Hierarchical Organizational Chart
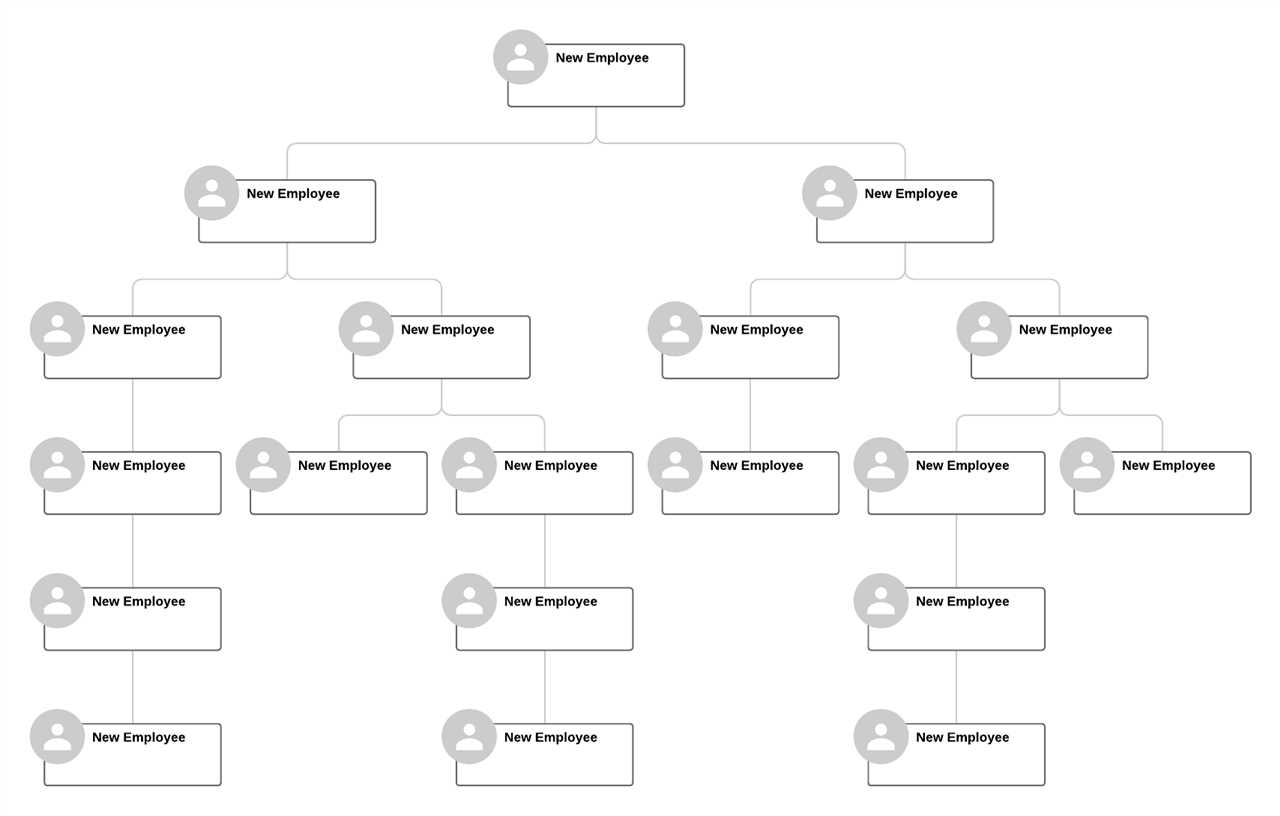
A hierarchical organizational chart is a visual representation of the structure of an organization, showing the relationships between different levels of management and employees. This type of chart is commonly used in traditional, hierarchical organizations where decision-making authority flows from top to bottom.
Key Features
Each level is connected by lines or arrows that indicate the reporting relationships and lines of authority. The lines usually point downward, indicating the flow of decision-making and communication from higher to lower levels.
Advantages
One of the main advantages of a hierarchical organizational chart is its simplicity and clarity. It provides a clear visual representation of the chain of command and the reporting relationships within the organization.
It also helps in defining roles and responsibilities, as each position is clearly defined within the chart. This can help in avoiding confusion and conflicts regarding authority and decision-making.
Additionally, the hierarchical structure allows for efficient decision-making and clear lines of communication. Decisions can be made at the top level and easily communicated down the chain of command, ensuring that everyone is aware of their roles and responsibilities.
Disadvantages
While the hierarchical organizational chart has its advantages, it also has some disadvantages. One of the main drawbacks is its rigidity and inflexibility. The hierarchical structure may hinder innovation and creativity, as decision-making is concentrated at the top and there may be limited opportunities for input from lower-level employees.
Furthermore, the hierarchical structure can lead to a lack of autonomy and empowerment for employees. Lower-level employees may feel restricted by the rigid reporting relationships and may not have the authority to make decisions or take initiative.
Conclusion
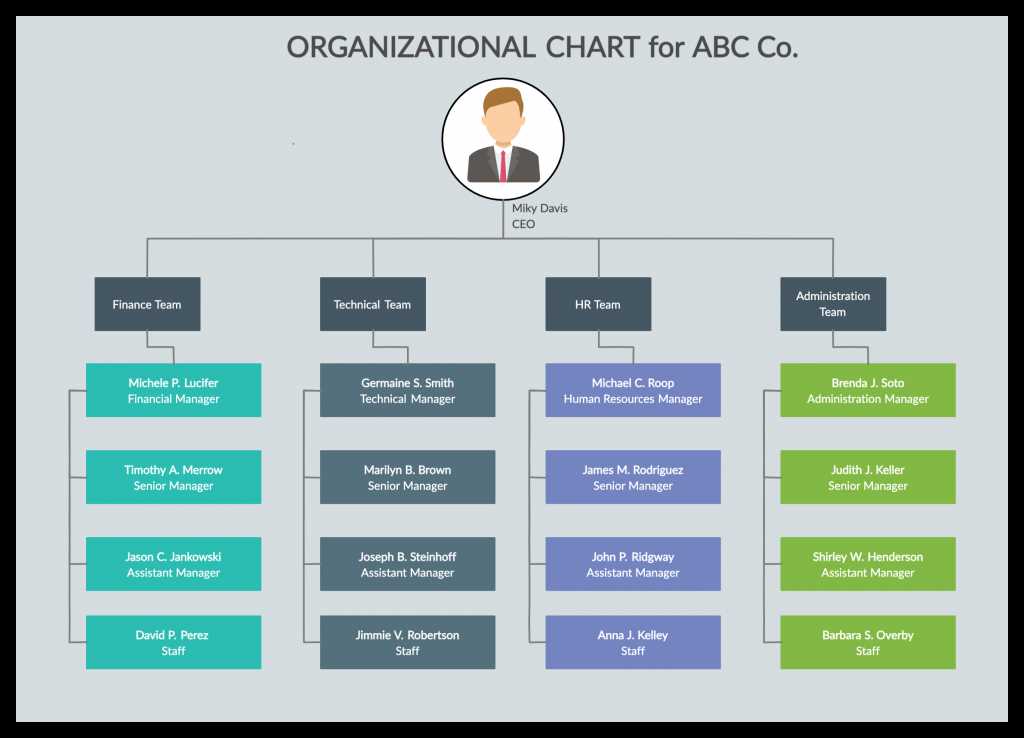
The hierarchical organizational chart is a traditional and widely used structure in many organizations. It provides a clear visual representation of the chain of command and reporting relationships. While it has its advantages in terms of clarity and efficiency, it may also have limitations in terms of flexibility and employee empowerment. Organizations should consider their specific needs and goals when choosing the appropriate organizational structure.
Matrix Organizational Chart
A matrix organizational chart is a type of organizational structure that combines elements of both functional and divisional structures. It is designed to facilitate effective communication and collaboration between different departments or teams within an organization.
In a matrix organizational chart, employees are grouped based on their functional expertise, such as marketing, finance, or operations, and also by project or product teams. This creates a dual reporting system, where employees report to both a functional manager and a project manager.
The matrix organizational chart is characterized by a grid-like structure, with employees represented in both vertical and horizontal lines. The vertical lines represent the functional hierarchy, with managers at the top and employees below. The horizontal lines represent the project or product teams, with team leaders at the top and team members below.
One of the main advantages of a matrix organizational chart is that it allows for flexibility and adaptability. Employees can be easily reassigned to different projects or teams, based on the needs of the organization. This promotes cross-functional collaboration and the sharing of resources and expertise.
However, the matrix organizational chart can also lead to challenges and complexities. Employees may face conflicting priorities and demands from multiple managers. Communication and decision-making processes can become more complex and time-consuming.
To overcome these challenges, organizations implementing a matrix organizational chart should establish clear roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines. Effective communication channels and collaboration tools should be put in place to ensure smooth coordination between different departments and teams.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Overall, the matrix organizational chart is a dynamic and flexible structure that can be effective in organizations where cross-functional collaboration and project-based work are important. However, it requires careful planning and management to ensure its success.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
