Types of Fixed-Rate Mortgages
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| 30-Year Fixed-Rate Mortgage | This type of mortgage has a fixed interest rate and monthly payment for a period of 30 years. It is the most popular option among borrowers due to its long repayment term, which results in lower monthly payments. |
| 15-Year Fixed-Rate Mortgage | This type of mortgage has a fixed interest rate and monthly payment for a period of 15 years. It offers a shorter repayment term compared to the 30-year option, resulting in higher monthly payments but lower overall interest costs. |
| 20-Year Fixed-Rate Mortgage | This type of mortgage has a fixed interest rate and monthly payment for a period of 20 years. It offers a middle ground between the 30-year and 15-year options, with lower monthly payments compared to the 15-year option but higher overall interest costs compared to the 30-year option. |
| 10-Year Fixed-Rate Mortgage | This type of mortgage has a fixed interest rate and monthly payment for a period of 10 years. It offers the shortest repayment term among the fixed-rate options, resulting in the highest monthly payments but the lowest overall interest costs. |
Comparison with Adjustable Rate Mortgages
Fixed-Rate Mortgages

A fixed-rate mortgage is a type of mortgage where the interest rate remains the same for the entire duration of the loan. This means that your monthly mortgage payments will stay the same, providing you with stability and predictability. Fixed-rate mortgages are popular among homeowners who prefer to have a consistent monthly payment and want to avoid any surprises in the future.
Adjustable Rate Mortgages
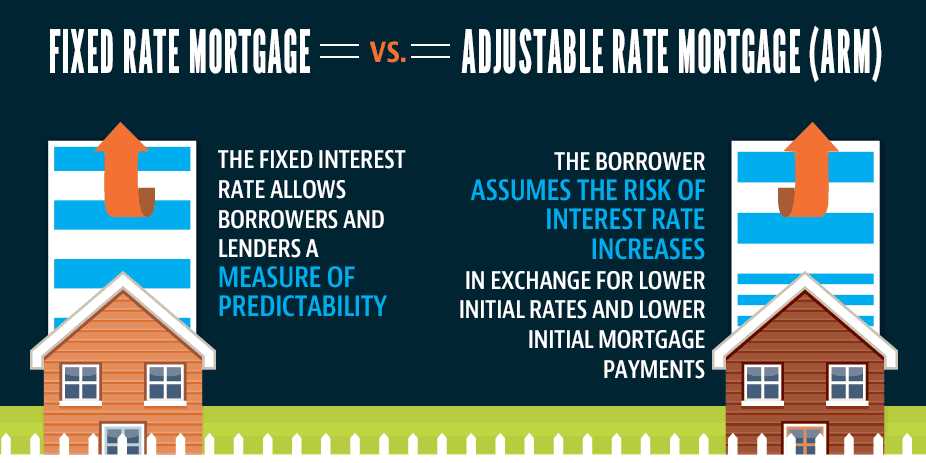
On the other hand, an adjustable rate mortgage (ARM) is a type of mortgage where the interest rate can change over time. Typically, the interest rate is fixed for an initial period, such as 5, 7, or 10 years, and then adjusts periodically based on market conditions. This means that your monthly mortgage payments can go up or down depending on the changes in the interest rate. ARMs are often chosen by homeowners who expect interest rates to decrease in the future or plan to sell the property before the initial fixed-rate period ends.
Now, let’s compare fixed-rate mortgages with adjustable rate mortgages to help you make an informed decision:
Initial Interest Rate: Fixed-rate mortgages typically have a higher initial interest rate compared to adjustable rate mortgages. This is because the lender needs to account for the potential risk of interest rate fluctuations in the future. On the other hand, adjustable rate mortgages often have a lower initial interest rate, which can be attractive to homeowners who want to take advantage of lower rates in the beginning.
Flexibility: Another factor to consider is the flexibility of the mortgage. With a fixed-rate mortgage, you have the security of knowing that your interest rate and monthly payment will stay the same. This can be beneficial if you prefer stability and want to avoid any surprises. On the other hand, an adjustable rate mortgage can offer more flexibility, as it allows you to take advantage of potential decreases in the interest rate. This can be beneficial if you plan to sell the property before the initial fixed-rate period ends or if you expect interest rates to decrease in the future.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
