Exploring the Relationship Between Supply and Demand
The relationship between supply and demand is a fundamental concept in economics. It is the driving force behind the market economy and plays a crucial role in determining prices and quantities of goods and services.
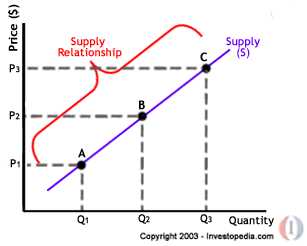
Supply refers to the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to offer for sale at a given price. Demand, on the other hand, refers to the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at a given price.
At the point where the supply and demand curves intersect, the market reaches equilibrium. This is the price and quantity at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. Any deviation from this equilibrium will result in either a shortage or a surplus.
There are several factors that can influence the relationship between supply and demand. Changes in consumer preferences, income levels, population, and government policies can all affect the demand for a good or service. Similarly, changes in production costs, technology, input prices, and government regulations can influence the supply of a good or service.
Factors Influencing Supply and Demand in the Economy
1. Price
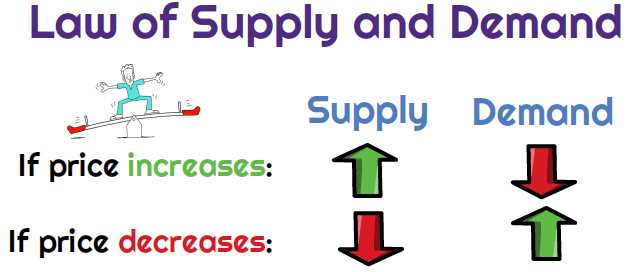
Price is one of the most significant factors influencing supply and demand. When the price of a product or service increases, the quantity supplied tends to increase as well. This is because producers are motivated to supply more goods or services at higher prices, as it allows them to generate higher profits. On the other hand, when the price decreases, the quantity supplied decreases as well, as producers find it less profitable to supply goods or services at lower prices.
2. Production Costs
3. Technology
Technological advancements can have a significant impact on supply and demand. Improved technology can lead to increased production efficiency, reducing production costs and enabling producers to supply more goods or services at a lower price. This can result in an increase in supply. Conversely, if technology becomes outdated or less efficient, it can lead to higher production costs and a decrease in supply.
4. Consumer Preferences
Consumer preferences and tastes can greatly influence both supply and demand. If consumers develop a preference for a particular product or service, the demand for it is likely to increase. This can lead to an increase in supply as producers respond to the growing demand. On the other hand, if consumer preferences shift away from a certain product or service, the demand for it may decrease, leading to a decrease in supply.
5. Government Policies
Government policies and regulations can have a significant impact on supply and demand. For example, taxes and subsidies can affect production costs and, consequently, supply. Additionally, regulations on imports and exports can influence the availability of goods and services in the market, affecting both supply and demand. Government interventions can also impact consumer behavior and preferences, indirectly influencing supply and demand.
Overall, the factors influencing supply and demand in the economy are interconnected and complex. By considering these factors, economists and policymakers can gain insights into market dynamics and make informed decisions to promote economic stability and growth.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
