What is the Median?

The median is a statistical measure that represents the middle value of a dataset when it is arranged in ascending or descending order. It is different from the mean, which is the average value of a dataset. The median is useful in situations where extreme values or outliers can skew the mean and give a misleading representation of the data.
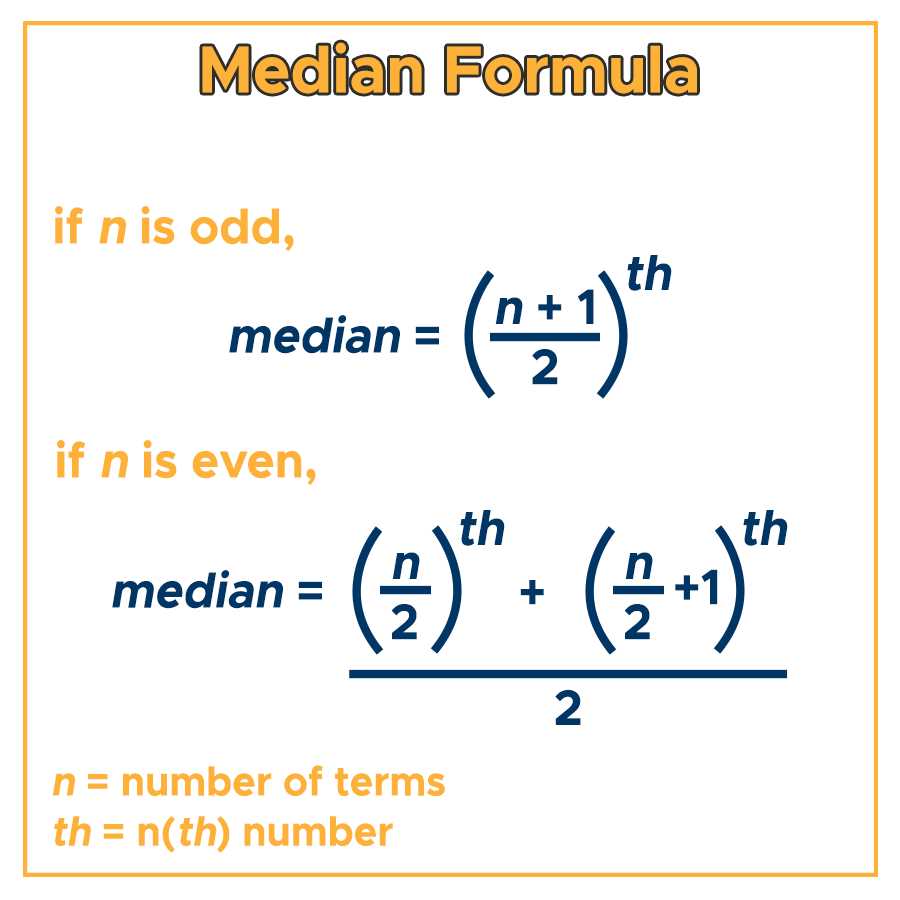
To calculate the median, the dataset must first be arranged in order. If the dataset has an odd number of values, the median is the middle value. For example, in the dataset {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}, the median is 5. If the dataset has an even number of values, the median is the average of the two middle values. For example, in the dataset {2, 4, 6, 8}, the median is (4 + 6) / 2 = 5.
The median is a robust measure of central tendency because it is not affected by extreme values. This makes it particularly useful in analyzing skewed distributions or datasets with outliers. For example, if a dataset of household incomes has a few extremely high values, the median income would provide a more accurate representation of the typical income level compared to the mean income.
How to Calculate the Median
The median is a measure of central tendency that represents the middle value in a dataset. It is often used in statistics and economics to understand the distribution of data and make comparisons between different groups or populations.
To calculate the median, follow these steps:
- Step 1: Arrange the data in ascending order.
- Step 2: Determine the total number of observations in the dataset.
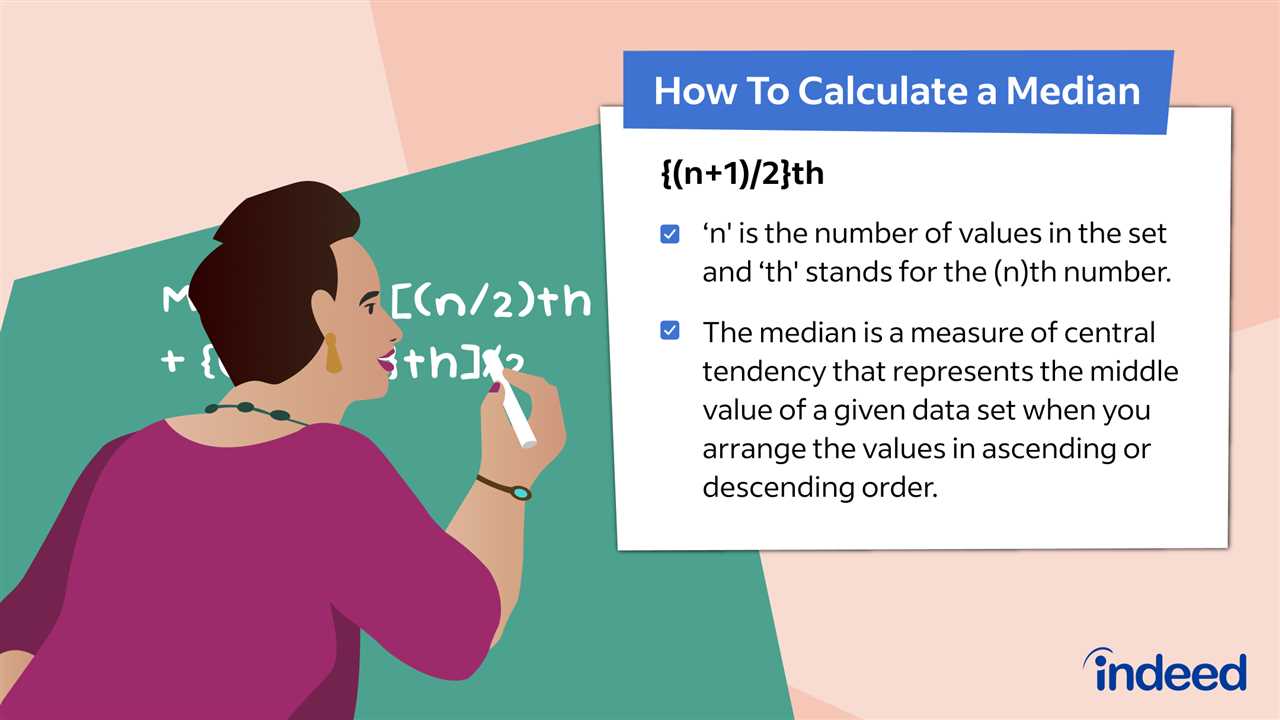
- Step 3: If the number of observations is odd, the median is the middle value. If the number of observations is even, the median is the average of the two middle values.
Let’s look at an example to illustrate the calculation of the median:
Example:
Consider the following dataset of test scores: 85, 90, 92, 78, 88, 95, 80.
Step 1: Arrange the data in ascending order: 78, 80, 85, 88, 90, 92, 95.
Step 2: Determine the total number of observations: 7.
Step 3: Since the number of observations is odd, the median is the middle value, which is 88.
By calculating the median, you can gain insights into the distribution of data and make informed decisions based on the central tendency of the dataset.
Examples and Explanation
Example 1:
Example 2:
The median is a useful measure of central tendency because it is not affected by extreme values or outliers in the dataset. It provides a more robust representation of the typical value compared to the mean.
To calculate the median, follow these steps:
- Arrange the data in ascending order.
- If the number of data points is odd, the median is the middle value.
- If the number of data points is even, the median is the average of the two middle values.
It is important to note that the median is only applicable to datasets with ordinal or interval-level data. It cannot be calculated for nominal or categorical data.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
