Bare Trust: Definition
In a bare trust, the trustee has a legal obligation to manage and protect the assets for the benefit of the beneficiary. However, they cannot make any decisions regarding the assets without the explicit consent of the beneficiary. The trustee’s role is limited to holding and transferring the assets as directed by the beneficiary.
A bare trust is often used in estate planning, where the settlor wishes to transfer assets to a beneficiary but wants to retain some level of control over those assets. By creating a bare trust, the settlor can ensure that the assets are held by a trustee for the benefit of the beneficiary, while still maintaining a level of influence over how the assets are managed and distributed.
Another important aspect of a bare trust is that the trustee has a fiduciary duty to act in the best interests of the beneficiary. This means that the trustee must manage the assets responsibly and prudently, ensuring that they are protected and preserved for the beneficiary’s benefit.
Advantages of a Bare Trust
There are several advantages to using a bare trust:
- Simplicity: Bare trusts are relatively simple to set up and administer compared to other trust structures. They do not require complex legal documentation or ongoing management.
- Flexibility: Bare trusts offer flexibility in terms of asset management. The beneficiary has control over the assets and can make decisions regarding their use and distribution.
- Asset protection: By placing assets in a bare trust, they are protected from creditors and other potential claims. This can be particularly beneficial in estate planning.
Key Features of a Bare Trust
- Legal Title: The trustee holds legal title to the assets or property in a bare trust.
- No Active Role: The trustee has no active role in managing or controlling the assets.
- Estate Planning: Bare trusts are commonly used for estate planning purposes.
- Asset Protection: Assets held in a bare trust are protected from creditors and legal claims.
Bare Trust: Advantages
1. Simplicity and Flexibility:
One of the main advantages of a bare trust is its simplicity. Unlike other types of trusts that may have complex legal structures and requirements, a bare trust is straightforward and easy to set up. It does not require the involvement of a trustee or the need for ongoing administration. This simplicity makes it a flexible option for individuals who want a simple and efficient way to transfer assets to beneficiaries.
2. Control and Privacy:
3. Tax Planning:
Bare trusts can be used as a tax planning tool. By transferring assets into a bare trust, the settlor can potentially reduce their estate tax liability. This is because the assets held in a bare trust are considered separate from the settlor’s estate for tax purposes. This can be particularly advantageous for individuals with large estates who want to minimize the impact of estate taxes on their beneficiaries.
4. Asset Protection:
5. Succession Planning:
Bare trusts can be an effective tool for succession planning. By transferring assets to a bare trust, the settlor can ensure a smooth and efficient transfer of wealth to their chosen beneficiaries. This can help avoid potential disputes or challenges to the distribution of assets after the settlor’s death.
Benefits of Utilizing a Bare Trust Structure
A bare trust structure offers several benefits to individuals and businesses looking to manage their assets and investments. Here are some of the key advantages of utilizing a bare trust:
1. Simplicity and Flexibility
2. Tax Efficiency
3. Asset Protection

Another benefit of a bare trust is its ability to provide asset protection. By placing assets into a bare trust, individuals can shield them from potential creditors or legal claims. This can be particularly useful for individuals who are concerned about protecting their wealth or assets from potential risks or liabilities.
4. Estate Planning
Bare trusts are often used as part of estate planning strategies. They can be used to ensure a smooth transfer of assets to beneficiaries upon the individual’s death, avoiding the need for probate and potentially reducing inheritance tax. By setting up a bare trust, individuals can have peace of mind knowing that their assets will be distributed according to their wishes.
5. Privacy
A bare trust offers a level of privacy that may not be available with other trust structures. Since the beneficiary has direct control and ownership of the assets, the details of the trust and its assets may not need to be disclosed publicly. This can be advantageous for individuals who value their privacy and want to keep their financial affairs confidential.
| Advantages of a Bare Trust |
|---|
| Simplicity and flexibility |
| Tax efficiency |
| Asset protection |
| Estate planning |
| Privacy |
Bare Trust vs Other Trust Types
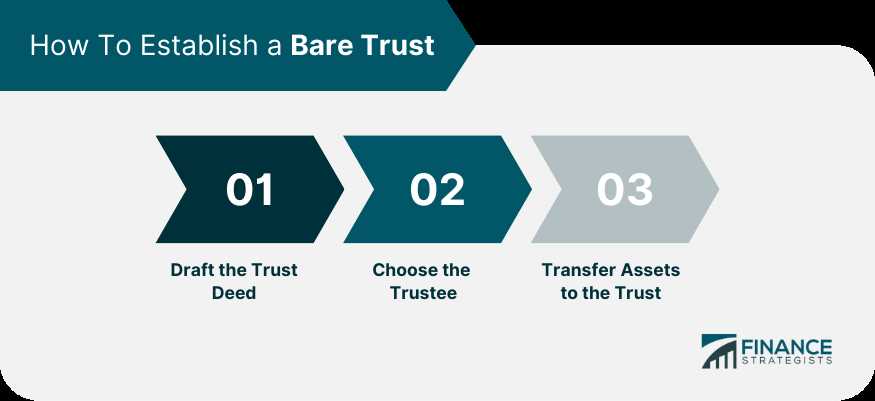
Advantages of a Bare Trust
There are several advantages to utilizing a bare trust structure:
1. Simplicity: Bare trusts are relatively straightforward and easy to set up compared to other trust types. They do not require complex legal documents or ongoing administrative tasks.
Comparing Bare Trusts to Other Trust Structures
While bare trusts offer simplicity, flexibility, and tax efficiency, they may not be suitable for all situations. It is important to consider the specific needs and goals of the individual or family when choosing a trust structure.
Compared to discretionary trusts, bare trusts do not provide the same level of asset protection or control for the trustee. Discretionary trusts allow the trustee to make decisions about how and when to distribute assets to beneficiaries, providing more flexibility in managing family wealth and protecting assets from potential creditors.
Charitable trusts, on the other hand, are specifically designed for philanthropic purposes and allow individuals to donate assets to charitable organizations while still retaining some control over how the assets are used.
Comparing Bare Trusts to Different Trust Structures
One of the main advantages of a bare trust is its simplicity. Unlike other trust structures that may require complex legal documents and ongoing administration, a bare trust can be set up and managed with minimal formalities. This makes it an attractive option for individuals who want a straightforward and hassle-free way to hold and transfer assets.
Another advantage of a bare trust is its flexibility. Unlike other trust structures that may have specific purposes or restrictions, a bare trust can be used for a wide range of purposes, including holding property, investments, or other valuable assets. This flexibility allows individuals to tailor the trust to their specific needs and objectives.
Furthermore, a bare trust offers tax advantages. In many jurisdictions, the income and capital gains generated by the trust assets are taxed directly in the hands of the beneficiary. This can result in significant tax savings, especially for individuals in lower tax brackets.
When comparing bare trusts to other trust structures, it is important to consider the level of control and ownership the beneficiary has over the trust assets. While other trust structures may offer greater asset protection or tax planning opportunities, they often come with more restrictions and limitations on the beneficiary’s control and ownership.
| Advantages of Bare Trusts | Advantages of Other Trust Structures |
|---|---|
| Simple and easy to set up and manage | Greater asset protection |
| Flexibility in holding and transferring assets | Opportunities for tax planning |
| Tax advantages for beneficiaries | Specific purposes or restrictions |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
