Examples of Perfect Competition

Agricultural Products

Stock Market
Online Retail
The online retail industry, with its vast number of sellers offering similar products, can be seen as an example of perfect competition. Customers have access to multiple sellers offering identical products, and the market price is determined by supply and demand dynamics.
Foreign Exchange Market

The foreign exchange market, where currencies are traded, can be considered as an example of perfect competition. There are numerous buyers and sellers of different currencies, and the exchange rates are determined by market forces without any single entity having the power to influence them significantly.
| Characteristics of Perfect Competition |
|---|
| Many buyers and sellers |
| Identical products |
| No barriers to entry or exit |
| Perfect information |
| No market power |
Working Mechanism of Perfect Competition
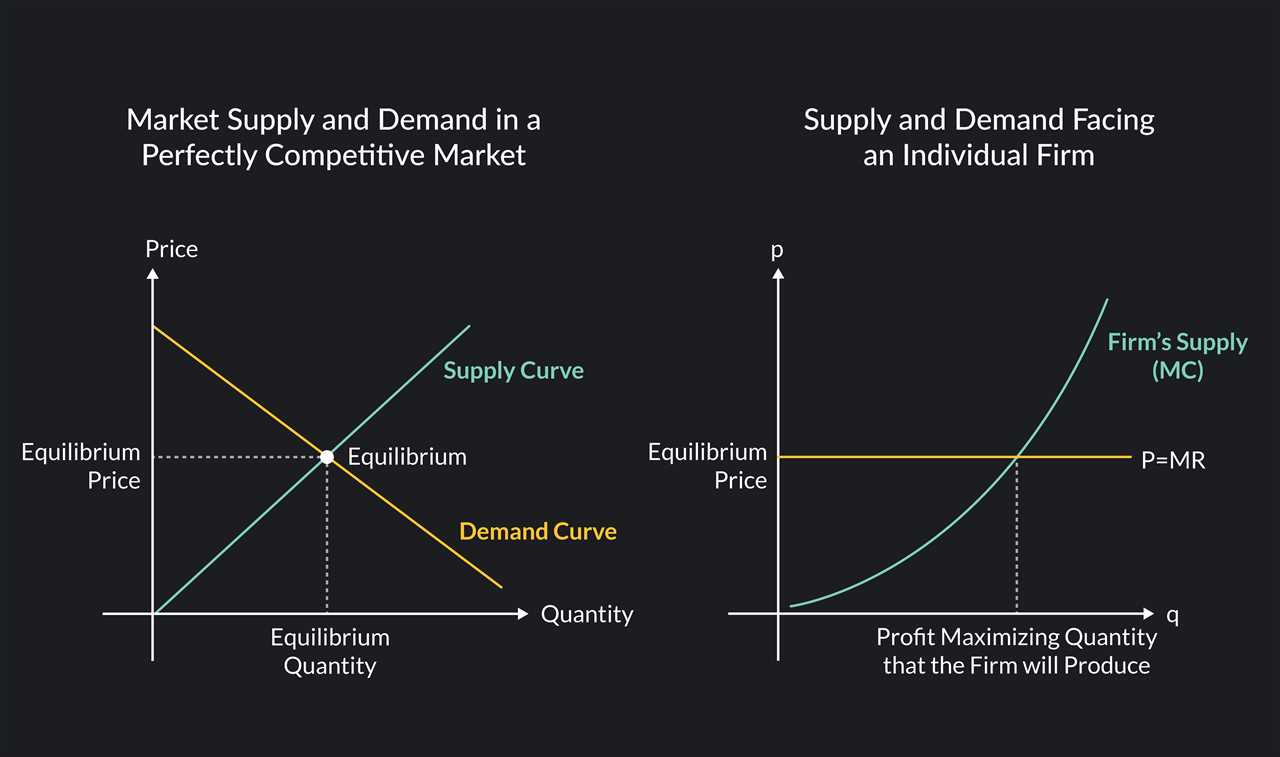
The working mechanism of perfect competition can be explained in the following steps:
- Many buyers and sellers: In a perfectly competitive market, there are a large number of buyers and sellers, each with a negligible market share. This ensures that no single buyer or seller can influence the market price.
- Homogeneous products: The products sold in a perfectly competitive market are identical or homogeneous. This means that buyers perceive no difference between the products offered by different sellers.
- Perfect information: Buyers and sellers in a perfectly competitive market have perfect information about the market conditions, including prices, quality, and availability of products. This allows them to make informed decisions.
- Price determination: In perfect competition, the price is determined by the forces of supply and demand. The market equilibrium is achieved when the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded at a particular price level.
- Free entry and exit: Firms can freely enter or exit the market in perfect competition. There are no barriers to entry, such as government regulations or high startup costs. This ensures that firms can easily enter the market to take advantage of profits or exit the market if they are facing losses.
Overall, the working mechanism of perfect competition ensures that the market operates efficiently and allocates resources in the most optimal way. It promotes competition, innovation, and consumer welfare.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
