How the Occurrence Policy Works
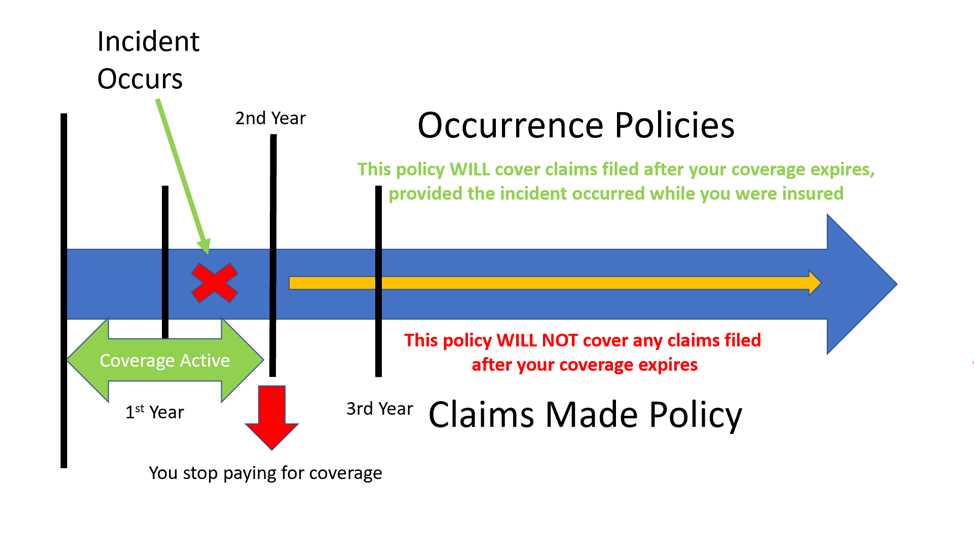
Unlike other types of insurance policies, such as claims-made policies, the occurrence policy provides coverage for claims based on when the incident occurred, rather than when the claim is made. This can be beneficial for policyholders, as it provides a greater level of certainty and protection, especially in cases where claims may be made long after the incident occurred.
Under the occurrence policy, the insurer is responsible for covering all claims that arise from incidents that occurred during the policy period, regardless of when the claims are made. This means that even if the policy is no longer in effect at the time the claim is reported, the insurer is still obligated to provide coverage.
Example:
Let’s say a company has an occurrence policy for the year 2021. During that year, an employee of the company is injured on the job. However, the employee does not report the injury until 2023. Under an occurrence policy, the insurer would still be responsible for covering the claim, even though it was reported two years after the incident occurred.
This is in contrast to a claims-made policy, where coverage would only be provided if the claim is reported during the policy period. If the employee in the above example had a claims-made policy, the claim would not be covered because it was reported after the policy period ended.
Overall, the occurrence policy offers a more comprehensive and long-term form of coverage compared to other types of insurance policies. It provides peace of mind to policyholders, knowing that they are protected against claims that may arise in the future, even if they are not reported immediately.
Advantages of the Occurrence Policy
The occurrence policy is a type of insurance policy that provides coverage for claims that arise from incidents that occur during the policy period, regardless of when the claim is actually made. This type of policy offers several advantages over other types of insurance policies, making it a preferred choice for many businesses.
1. Long-Term Coverage
2. Stability and Predictability
Another advantage of the occurrence policy is its stability and predictability. With an occurrence policy, businesses can accurately forecast their insurance costs since they know that any claims arising from incidents during the policy period will be covered, regardless of when the claim is made. This can help businesses budget effectively and avoid unexpected financial burdens due to claims made in the future.
3. Tail Coverage
Occurrence policies also offer the option of purchasing tail coverage, which provides extended coverage for claims that may arise after the policy has expired or been canceled. This can be particularly useful for businesses that may face claims after changing insurance providers or going out of business. Tail coverage ensures that businesses are still protected from claims that may arise in the future, even if they no longer have an active occurrence policy.
4. Simplified Claims Process
The occurrence policy also simplifies the claims process for businesses. Since the policy covers claims based on when the incident occurred, businesses do not need to worry about proving that the incident happened during the policy period. This can save time and resources during the claims process, allowing businesses to focus on resolving the claim rather than proving coverage.
Disadvantages of the Occurrence Policy

While the occurrence policy has its advantages, it also has some drawbacks that businesses should consider before opting for this type of insurance coverage.
1. Higher Premiums:
One of the main disadvantages of the occurrence policy is that it typically comes with higher premiums compared to other types of insurance policies. This is because the occurrence policy provides coverage for any claims that arise during the policy period, regardless of when the claim is reported. As a result, insurers may charge higher premiums to account for the potential long-term liability.
2. Limited Coverage for Unknown Claims:
Another drawback of the occurrence policy is that it may not provide coverage for unknown claims that arise after the policy period has ended. If a claim is made after the policy has expired, the occurrence policy may not cover the claim, leaving the business exposed to potential financial losses. This limitation can be particularly problematic for businesses that face long-tail claims, which may take years or even decades to surface.
3. Difficulty in Estimating Future Costs:
Due to the long-tail nature of some claims, estimating future costs can be challenging under an occurrence policy. Since the policy covers claims that arise during the policy period, businesses may find it difficult to accurately predict and budget for potential future claims. This uncertainty can make financial planning more complex and may lead to unexpected financial burdens.
4. Potential for Coverage Gaps:
Another disadvantage of the occurrence policy is the potential for coverage gaps. If a business switches insurers or cancels the policy, any claims that arise after the policy period ends may not be covered. This can leave the business vulnerable to significant financial losses if a claim is made during the coverage gap. It is important for businesses to carefully manage their insurance coverage to avoid any potential gaps in protection.
5. Limited Flexibility:
The occurrence policy offers limited flexibility compared to other types of insurance policies. Once the policy period ends, the coverage is no longer in effect, and any claims that arise after that period may not be covered. This lack of flexibility can be problematic for businesses that need continuous coverage or face ongoing risks.
Overall, while the occurrence policy has its benefits, businesses should carefully consider the disadvantages and assess their specific needs before deciding on this type of insurance coverage.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
