Key Concepts of the Pareto Principle
1. The 80-20 Distribution
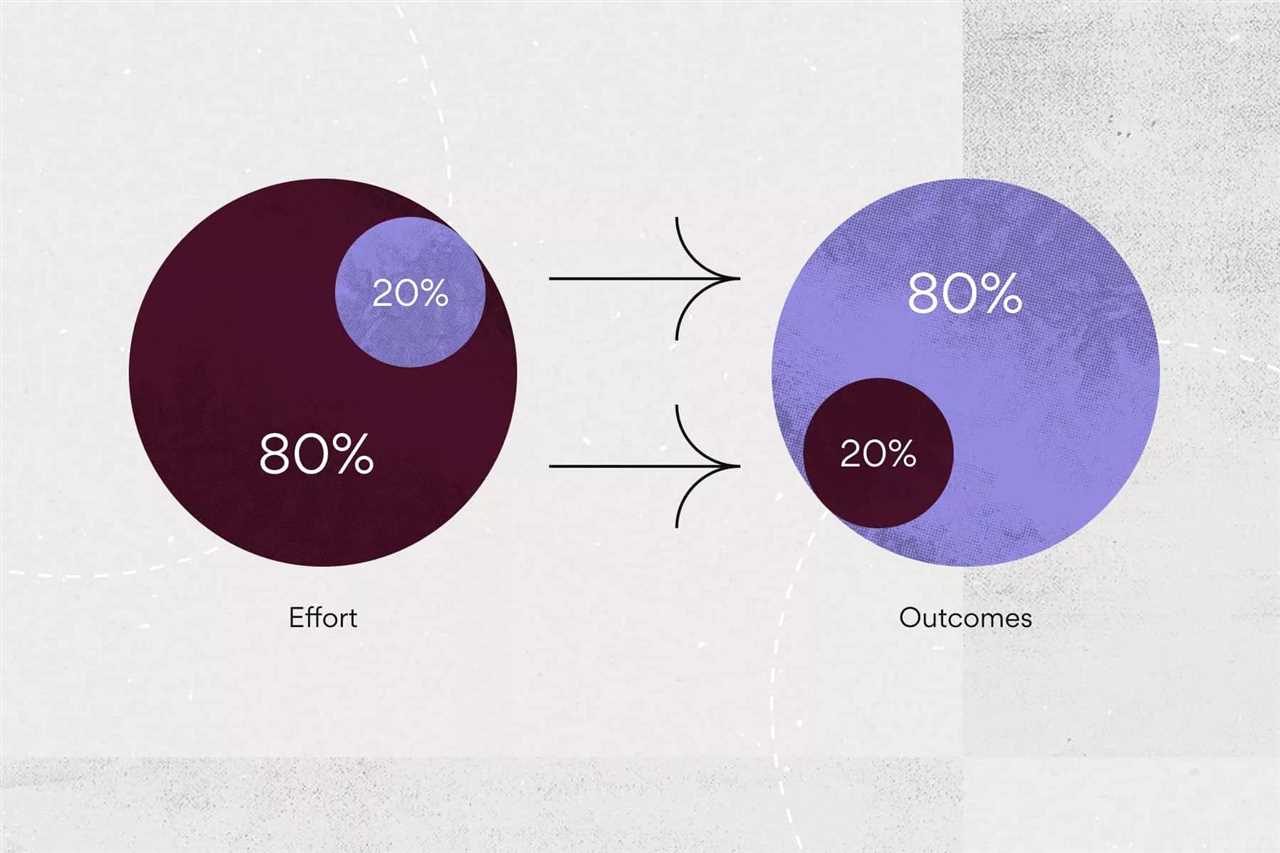
The core concept of the Pareto Principle is the unequal distribution of inputs and outputs. In many cases, a small number of inputs or causes lead to a large majority of the outputs or effects. This distribution can be observed in various aspects of life, such as wealth distribution, business profits, customer behavior, and even personal productivity.
2. Identifying the Vital Few
Another key concept of the Pareto Principle is the idea of identifying the vital few. The vital few refer to the small number of inputs or causes that have the most significant impact on the outputs or effects. By focusing on these vital few, individuals and organizations can maximize their efficiency and effectiveness.
For instance, in portfolio management, applying the Pareto Principle involves identifying the vital few investments that generate the majority of the portfolio’s returns. By concentrating on these high-performing investments, investors can optimize their portfolio and potentially achieve better results.
3. The Power of Prioritization
For example, in personal productivity, applying the Pareto Principle means identifying the 20% of tasks that will deliver 80% of the desired outcomes. By prioritizing these tasks, individuals can make the most of their time and energy, achieving more significant results in less time.
4. Continuous Improvement
The Pareto Principle also promotes the idea of continuous improvement. By regularly analyzing and reassessing the inputs and outputs, individuals and organizations can identify new vital few and optimize their processes further. This ongoing evaluation and refinement help maintain efficiency and effectiveness over time.
For instance, in business, regularly reviewing customer data can reveal new patterns or trends that can be leveraged to improve customer satisfaction and profitability. By continuously applying the Pareto Principle, businesses can stay ahead of the competition and adapt to changing market conditions.
Applying the 80-20 Rule in Portfolio Construction

When applying the 80-20 rule in portfolio construction, the first step is to analyze the portfolio holdings and determine which assets or positions contribute the most to the overall performance. This can be done by calculating the contribution of each asset to the portfolio’s returns or risk metrics.
Once the key drivers are identified, the next step is to allocate a larger portion of the portfolio to those assets or positions. This means that the portfolio will be concentrated in a smaller number of holdings that have a higher potential impact on performance.
However, it is important to note that concentration also comes with increased risk. By allocating a larger portion of the portfolio to a few assets, the portfolio becomes more susceptible to the performance of those specific assets. Therefore, careful consideration should be given to the risk-reward trade-off when implementing the 80-20 rule in portfolio construction.
By applying the 80-20 rule in portfolio construction, investors can focus on optimizing the key drivers of performance and potentially achieve better results. However, it is important to carefully consider the risk implications and regularly monitor the portfolio to ensure that the desired allocation is maintained.
Benefits of Using the Pareto Principle in Portfolio Management
1. Focus on High-Impact Investments
One of the main benefits of using the Pareto Principle in portfolio management is that it allows investors to focus on high-impact investments. By identifying the 20% of investments that generate 80% of the returns, investors can allocate more resources to these investments and potentially increase their overall portfolio performance. This approach helps investors avoid wasting time and resources on low-impact investments that may not contribute significantly to their portfolio’s growth.
2. Efficient Resource Allocation
3. Risk Management
The Pareto Principle can also be beneficial for risk management in portfolio construction. By focusing on the 20% of investments that generate the majority of the returns, investors can identify and manage the potential risks associated with these key investments. They can conduct thorough risk assessments and implement appropriate risk mitigation strategies to protect their portfolio from potential losses. This approach helps investors minimize their exposure to risk and increase the overall stability of their portfolio.
4. Simplified Decision-Making
Using the Pareto Principle in portfolio management can simplify the decision-making process for investors. By focusing on the key investments that generate the majority of the returns, investors can avoid getting overwhelmed by a large number of investment options. They can prioritize their decisions and focus on the investments that are most likely to have a significant impact on their portfolio’s performance. This simplified decision-making process can save time and reduce the cognitive load associated with managing a portfolio.
5. Enhanced Portfolio Performance
Ultimately, the main benefit of using the Pareto Principle in portfolio management is the potential for enhanced portfolio performance. By identifying and focusing on the high-impact investments, efficiently allocating resources, managing risks, and simplifying decision-making, investors can optimize their portfolio’s performance. This approach can lead to higher returns, improved risk-adjusted performance, and better overall portfolio outcomes.
| Benefits of Using the Pareto Principle in Portfolio Management |
|---|
| Focus on High-Impact Investments |
| Efficient Resource Allocation |
| Risk Management |
| Simplified Decision-Making |
| Enhanced Portfolio Performance |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
