What is Fourth World?

The term “Fourth World” refers to a concept that describes the most marginalized and disadvantaged populations in the world. It is often used to refer to indigenous peoples, ethnic minorities, and other marginalized groups who face extreme poverty, social exclusion, and lack of access to basic services and opportunities.
Unlike the First, Second, and Third Worlds, which are primarily based on economic and political classifications, the Fourth World focuses on the social and cultural aspects of marginalization. It recognizes that poverty and inequality are not solely economic issues, but also deeply rooted in historical, social, and cultural factors.
Fourth World populations often face discrimination, marginalization, and the loss of their traditional lands and resources. They often have limited access to education, healthcare, clean water, and other essential services. They also face challenges in preserving their cultural identity, language, and traditional knowledge.
The term “Fourth World” was first coined in the 1970s by the anthropologist Michael Ignatieff, who used it to describe indigenous peoples in Canada. Since then, it has been adopted by scholars, activists, and organizations around the world to highlight the unique challenges faced by marginalized populations.
Efforts to address the challenges faced by Fourth World populations include advocating for their rights, promoting inclusive policies and programs, and empowering communities to participate in decision-making processes. These efforts aim to ensure that Fourth World populations are not left behind and have equal opportunities to thrive and contribute to society.
Definition and Meaning

The term “Fourth World” refers to a socio-economic classification that encompasses the most marginalized and impoverished populations in the world. It is used to describe communities and groups that are excluded from the benefits of globalization and are often characterized by extreme poverty, limited access to basic services, and a lack of political power.
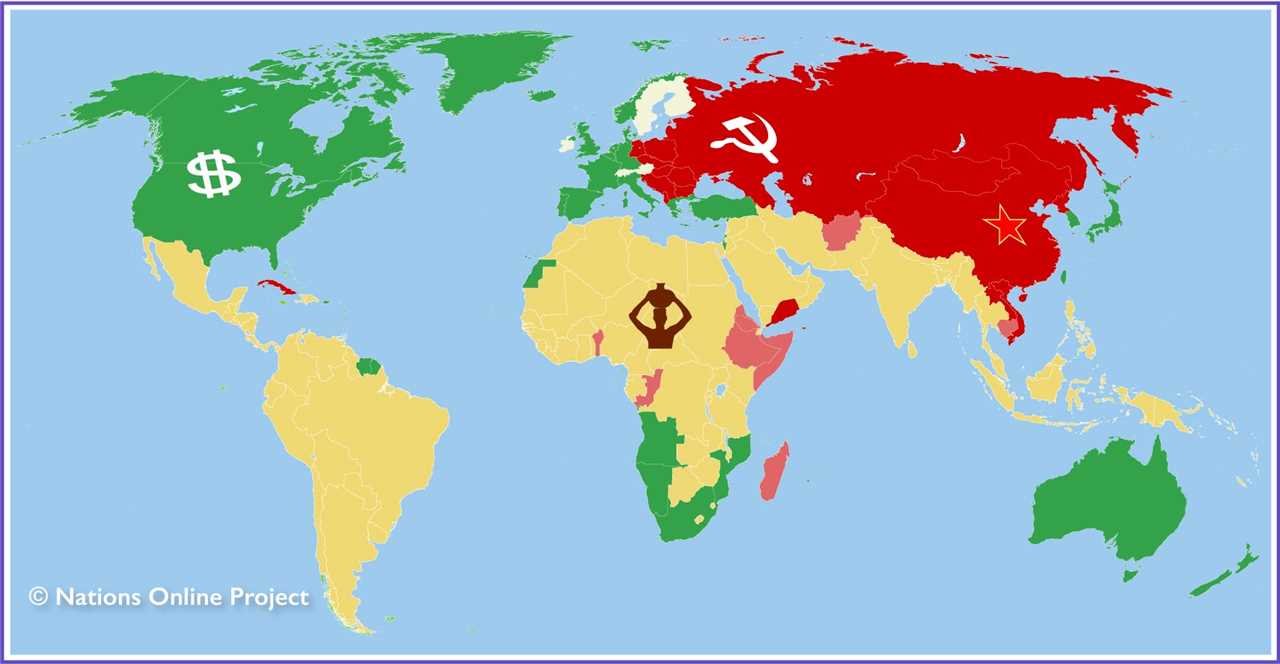
The Fourth World is distinct from the First, Second, and Third Worlds, which were terms used during the Cold War to categorize countries based on their political and economic systems. The First World referred to the capitalist, industrialized countries, the Second World referred to the socialist countries, and the Third World referred to the developing countries.
The Fourth World, on the other hand, does not refer to a specific group of countries, but rather to a global phenomenon of poverty and marginalization that exists within all countries. It includes indigenous peoples, ethnic minorities, refugees, and other vulnerable populations who face systemic discrimination and exclusion.
The term “Fourth World” was first coined by the anthropologist Michael M. Cernea in the 1970s to draw attention to the plight of these marginalized communities. It was intended to highlight the need for targeted policies and interventions to address the unique challenges faced by these populations.
Over time, the concept of the Fourth World has evolved to encompass not only economic and social exclusion, but also cultural and political marginalization. It recognizes that poverty is not just a lack of material resources, but also a lack of voice, agency, and recognition.
Efforts to address the issues faced by Fourth World communities include initiatives to promote inclusive development, protect indigenous rights, and empower marginalized groups. These efforts aim to ensure that all individuals and communities have equal opportunities to participate in and benefit from economic, social, and political processes.
History of the Term Fourth World
The term “Fourth World” was first coined by George Manuel, a leader of the National Indian Brotherhood in Canada, in the 1970s. Manuel used the term to describe the most marginalized and disadvantaged communities in the world, including indigenous peoples, tribal groups, and other marginalized populations.
The concept of the Fourth World emerged as a response to the limitations of the traditional categorization of countries into First, Second, and Third Worlds. These categories were based on economic and political factors, such as GDP and political alliances, and did not adequately capture the unique challenges faced by marginalized communities.
In contrast, the Fourth World concept recognizes that poverty, inequality, and social exclusion are not limited to specific countries or regions, but are experienced by communities across the globe. It highlights the need for a more inclusive and holistic approach to development that takes into account the specific needs and aspirations of marginalized populations.
Since its inception, the term Fourth World has gained recognition and acceptance among scholars, activists, and policymakers. It has been used to draw attention to the plight of indigenous peoples, promote their rights and self-determination, and advocate for policies that address the root causes of their marginalization.
Over the years, the concept of the Fourth World has evolved and expanded to include other marginalized groups, such as refugees, ethnic minorities, and people living in extreme poverty. It has become a powerful tool for raising awareness about the interconnectedness of global issues and the need for collective action to address them.
Origin and Evolution
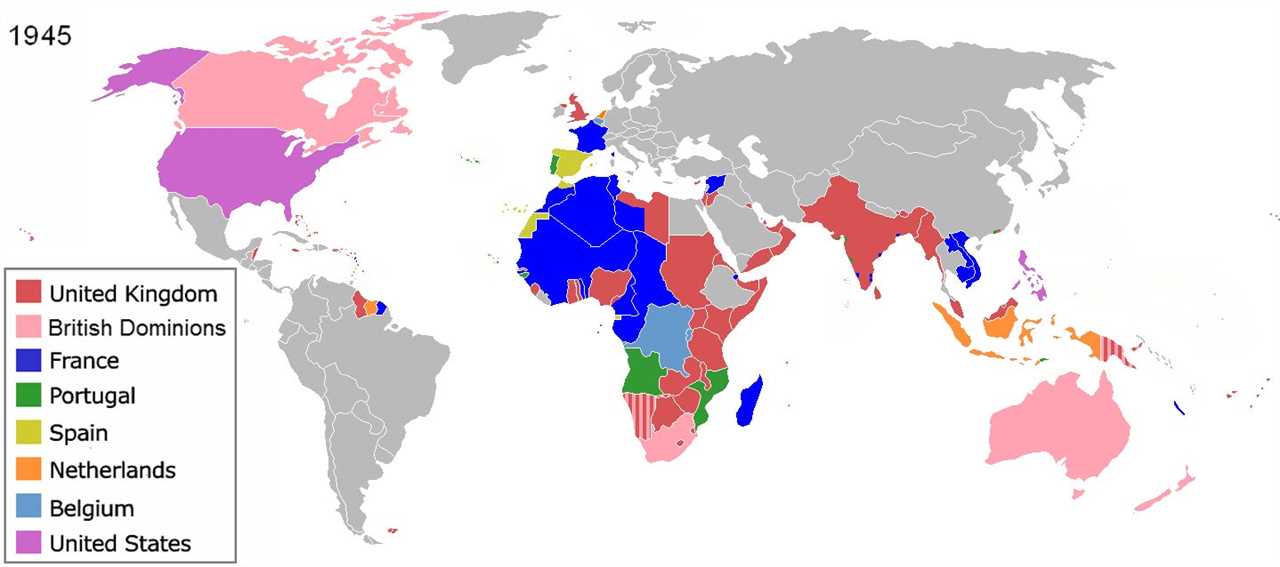
The term “Fourth World” was first coined by George Manuel, a leader of the National Indian Brotherhood in Canada, in the 1970s. Manuel used the term to describe the indigenous peoples who were marginalized and oppressed within their own countries.
Since then, the concept of the Fourth World has evolved and expanded to include not only indigenous peoples, but also other marginalized groups such as ethnic minorities, refugees, and the urban poor. The Fourth World is characterized by extreme poverty, social exclusion, and a lack of political power.
In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the importance of addressing the issues faced by the Fourth World. International organizations, governments, and civil society groups have started to take action to promote the rights and well-being of these marginalized communities.
Challenges and Solutions
One of the main challenges in addressing the issues faced by the Fourth World is the lack of political representation and voice. Many marginalized communities are excluded from decision-making processes and are not able to advocate for their own needs and interests.
To address this challenge, it is important to empower marginalized communities and ensure their participation in decision-making processes. This can be done through initiatives such as community organizing, capacity building, and the promotion of inclusive governance structures.
Another challenge is the lack of access to basic services and resources. Many marginalized communities lack access to healthcare, education, clean water, and sanitation. This perpetuates the cycle of poverty and marginalization.
To overcome this challenge, it is crucial to invest in the development of infrastructure and social services in marginalized communities. This includes improving access to healthcare facilities, building schools, and providing clean water and sanitation facilities.
The Way Forward
The concept of the Fourth World highlights the need for a more inclusive and equitable society. It calls for the recognition of the rights and dignity of all individuals, regardless of their social or economic status.
Addressing the issues faced by the Fourth World requires a multi-faceted approach that includes policy changes, social mobilization, and the empowerment of marginalized communities. It also requires the collaboration and cooperation of governments, international organizations, civil society, and the private sector.
By working together, we can create a world where no one is left behind and where all individuals have the opportunity to thrive and fulfill their potential.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
