How Make-Whole Call Provision Works
A make-whole call provision is a feature commonly found in bond agreements that allows the issuer to redeem the bonds before their maturity date. This provision is designed to compensate bondholders for the loss of future interest payments that they would have received if the bonds were held until maturity.
Once the make-whole amount is determined, the issuer can decide whether to exercise the make-whole call provision and redeem the bonds. If the make-whole amount is higher than the market price of the bonds, it may not be financially advantageous for the issuer to call the bonds. However, if the make-whole amount is lower than the market price, the issuer may choose to exercise the provision and redeem the bonds.
Example:
Let’s say a company issued bonds with a make-whole call provision. The bonds have a remaining term of 5 years and a coupon rate of 5%. The benchmark rate is 3% and the spread is 2%. The market price of the bonds is $1,100.
If the issuer decides to exercise the make-whole call provision, it would calculate the present value of the remaining interest payments using the discount rate of 5% (3% benchmark rate + 2% spread). Let’s assume the present value of the remaining interest payments is $100.
Since the market price of the bonds is higher than the make-whole amount, it may not be financially advantageous for the issuer to call the bonds. The issuer would only exercise the make-whole call provision if the market price of the bonds is lower than the make-whole amount.
Overall, the make-whole call provision provides flexibility for issuers to redeem bonds before maturity while compensating bondholders for the loss of future interest payments. It is important for investors to carefully consider the terms of the make-whole call provision when investing in bonds to understand the potential risks and rewards.
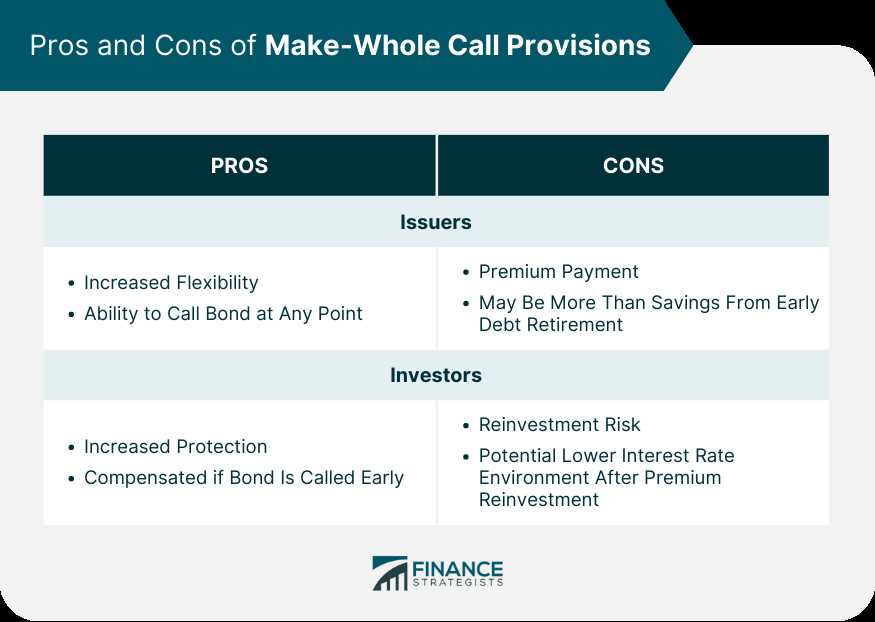
Advantages of Make-Whole Call Provision
The make-whole call provision offers several advantages to both issuers and bondholders. These advantages include:
1. Flexibility for Issuers
The make-whole call provision provides issuers with greater flexibility in managing their debt. Unlike traditional call provisions, which typically have fixed call dates and prices, the make-whole call provision allows issuers to redeem their bonds at any time, subject to certain conditions. This flexibility allows issuers to take advantage of favorable market conditions or changes in their financial situation.
2. Protection for Bondholders
Make-whole call provisions also offer protection to bondholders. When an issuer exercises the make-whole call provision, they are required to pay the bondholders the present value of the remaining cash flows on the bond, plus a make-whole premium. This ensures that bondholders receive the full value of their investment, even if the bond is called prior to its maturity date.
3. Fair Compensation for Bondholders
The make-whole premium paid to bondholders provides fair compensation for the early redemption of their bonds. This premium is calculated based on the market interest rates at the time of the call, ensuring that bondholders are adequately compensated for the loss of future interest payments. This helps to protect bondholders from potential losses due to early redemption.
4. Enhanced Marketability
Bonds with make-whole call provisions are often more marketable than those without. The make-whole call provision provides additional flexibility and protection for both issuers and bondholders, making the bonds more attractive to investors. This increased marketability can result in lower borrowing costs for issuers and higher prices for bondholders when they decide to sell their bonds.
| Advantages for Issuers | Advantages for Bondholders |
|---|---|
| Flexibility in managing debt | Protection of investment |
| Opportunity to take advantage of market conditions | Fair compensation for early redemption |
| Enhanced marketability |
Overall, the make-whole call provision is a valuable tool for both issuers and bondholders. It provides flexibility, protection, fair compensation, and enhanced marketability, making it a popular choice in the fixed income market.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
