies work together to address issues such as climate change, energy efficiency, and inclusive growth.
Overview of APEC

The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) is an intergovernmental forum that promotes economic cooperation and trade in the Asia-Pacific region. It was established in 1989 with the goal of fostering sustainable economic growth and prosperity for its member economies.
APEC consists of 21 member economies, including the United States, China, Japan, Australia, and Canada, among others. These economies account for approximately 60% of the world’s GDP and are home to around 2.8 billion people.
The main objective of APEC is to create a free and open trade and investment environment in the region. It aims to achieve this through various initiatives, such as reducing trade barriers, promoting market access, and facilitating economic integration.
APEC operates on the principle of consensus-based decision-making, which means that all member economies must agree on any proposed actions or policies. This allows for a cooperative and inclusive approach to addressing economic challenges and promoting regional economic integration.
One of the key features of APEC is its commitment to the Bogor Goals, which were established in 1994. These goals aim to achieve free and open trade and investment in the Asia-Pacific region by 2020 for developed economies and by 2025 for developing economies.
APEC also focuses on addressing other important issues, such as sustainable development, digital economy, and women’s economic empowerment. It provides a platform for member economies to discuss and collaborate on these issues, sharing best practices and promoting cooperation.
Overall, APEC plays a crucial role in promoting economic growth and integration in the Asia-Pacific region. Through its various initiatives and cooperative approach, it aims to create a more prosperous and interconnected region for the benefit of all member economies.
| Member Economies | Year of Joining |
|---|---|
| United States | 1989 |
| China | 1991 |
| Japan | 1989 |
| Australia | 1989 |
| Canada | 1989 |
| … (other member economies) | … |
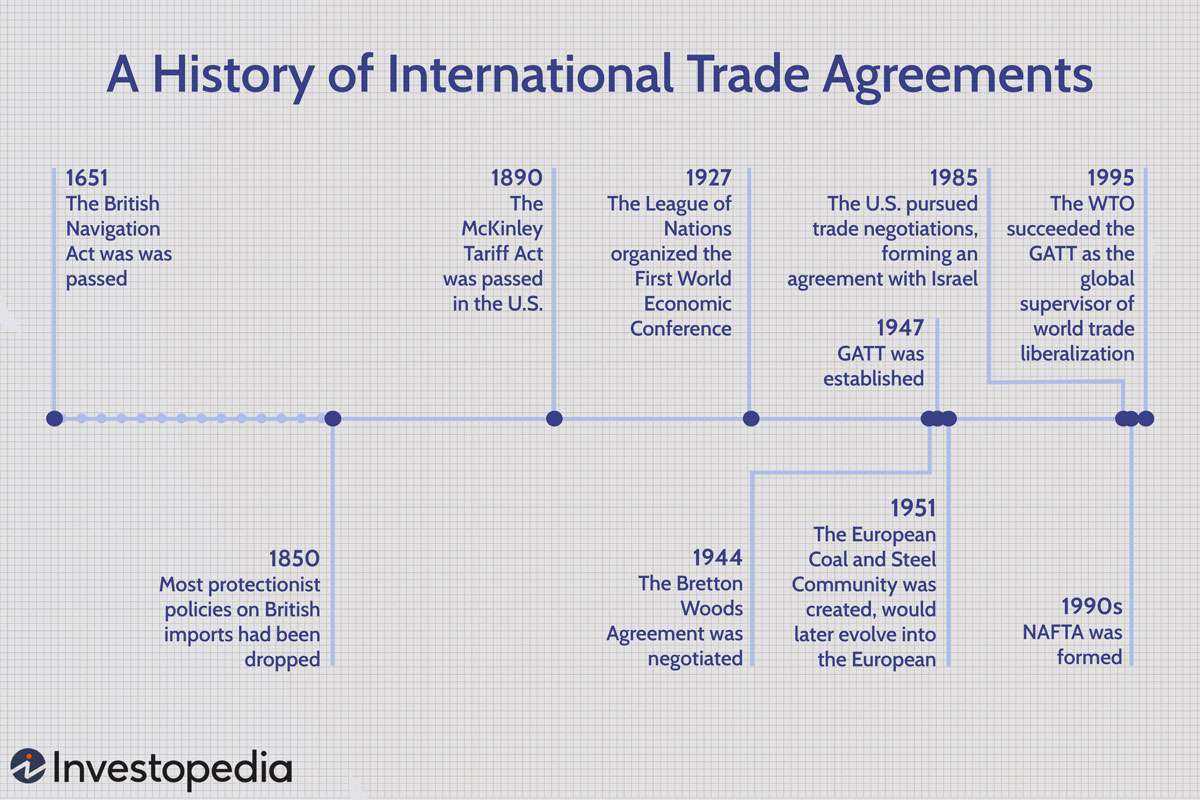
History of APEC

The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) was established in 1989 with the goal of promoting economic cooperation and integration among its member economies. It was created in response to the growing interdependence of the Asia-Pacific region and the need for a forum to address economic issues and promote regional economic growth.
Key Milestones
Over the years, APEC has achieved several key milestones in its efforts to promote regional economic integration. Some of the notable milestones include:
- Bogor Goals: In 1994, APEC leaders adopted the Bogor Goals, which aimed to achieve free and open trade and investment in the Asia-Pacific region by 2020. The goals included the reduction of trade barriers, the liberalization of investment, and the facilitation of business activities.
- Individual Action Plans: APEC member economies developed Individual Action Plans (IAPs) to outline their specific commitments and actions towards achieving the Bogor Goals. The IAPs served as a roadmap for economic reforms and liberalization.
Benefits and Challenges
APEC has brought numerous benefits to its member economies. It has facilitated trade and investment, promoted economic growth, and fostered cooperation among its diverse member economies. APEC has also provided a platform for dialogue and exchange of ideas, allowing member economies to address common challenges and find solutions.
However, APEC also faces several challenges. One of the main challenges is the increasing complexity of regional economic issues and the need for deeper economic integration. APEC member economies have diverse economic systems, levels of development, and policy priorities, which can make it difficult to reach consensus on certain issues.
Another challenge is the evolving global economic landscape. APEC member economies need to adapt to rapid technological advancements, changing trade patterns, and emerging issues such as climate change and digital economy. APEC will need to continue to evolve and adapt to effectively address these challenges and promote sustainable economic growth in the Asia-Pacific region.
Conclusion
The history of APEC reflects its commitment to promoting economic cooperation and integration in the Asia-Pacific region. Over the years, APEC has achieved significant milestones and played a crucial role in facilitating trade, promoting economic growth, and fostering cooperation among its member economies. However, APEC also faces challenges in the evolving global economic landscape. It will need to continue to adapt and evolve to effectively address these challenges and promote sustainable economic development in the region.
Government and Policy in APEC

The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) is an intergovernmental forum that promotes economic cooperation and trade among its member economies. APEC operates on the basis of non-binding commitments and consensus, allowing member economies to work together towards common goals while respecting their individual policies and priorities.
The government and policy framework in APEC is designed to facilitate economic integration and cooperation among member economies. The forum provides a platform for member economies to discuss and address regional economic issues, develop policies, and implement initiatives that promote sustainable economic growth and development.
One of the key features of APEC’s government and policy framework is its commitment to open and free trade. APEC member economies strive to reduce barriers to trade and investment, promote fair and transparent business practices, and enhance economic connectivity in the region. This is achieved through various mechanisms, including the implementation of the APEC Trade Facilitation Action Plan and the APEC Business Travel Card scheme.
APEC also focuses on promoting inclusive and sustainable growth. Member economies recognize the importance of addressing social and environmental challenges in order to ensure long-term economic prosperity. APEC’s government and policy framework includes initiatives to promote women’s economic empowerment, enhance environmental sustainability, and support small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the region.
Furthermore, APEC places a strong emphasis on capacity building and technical cooperation. Member economies collaborate to strengthen their institutional and regulatory frameworks, enhance their policy-making capabilities, and improve their trade and investment facilitation measures. APEC’s government and policy framework supports the exchange of best practices, knowledge sharing, and the provision of technical assistance to help member economies overcome challenges and seize opportunities for economic development.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
