Definition and Functioning of Open-End Credit

How Does Open-End Credit Work?
Open-end credit typically has a variable interest rate, which means the interest rate can change over time based on market conditions. The interest is calculated based on the outstanding balance, and borrowers are required to make minimum monthly payments to avoid late fees and penalties.
Advantages of Open-End Credit

Open-end credit offers several advantages to borrowers:
- Convenience: Open-end credit is often accessible through credit cards, making it convenient for everyday purchases.
- Build Credit History: Responsible use of open-end credit can help borrowers build a positive credit history, which can be beneficial for future borrowing.
Disadvantages of Open-End Credit
While open-end credit offers flexibility, it also comes with some disadvantages:
- High Interest Rates: Open-end credit often has higher interest rates compared to closed-end credit, which can result in significant interest charges if the balance is not paid off in full.
- Temptation to Overspend: The availability of credit can tempt borrowers to overspend and accumulate debt that may be difficult to repay.
- Variable Interest Rates: The variable interest rates associated with open-end credit can make it challenging to predict and budget for monthly payments.
- Potential for Debt Cycle: If borrowers continuously borrow and only make minimum payments, they can fall into a debt cycle where the outstanding balance continues to grow.
Overall, open-end credit can be a useful financial tool for those who manage it responsibly. It provides flexibility and convenience, but borrowers should be cautious about overspending and be mindful of the potential costs associated with high interest rates.
Comparison to Closed-End Credit
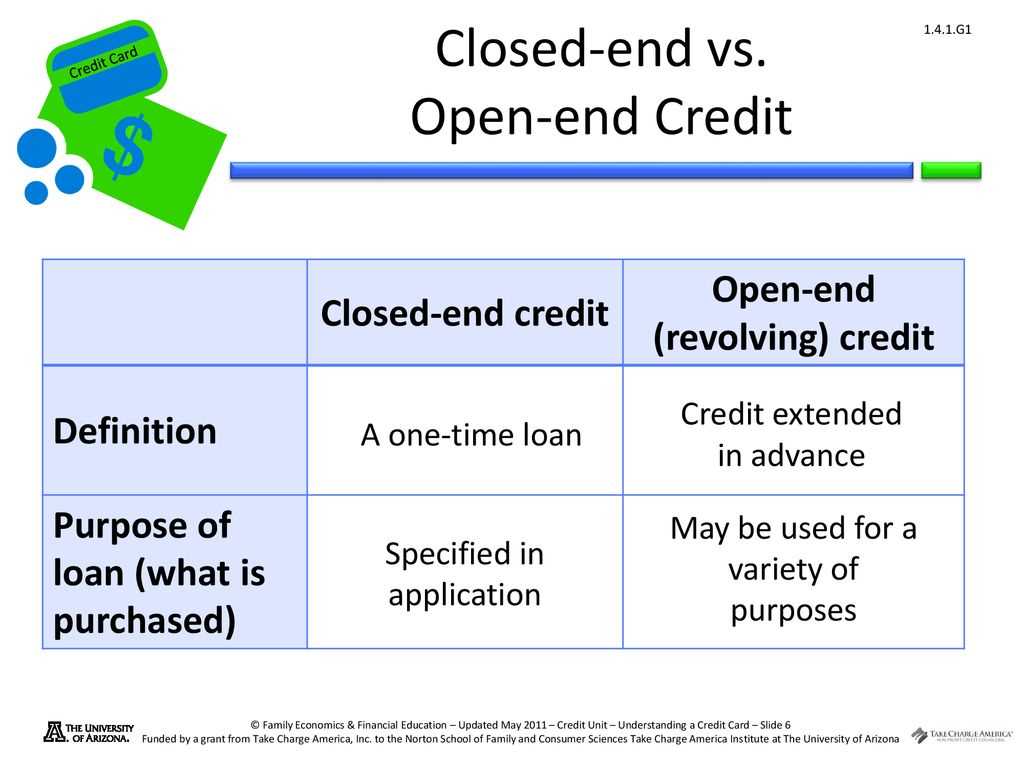
One of the main differences between open-end credit and closed-end credit is the repayment structure. With closed-end credit, borrowers are required to make fixed monthly payments until the loan is fully repaid. This can be beneficial for borrowers who prefer a structured repayment plan and want to know exactly how much they need to pay each month.
On the other hand, open-end credit offers more flexibility in terms of repayment. Borrowers can choose to pay the minimum payment due, which is typically a small percentage of the outstanding balance, or they can choose to pay off the balance in full. This flexibility can be useful for borrowers who may not be able to make fixed monthly payments or who want to take advantage of the ability to carry a balance.
Another difference between open-end credit and closed-end credit is the interest rates. Closed-end credit typically has a fixed interest rate, which means that borrowers will pay the same interest rate for the duration of the loan. In contrast, open-end credit often has variable interest rates, which means that the interest rate can change over time based on market conditions.
Additionally, open-end credit often comes with additional fees and charges, such as annual fees or transaction fees. These fees can vary depending on the lender and the specific terms of the credit agreement. Closed-end credit may also have fees associated with it, but they are typically more straightforward and easier to understand.
Open-end credit and closed-end credit have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two depends on the borrower’s individual needs and financial situation. Closed-end credit offers a structured repayment plan and fixed interest rates, while open-end credit provides flexibility in terms of repayment and borrowing. It is important for borrowers to carefully consider their options and choose the type of credit that best suits their needs.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
