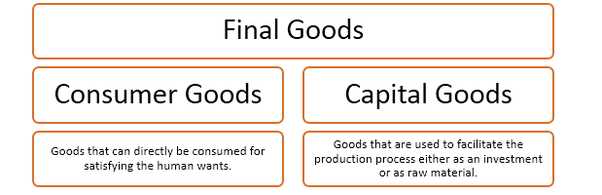
What are Capital Goods?
In the world of finance, capital goods refer to physical assets that are used in the production of goods or services. These assets are typically long-term in nature and are used by businesses to generate income and increase productivity.
Capital goods can include a wide range of items, such as machinery, equipment, vehicles, buildings, and technology. These assets are essential for businesses to operate efficiently and effectively.
Importance of Capital Goods
Capital goods play a crucial role in the economy by enabling businesses to produce goods and services. Without these assets, businesses would struggle to operate and meet the demands of consumers.
Investing in capital goods can lead to increased productivity, improved efficiency, and ultimately, higher profits. By acquiring the necessary tools and equipment, businesses can streamline their operations and deliver high-quality products to their customers.
Furthermore, capital goods can also contribute to economic growth. When businesses invest in new machinery or technology, they create jobs and stimulate innovation. This, in turn, can lead to increased production, higher incomes, and a stronger economy overall.
Examples of Capital Goods
There are numerous examples of capital goods that are used in various industries. Some common examples include:
- Machinery: such as manufacturing equipment, construction machinery, or agricultural machinery.
- Transportation: including trucks, airplanes, ships, or trains.
- Buildings: such as factories, warehouses, or office buildings.
- Technology: including computers, servers, or software.
- Tools and equipment: such as power tools, medical equipment, or laboratory instruments.
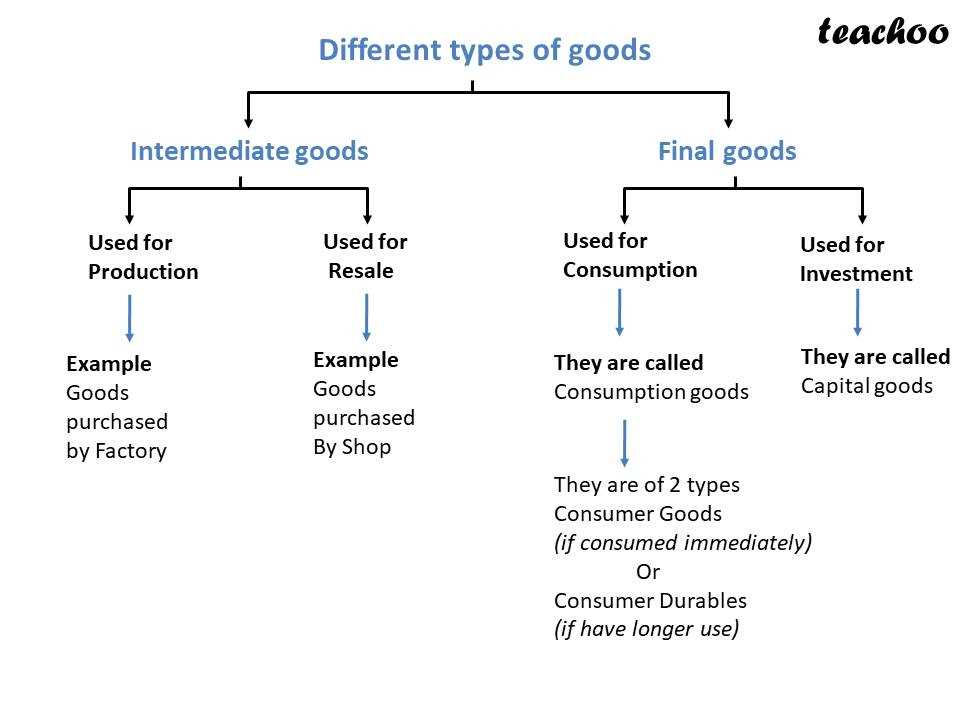
Types of Capital Goods
Capital goods are assets that are used by businesses to produce goods or provide services. There are several types of capital goods that play a crucial role in various industries. Let’s take a closer look at some of them:
1. Machinery and Equipment
Machinery and equipment are essential capital goods used in manufacturing, construction, and other industries. This category includes items such as production machines, assembly lines, forklifts, cranes, and computer systems. These assets enable businesses to automate processes, increase productivity, and improve efficiency.
2. Buildings and Infrastructure

Buildings and infrastructure are another type of capital goods that provide the physical space and facilities necessary for business operations. This category includes factories, warehouses, office buildings, transportation networks, and utilities. These assets are long-term investments that support the growth and development of businesses.
3. Vehicles
Vehicles, such as trucks, vans, and delivery vehicles, are capital goods used for transportation and logistics purposes. They enable businesses to transport goods and provide services to customers efficiently. In industries like e-commerce and retail, vehicles play a crucial role in the supply chain and last-mile delivery.
4. Tools and Instruments
Tools and instruments are capital goods used by businesses in various sectors, including construction, healthcare, and scientific research. This category includes items such as power tools, medical equipment, laboratory instruments, and measuring devices. These assets enable businesses to perform specific tasks and carry out their operations effectively.
These are just a few examples of the types of capital goods that businesses rely on to operate and thrive. Each industry may have its own specific capital goods requirements, but the common goal is to invest in assets that contribute to long-term growth and profitability.
Examples of Capital Goods
Capital goods are essential for the production of other goods and services. They are typically used by businesses and organizations to generate income and increase productivity. Here are some examples of capital goods:
1. Machinery and Equipment
Machinery and equipment are crucial capital goods used in various industries. This includes heavy machinery like excavators, cranes, and bulldozers used in construction, manufacturing equipment such as assembly lines and industrial robots, and specialized equipment used in sectors like agriculture, healthcare, and transportation.
2. Buildings and Infrastructure
Buildings and infrastructure are long-term capital investments that provide a physical space for businesses to operate. This includes factories, warehouses, office buildings, retail stores, and transportation infrastructure like roads, bridges, and airports.
3. Vehicles
Vehicles used for commercial purposes, such as trucks, vans, and delivery vehicles, are considered capital goods. These vehicles are essential for transporting goods and services from one location to another, enabling businesses to reach their customers efficiently.
4. Technology and Software
Technological advancements have made technology and software crucial capital goods for businesses. This includes computers, servers, software applications, and communication systems that enhance productivity, streamline operations, and enable businesses to stay competitive in the digital age.
5. Tools and Instruments
Tools and instruments used in various industries, such as construction tools, medical instruments, and scientific equipment, are considered capital goods. These tools and instruments enable businesses to perform specific tasks and carry out their operations effectively.
| Capital Goods | Examples |
|---|---|
| Machinery and Equipment | Excavators, cranes, assembly lines, industrial robots |
| Buildings and Infrastructure | Factories, warehouses, office buildings, roads, bridges |
| Vehicles | Trucks, vans, delivery vehicles |
| Technology and Software | Computers, servers, software applications, communication systems |
| Tools and Instruments | Construction tools, medical instruments, scientific equipment |
These examples highlight the diverse range of capital goods that businesses utilize to enhance their operations, increase productivity, and drive economic growth.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
