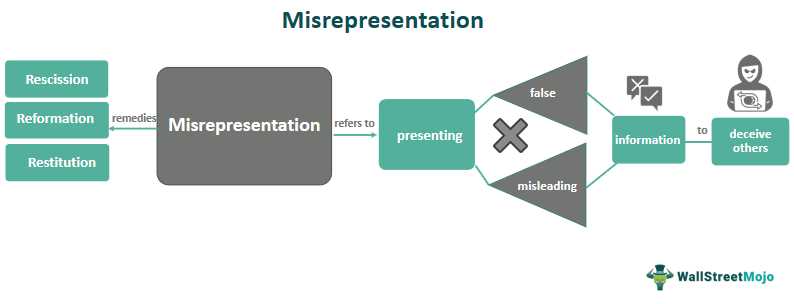
Definition of Misrepresentation
Types of Misrepresentation
There are several types of misrepresentation that can occur:
- Innocent Misrepresentation: This type of misrepresentation happens when a person provides false information without knowing that it is false. They genuinely believe that the information is true and have no intention to deceive.
- Negligent Misrepresentation: Negligent misrepresentation occurs when a person provides false information without exercising reasonable care or due diligence. Although they may not have the intention to deceive, they fail to verify the accuracy of the information.
- Fraudulent Misrepresentation: Fraudulent misrepresentation involves intentionally providing false information with the purpose of deceiving others. The person making the misrepresentation knows that the information is false and intends to manipulate or gain an advantage.
Common Mechanisms of Misrepresentation
Misrepresentation can occur through various mechanisms. Some common mechanisms include:
- False Statements: Making false statements or providing inaccurate information.
- Exaggeration: Overstating or exaggerating the facts to create a false impression.
- Manipulation of Data: Altering or manipulating data or statistics to support a false claim or argument.
- False Advertising: Using deceptive or misleading advertising techniques to promote a product or service.
- Forgery: Creating or altering documents or signatures with the intention to deceive.
Misrepresentation can have significant consequences, including financial loss, damage to reputation, legal implications, and strained relationships. It is important to be vigilant and take steps to prevent and address misrepresentation to maintain trust and integrity in various aspects of life.
Preventing and Addressing Misrepresentation
To prevent and address misrepresentation, it is crucial to:
- Verify Information: Always verify the accuracy and authenticity of information before accepting it as true.
- Exercise Due Diligence: Take the necessary steps to ensure that information provided is reliable and trustworthy.
- Seek Legal Advice: Consult with legal professionals when dealing with complex transactions or situations to ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
- Report Misrepresentation: If you suspect or encounter misrepresentation, report it to the relevant authorities or seek legal recourse.
- Build Trust: Foster a culture of transparency, honesty, and accountability to minimize the occurrence of misrepresentation.
Types of Misrepresentation
Misrepresentation can take various forms, each with its own implications and consequences. It is important to understand these different types in order to effectively identify and address instances of misrepresentation. The following are some of the most common types of misrepresentation:
1. Innocent Misrepresentation
2. Negligent Misrepresentation
Negligent misrepresentation occurs when a person makes a false statement without exercising reasonable care to ensure its accuracy. Unlike innocent misrepresentation, negligent misrepresentation involves a failure to fulfill a duty of care in providing accurate information. This type of misrepresentation can result in liability for damages.
3. Fraudulent Misrepresentation

4. Concealment
Concealment involves the intentional withholding of information that should have been disclosed. This can be considered a form of misrepresentation as it prevents the other party from making an informed decision. Concealment can occur through the omission of material facts or the failure to disclose relevant information.
5. Nondisclosure

Nondisclosure refers to the failure to provide information that should have been disclosed. While similar to concealment, nondisclosure typically involves a failure to disclose information that a party has a duty to disclose. This can occur in situations where there is a fiduciary relationship or a legal obligation to disclose certain information.
Common Mechanisms of Misrepresentation
1. False Information

One of the most straightforward mechanisms of misrepresentation is the dissemination of false information. This can involve providing inaccurate or fabricated data, statistics, or statements. False information can be spread through various channels, such as verbal communication, written documents, or online platforms.
2. Concealment
Concealment refers to the deliberate act of hiding or withholding relevant information that could potentially affect someone’s decision-making process. This can include omitting important details, not disclosing conflicts of interest, or failing to provide complete and accurate information. Concealment is often used to create a false perception or to manipulate others into making decisions that are not in their best interest.
3. Exaggeration
Exaggeration involves amplifying or overstating certain facts or characteristics to create a more favorable impression. This can be done through the use of hyperbole, embellishment, or selective presentation of information. Exaggeration is commonly used in advertising, marketing, and sales to make products or services appear more desirable or superior than they actually are.
4. Misleading Comparisons
Misleading comparisons occur when individuals or entities compare two or more things in a way that distorts or misrepresents their true nature or qualities. This can involve cherry-picking favorable attributes, manipulating data, or using misleading benchmarks. Misleading comparisons are often employed to make a product, service, or idea seem better or more advantageous than alternatives.
5. False Credentials
False credentials involve presenting oneself or a product as having qualifications, experience, or certifications that are not genuine or verified. This can include falsely claiming to have a specific degree, professional license, or membership in a reputable organization. False credentials are often used to gain trust, credibility, or authority in order to deceive others.
Impact of Misrepresentation
Misrepresentation can have significant consequences in various aspects of life, including business, relationships, and legal matters. The impact of misrepresentation can be detrimental and can lead to financial loss, damaged reputation, and legal disputes.
1. Financial Consequences: Misrepresentation can result in financial loss for individuals or businesses. For example, if a seller misrepresents the condition of a product, the buyer may incur expenses for repairs or replacements. In business transactions, misrepresentation can lead to financial damages, breach of contract, or even bankruptcy.
2. Damaged Reputation: Misrepresentation can tarnish the reputation of individuals or organizations. When false information is spread or misrepresented, it can lead to a loss of trust and credibility. This can have long-term effects on personal and professional relationships, making it difficult to rebuild trust and regain a positive reputation.
3. Legal Consequences: Misrepresentation can result in legal disputes and liabilities. If false information is provided during a contract negotiation, it can be considered fraudulent misrepresentation, which is illegal and can lead to legal action. Legal consequences may include fines, penalties, or even imprisonment, depending on the severity of the misrepresentation.
4. Emotional Impact: Misrepresentation can also have emotional consequences for individuals who have been deceived or misled. Discovering that one has been lied to or manipulated can lead to feelings of betrayal, anger, and disappointment. These emotional impacts can affect personal well-being and relationships.
5. Trust and Relationship Breakdown: Misrepresentation can damage trust between individuals or organizations. When trust is broken, it can be challenging to rebuild and restore relationships. This can have long-lasting effects on personal and professional connections, leading to strained relationships or even complete breakdowns.
Overall, misrepresentation can have far-reaching consequences that extend beyond the initial act of deception. It is essential to be aware of the potential impact and take preventive measures to avoid misrepresentation in various aspects of life.
Preventing and Addressing Misrepresentation
Educating the Public
Implementing Ethical Standards
Organizations and professionals should adhere to ethical standards that discourage misrepresentation. This includes being transparent and honest in all communications, ensuring that information is accurate and up-to-date, and avoiding any misleading or deceptive practices. By setting and enforcing ethical standards, organizations can create a culture of integrity and trust.
Additionally, individuals should be encouraged to report instances of misrepresentation to the appropriate authorities or governing bodies. This can help identify and address cases of misrepresentation, holding those responsible accountable for their actions.
Strengthening Legal Frameworks
Legal frameworks play a crucial role in preventing and addressing misrepresentation. Laws and regulations should be in place to protect individuals from false or misleading information, and to provide avenues for recourse in case of misrepresentation. This includes consumer protection laws, advertising standards, and fraud prevention measures.
Law enforcement agencies should also have the resources and capabilities to investigate and prosecute cases of misrepresentation. This can act as a deterrent and send a strong message that misrepresentation will not be tolerated.
Building Trust and Verification Systems
Building trust is essential in preventing misrepresentation. Organizations can establish trust by being transparent, providing accurate information, and delivering on their promises. This can be done through clear and concise communication, providing evidence or proof of claims, and offering guarantees or warranties.
Verification systems can also be implemented to ensure the accuracy and authenticity of information. This can include verifying credentials, conducting background checks, or using third-party verification services. By implementing such systems, individuals can have confidence in the information they receive and make informed decisions.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
