Diseconomies of Scale: Causes and Types Explained
Causes of Diseconomies of Scale
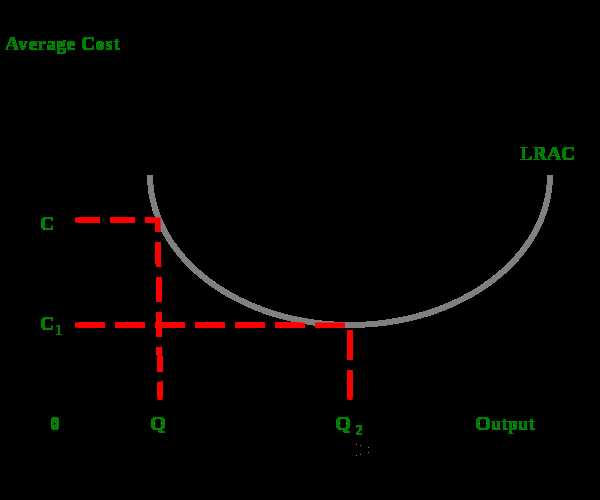
There are several factors that can lead to diseconomies of scale:
- Coordination Problems: With growth, the complexity of coordinating various tasks and activities within the organization increases. This can lead to bottlenecks, duplication of efforts, and a lack of synergy, all of which can drive up costs.
- Loss of Control: As a company becomes larger, it may become more difficult for management to maintain control over all aspects of the business. This can result in decision-making delays, misalignment of goals, and a decrease in overall efficiency.
- Increased Bureaucracy: Larger organizations often require more layers of management and administrative staff to handle the growing complexity. This can lead to increased bureaucracy, slower decision-making processes, and higher administrative costs.
Types of Diseconomies of Scale
There are different types of diseconomies of scale that can occur:
- Technical Diseconomies: These arise when the company’s production technology becomes outdated or inefficient as it grows larger. This can result in lower productivity, higher maintenance costs, and a decrease in overall efficiency.
- Managerial Diseconomies: These occur when the company’s management team becomes overwhelmed with the increased complexity and size of the organization. This can lead to slower decision-making, a lack of coordination, and higher costs.
- Financial Diseconomies: These arise when the company’s access to capital becomes limited or more expensive as it grows larger. This can result in higher borrowing costs, reduced investment opportunities, and a decrease in profitability.
- Marketing Diseconomies: These occur when the company’s marketing efforts become less effective or inefficient as it expands. This can lead to higher advertising costs, decreased customer satisfaction, and a decline in market share.
Causes of Diseconomies of Scale
Diseconomies of scale occur when a company’s costs per unit increase as it grows larger. There are several causes of diseconomies of scale that can lead to this increase in costs.
1. Communication and coordination problems: As a company grows, it becomes more difficult to communicate and coordinate activities among employees and departments. This can result in inefficiencies and delays, leading to higher costs.
3. Bureaucracy and red tape: Larger organizations often have more layers of management and decision-making processes. This can result in slower decision-making and increased bureaucracy, which can lead to higher costs.
4. Diseconomies of scope: As a company expands its product or service offerings, it may become more difficult to manage and coordinate these different lines of business. This can result in inefficiencies and higher costs.
5. Increased competition: As a company grows larger, it may attract more competitors. This can lead to increased competition and price pressure, which can erode profit margins and increase costs.
Types of Diseconomies of Scale

When a firm grows beyond a certain point, it may start experiencing diseconomies of scale. These diseconomies can arise due to various factors and can have a negative impact on the firm’s efficiency and profitability. Let’s take a look at some of the common types of diseconomies of scale:
1. Coordination Problems
As a firm expands its operations, it becomes increasingly difficult to coordinate and manage all the different departments and activities. Communication breakdowns, delays in decision-making, and conflicts between departments can arise, leading to inefficiencies and higher costs. This coordination problem is a type of diseconomy of scale that can hinder the firm’s overall performance.
2. Loss of Control
3. Increased Bureaucracy
As a firm expands, it often needs to introduce more layers of management and administrative staff to handle the increased complexity of operations. This can lead to an increase in bureaucracy, with more rules, procedures, and paperwork. The added bureaucracy can slow down decision-making processes and create inefficiencies within the organization.
4. Diseconomies of Scope
Overall, these are just a few examples of the types of diseconomies of scale that can occur when a firm grows beyond a certain size. It is important for firms to be aware of these potential challenges and take proactive measures to mitigate their impact on the business.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
