Definition and Meaning of Enhanced Oil Recovery
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) refers to a set of techniques and processes used in the oil industry to extract additional oil from reservoirs that have already undergone primary and secondary recovery methods. Primary recovery methods typically recover only about 10% to 20% of the oil in a reservoir, while secondary recovery methods can recover an additional 20% to 40%. EOR techniques aim to increase the recovery factor even further, potentially extracting up to 60% or more of the original oil in place.
EOR techniques involve injecting various substances into the reservoir to alter the physical and chemical properties of the oil, making it easier to flow and be extracted. These substances can include steam, gases, chemicals, or even microorganisms. The specific technique used depends on the characteristics of the reservoir, such as its depth, temperature, and the type of oil present.
There are three main categories of EOR techniques: thermal methods, gas injection methods, and chemical methods. Thermal methods involve injecting steam or hot water into the reservoir to reduce the viscosity of the oil and improve its flow. Gas injection methods involve injecting gases such as carbon dioxide or natural gas to displace the oil and push it towards production wells. Chemical methods involve injecting chemicals that can alter the interfacial tension between the oil and the reservoir rock, allowing the oil to flow more easily.
Enhanced Oil Recovery has become increasingly important in recent years as conventional oil reserves become depleted and the demand for energy continues to rise. By utilizing EOR techniques, oil companies can maximize the extraction of oil from existing reservoirs, potentially extending the life of these reservoirs and increasing overall oil production.
Examples of Enhanced Oil Recovery Techniques
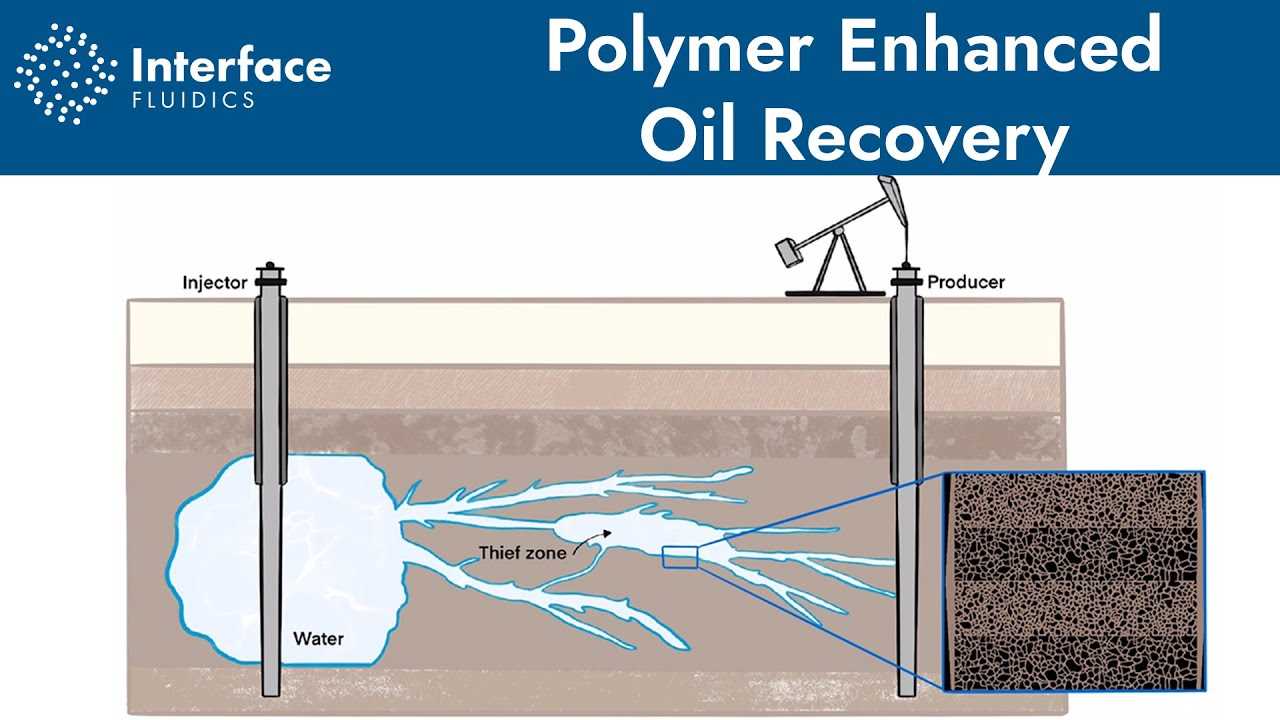
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) techniques are used to extract more oil from reservoirs that have already been through primary and secondary recovery methods. Here are some examples of EOR techniques:
1. Thermal Recovery
Thermal recovery methods involve the use of heat to reduce the viscosity of the oil, making it easier to extract. One common thermal recovery technique is steam injection, where steam is injected into the reservoir to heat the oil and increase its flowability. Another technique is in-situ combustion, where air or oxygen is injected into the reservoir to create a fire front that heats the oil and improves its mobility.
2. Chemical Injection
Chemical injection techniques involve the use of chemicals to alter the properties of the oil and improve its recovery. One example is polymer flooding, where polymers are injected into the reservoir to increase the viscosity of the water, creating a better sweep efficiency and displacing more oil. Another technique is surfactant flooding, where surfactants are injected to reduce the interfacial tension between the oil and water, allowing the oil to flow more easily.
3. Gas Injection
Gas injection techniques involve the injection of gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2) or natural gas, into the reservoir to improve oil recovery. One common gas injection technique is CO2 flooding, where CO2 is injected into the reservoir to dissolve in the oil and reduce its viscosity. This allows the oil to flow more easily and increases the amount of oil that can be recovered. Another technique is gas lift, where gas is injected into the bottom of the well to reduce the hydrostatic pressure and lift the oil to the surface.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
