Duopoly: Definition, Types, and Examples
A duopoly is a market structure in which there are only two dominant firms that control the majority of the market share. These two firms have a significant influence on the pricing and production decisions within the industry. Duopolies can exist in various sectors and industries, and they can take different forms.
There are two main types of duopoly: cooperative and competitive. In a cooperative duopoly, the two firms work together to control the market and maximize their profits. They may collude to set prices, divide the market, or engage in other forms of cooperation. This type of duopoly often leads to higher prices for consumers and limited competition.
On the other hand, a competitive duopoly is characterized by intense rivalry between the two firms. They compete aggressively for market share and strive to outperform each other. This type of duopoly can lead to innovation, lower prices, and better products for consumers.
Examples of duopoly can be found in various sectors and industries. One famous example is the soft drink industry, where Coca-Cola and PepsiCo dominate the market. These two companies have been competing fiercely for decades, constantly introducing new products and engaging in marketing battles.
Another example is the aircraft manufacturing industry, where Boeing and Airbus are the main players. These two companies control the global market for commercial aircraft and compete for contracts from airlines around the world.
What is a Duopoly?
A duopoly is a market structure in which there are only two dominant firms that control the majority of the market share. These two firms have a significant influence on the market and often compete with each other for customers and market share.
In a duopoly, the actions and decisions of one firm can directly impact the other firm and the overall market dynamics. This makes the relationship between the two firms complex and often characterized by strategic interactions and rivalry.
Unlike in a monopoly where there is only one dominant firm, in a duopoly, there is some level of competition between the two firms. However, this competition may not be as intense as in a perfectly competitive market where there are numerous firms.
The two firms in a duopoly may engage in various strategies to gain a competitive advantage over each other. This can include price competition, product differentiation, marketing campaigns, and innovation. The aim is to attract customers and increase market share.
Examples of duopoly can be found in various sectors and industries. For instance, in the soft drink industry, Coca-Cola and PepsiCo are the two dominant firms that control a significant portion of the market. In the operating system market, Microsoft and Apple are the main players. These examples highlight the presence of duopoly in different sectors and the impact it has on market dynamics.
Types of Duopoly
A duopoly is a market structure in which there are only two dominant firms that compete with each other for market share. There are several types of duopoly, each characterized by different factors and dynamics:
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Perfect Duopoly | In a perfect duopoly, the two firms have equal market share and compete on an equal footing. | Coca-Cola and PepsiCo in the soft drink industry. |
| Imperfect Duopoly | In an imperfect duopoly, one firm has a larger market share and holds a dominant position over the other firm. | Boeing and Airbus in the commercial aircraft industry. |
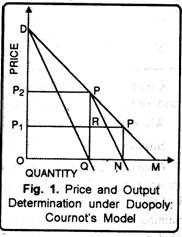
| Cournot Duopoly | In a Cournot duopoly, the two firms compete by setting their quantities of output, taking into account the other firm’s output. | Oil companies such as ExxonMobil and Chevron. |
| Bertrand Duopoly | In a Bertrand duopoly, the two firms compete by setting their prices, taking into account the other firm’s price. | Mobile phone service providers like Verizon and AT&T. |
| Stackelberg Duopoly | Automobile manufacturers such as Toyota and Honda. |
Examples of Duopoly in Various Sectors & Industries
1. Soft Drink Industry
2. Operating Systems
3. Aircraft Manufacturing
In the aircraft manufacturing industry, Boeing and Airbus are the two major competitors. These two companies dominate the market for commercial aircraft, with their planes being used by airlines around the world. They constantly compete for contracts from airlines and governments, pushing each other to innovate and improve their products.
4. Credit Card Networks

In the credit card industry, Visa and Mastercard have a duopoly. These two companies provide the infrastructure and technology for credit card transactions globally. They have established a strong network of merchants and financial institutions, making it difficult for new players to enter the market.
5. Online Retail
In the online retail sector, Amazon and Alibaba are the dominant players. Amazon is the largest e-commerce company in the United States, while Alibaba is the leading e-commerce company in China. These two companies have a duopoly in their respective markets, offering a wide range of products and services to consumers worldwide.
These examples demonstrate how duopolies can exist in various sectors and industries. In a duopoly, the two dominant firms often engage in fierce competition, striving to gain a larger market share and attract more customers. This competition can lead to innovation, lower prices, and better products for consumers.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
