What is ADB?
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank established in 1966 to promote economic and social progress in Asia and the Pacific. It provides financial assistance and technical support to its member countries for various development projects and programs.
ADB’s main objective is to reduce poverty and improve the quality of life in the region by supporting sustainable economic growth, regional integration, and environmental sustainability. It works closely with its member countries to identify their development needs and provide tailored solutions to address them.
ADB’s operations cover a wide range of sectors, including infrastructure development, energy, transport, agriculture, water supply and sanitation, education, health, and finance. It provides loans, grants, and technical assistance to support these sectors and help its member countries achieve their development goals.
ADB also plays a crucial role in promoting regional cooperation and integration in Asia and the Pacific. It supports regional initiatives and programs that promote trade, investment, and knowledge sharing among its member countries.
In summary, ADB is a regional development bank that works to promote economic and social progress in Asia and the Pacific. It provides financial assistance, technical support, and knowledge sharing to its member countries to help them achieve sustainable development and improve the lives of their people.
ADB’s mission and goals
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is committed to achieving a prosperous, inclusive, resilient, and sustainable Asia and the Pacific, while sustaining its efforts to eradicate extreme poverty. ADB’s mission is to help its developing member countries reduce poverty and improve the quality of life of their people by providing financial and technical assistance, as well as fostering regional cooperation and integration.
ADB’s goals are:
| 1. Poverty Reduction: | ADB aims to reduce poverty in the region by promoting inclusive economic growth, social development, and good governance. |
| 2. Sustainable Development: | ADB is committed to supporting environmentally sustainable and climate-resilient development to address the region’s pressing environmental challenges. |
| 3. Regional Cooperation and Integration: | ADB works towards fostering regional cooperation and integration to enhance economic growth, trade, and investment in the Asia-Pacific region. |
| 4. Private Sector Development: | ADB promotes private sector development to create jobs, enhance productivity, and improve living standards in its member countries. |
| 5. Knowledge Sharing and Capacity Building: | ADB actively shares knowledge and provides technical assistance to help its member countries build their capacity for sustainable development. |
By pursuing these goals, ADB aims to contribute to the achievement of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and improve the well-being of people in the Asia-Pacific region.
Operations of Asian Development Bank
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank that aims to promote economic growth and reduce poverty in Asia and the Pacific. It achieves this through various operations and initiatives.
1. Project Financing

ADB provides financial assistance to its member countries for the implementation of development projects. This includes funding for infrastructure development, such as roads, bridges, and power plants, as well as social projects, such as education and healthcare. The bank offers loans, grants, and guarantees to support these projects.
2. Technical Assistance
In addition to financial support, ADB also provides technical assistance to its member countries. This includes expertise and knowledge sharing in various sectors, such as agriculture, energy, transportation, and urban development. ADB’s technical assistance helps countries improve their capacity to plan and implement development projects effectively.
3. Policy Advice
ADB provides policy advice to its member countries to help them formulate and implement effective development policies. This includes recommendations on economic reforms, governance, and social development. ADB’s policy advice is based on extensive research and analysis conducted by its team of experts.
4. Capacity Building
ADB supports capacity building initiatives in its member countries to enhance their skills and knowledge in various sectors. This includes training programs, workshops, and seminars on topics such as project management, financial management, and environmental sustainability. By building the capacity of its member countries, ADB aims to promote sustainable development and poverty reduction.
5. Regional Cooperation and Integration
ADB promotes regional cooperation and integration among its member countries. This includes supporting initiatives that enhance trade, investment, and connectivity within the region. ADB also facilitates dialogue and collaboration among member countries to address common challenges and promote regional economic growth.
Financing projects
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) provides financing for various projects in its member countries. These projects aim to promote economic growth, reduce poverty, and improve the quality of life for people in the Asia-Pacific region.
ADB offers different types of financing, including loans, grants, and guarantees. The bank works closely with governments, private sector entities, and other development partners to identify and fund projects that align with its strategic priorities.
ADB’s financing supports a wide range of sectors, including infrastructure development, energy, transportation, agriculture, education, health, and water supply. The bank prioritizes projects that have a strong impact on poverty reduction, environmental sustainability, and regional integration.
ADB’s financing is provided on concessional terms, with low interest rates and longer repayment periods compared to commercial loans. This enables member countries to invest in critical infrastructure and social development projects that may not be feasible with market-based financing.
ADB also promotes co-financing arrangements, where it partners with other development institutions, bilateral agencies, and the private sector to leverage additional resources for project implementation. This helps to maximize the impact of ADB’s financing and ensure the sustainability of the projects.
In addition to financing, ADB provides technical assistance and policy advice to support project preparation, implementation, and monitoring. This includes capacity building, knowledge sharing, and the transfer of best practices to enhance the effectiveness and sustainability of development projects.
Overall, ADB’s financing projects play a crucial role in promoting inclusive and sustainable development in the Asia-Pacific region, contributing to poverty reduction, economic growth, and regional cooperation.
Technical Assistance and Knowledge Sharing

The Asian Development Bank (ADB) provides technical assistance and knowledge sharing to its member countries in order to support their development efforts. This assistance is aimed at helping countries address specific development challenges and achieve their development goals.
Types of Technical Assistance
ADB offers various types of technical assistance to its member countries:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Project Preparation and Design | ADB provides technical assistance to help countries prepare and design projects that are viable, sustainable, and aligned with their development priorities. |
| Institutional Capacity Building | ADB supports member countries in strengthening their institutions and building the capacity of their government agencies to implement development projects effectively. |
| Policy and Strategy Development | ADB assists countries in formulating and implementing policies and strategies that promote inclusive and sustainable development. |
| Knowledge Sharing and Dissemination | ADB facilitates the exchange of knowledge and best practices among its member countries, promoting learning and innovation in development processes. |
Benefits of Technical Assistance
The technical assistance provided by ADB offers several benefits to member countries:
- Enhanced project quality: Technical assistance helps countries improve the quality of their development projects, leading to better outcomes and impacts.
- Capacity development: Through technical assistance, member countries can strengthen their institutional capacity and enhance the skills of their government officials.
- Policy formulation: ADB’s support in policy and strategy development enables countries to formulate and implement effective policies that address their specific development challenges.
- Knowledge sharing: ADB’s knowledge sharing initiatives facilitate the exchange of ideas, experiences, and best practices among member countries, fostering learning and innovation.
Overall, technical assistance plays a crucial role in supporting the development efforts of ADB’s member countries, helping them achieve sustainable and inclusive growth.
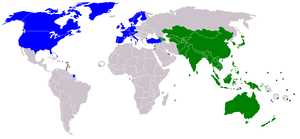
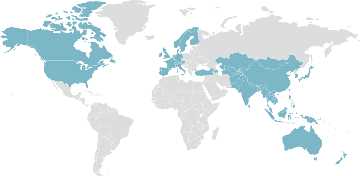
Membership of Asian Development Bank
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is an international financial institution that consists of 68 member countries, both from Asia and the Pacific region, as well as non-regional developed countries. The bank was established in 1966 with the aim of promoting economic and social progress in the region through poverty reduction and sustainable development.
ADB’s membership includes both developing and developed countries, which allows for a diverse range of perspectives and expertise in addressing the region’s development challenges. The bank’s members contribute to its capital and have the right to participate in its governance and decision-making processes.
Membership in ADB is open to countries that are members of the United Nations or its specialized agencies. Prospective members must also demonstrate a commitment to the bank’s objectives and principles, including promoting inclusive growth, environmental sustainability, and regional cooperation.
ADB’s membership provides countries with access to financial resources, technical assistance, and knowledge sharing to support their development efforts. Member countries can benefit from ADB’s expertise in various sectors, such as infrastructure development, energy, education, healthcare, and agriculture.
Furthermore, ADB’s membership offers opportunities for countries to collaborate and form partnerships with other member countries, as well as with international organizations and the private sector. This collaboration can help countries leverage resources and expertise to implement projects and programs that contribute to their economic growth and social development.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
